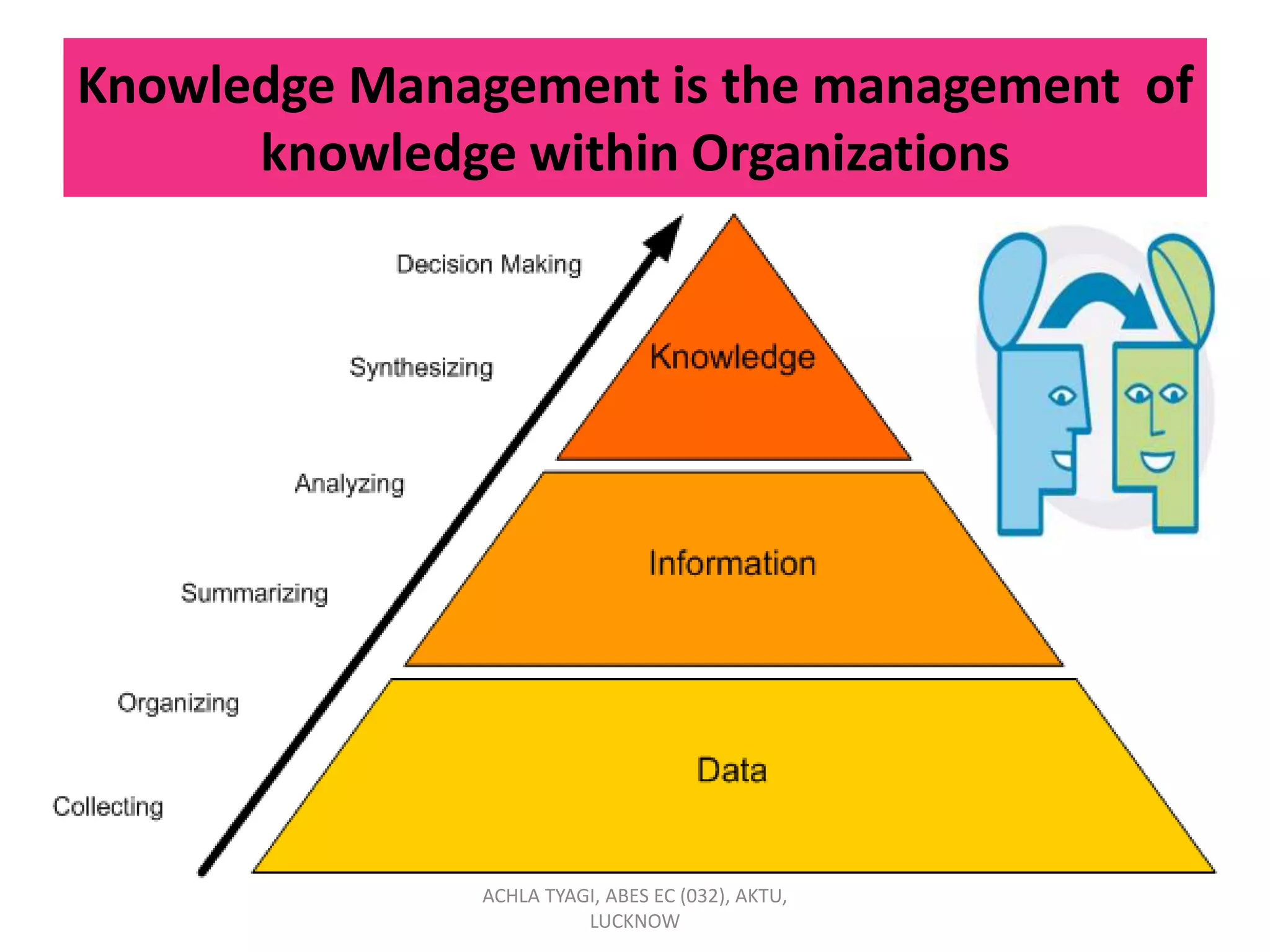
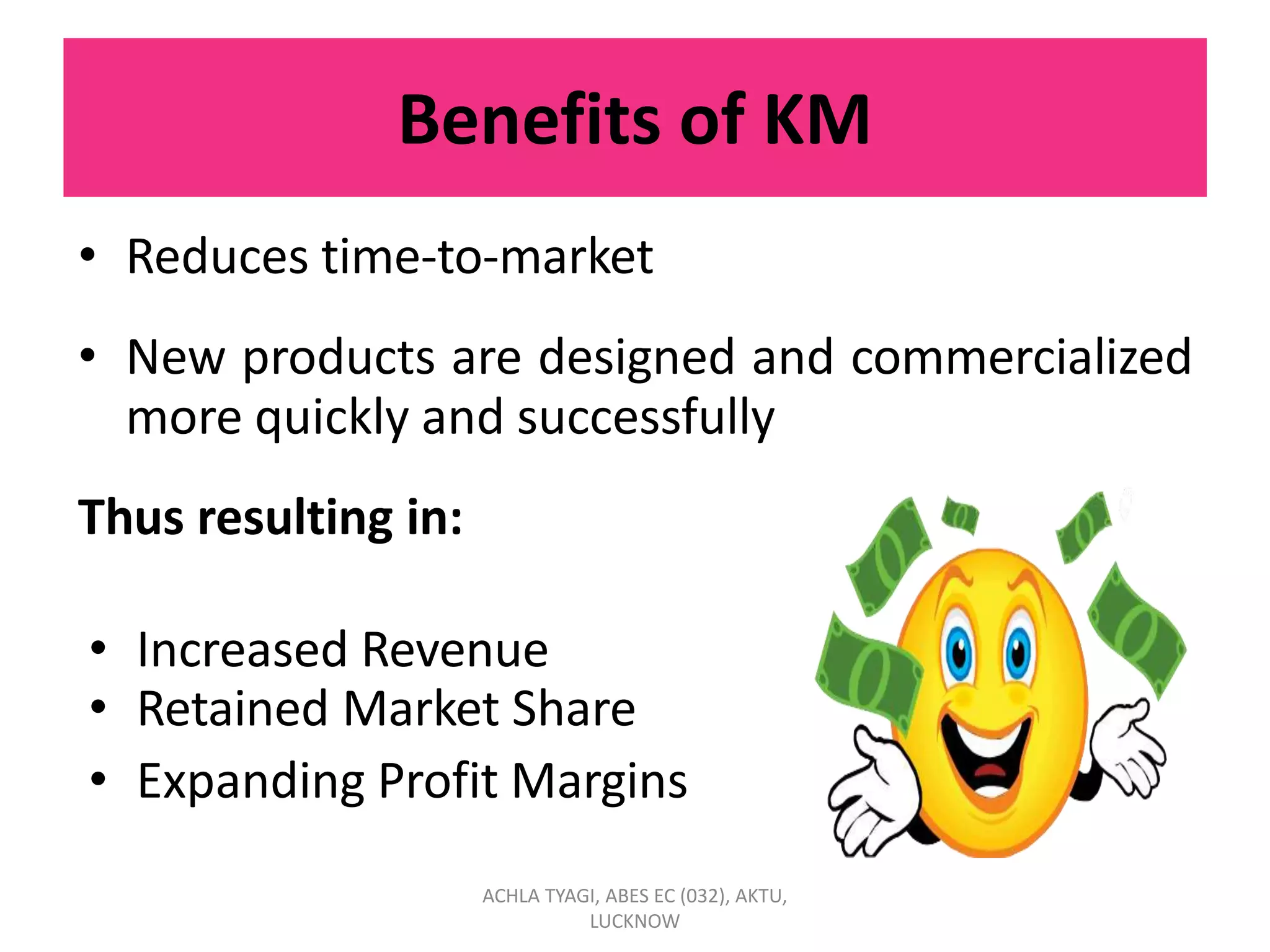
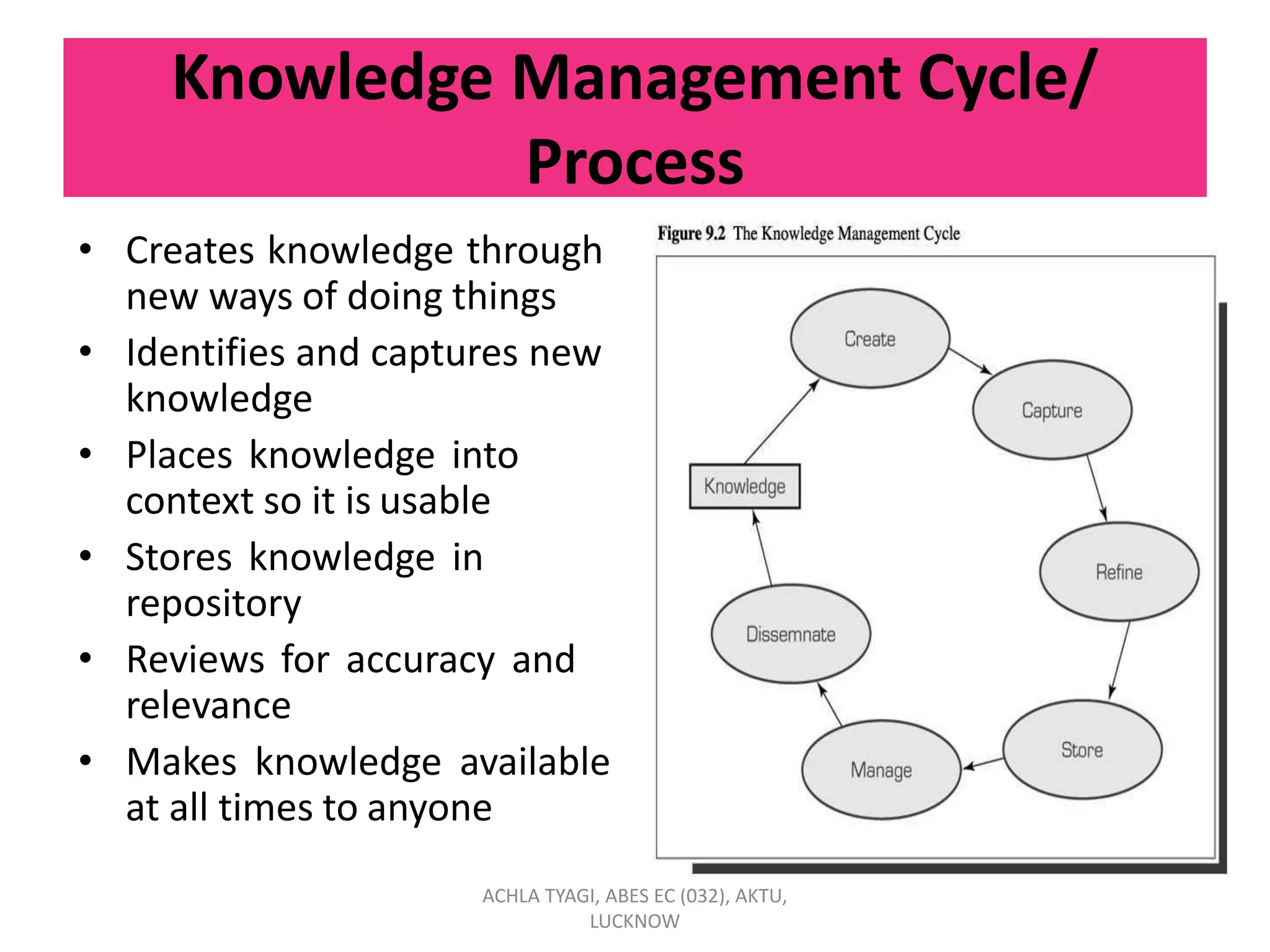
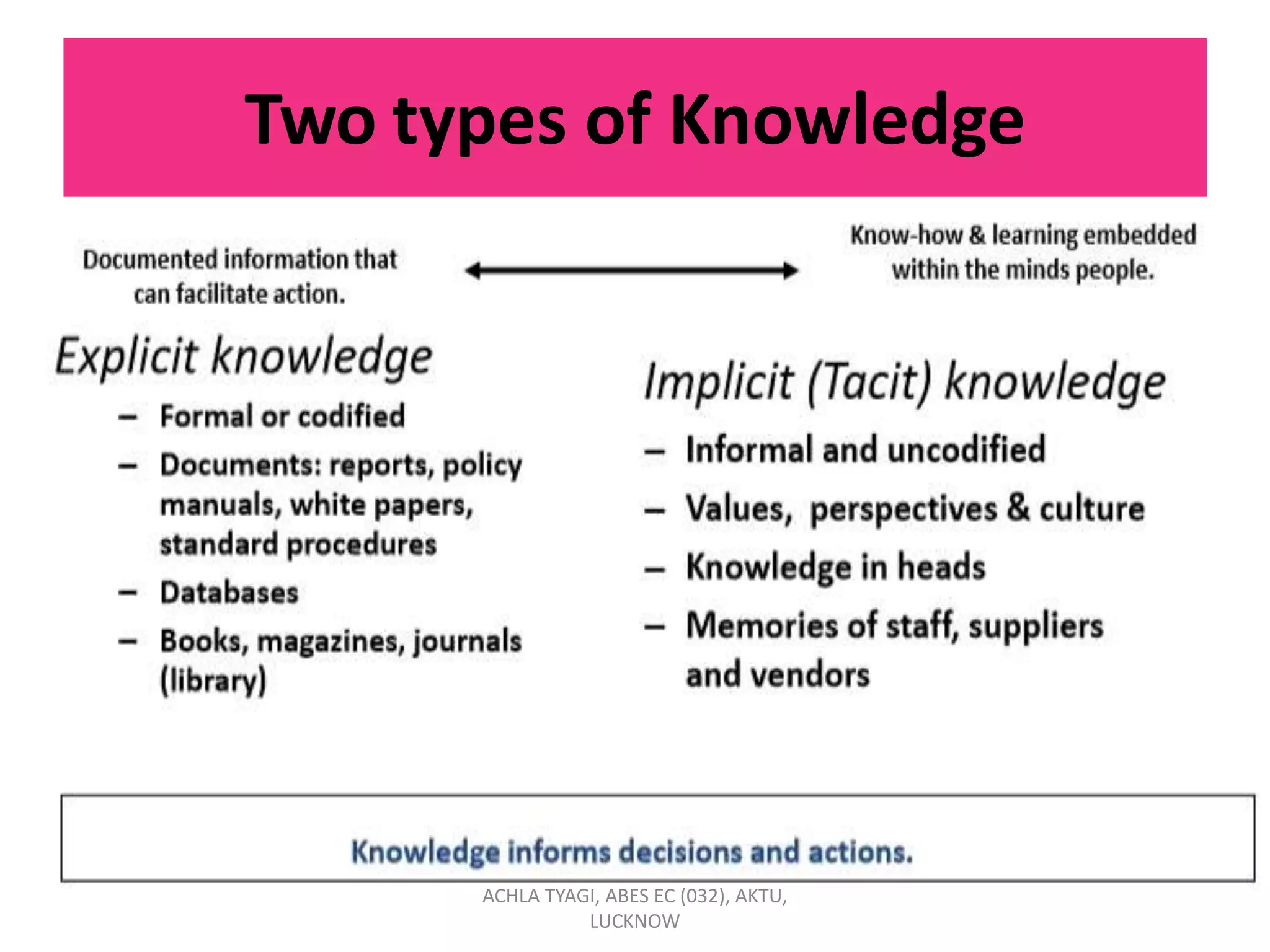
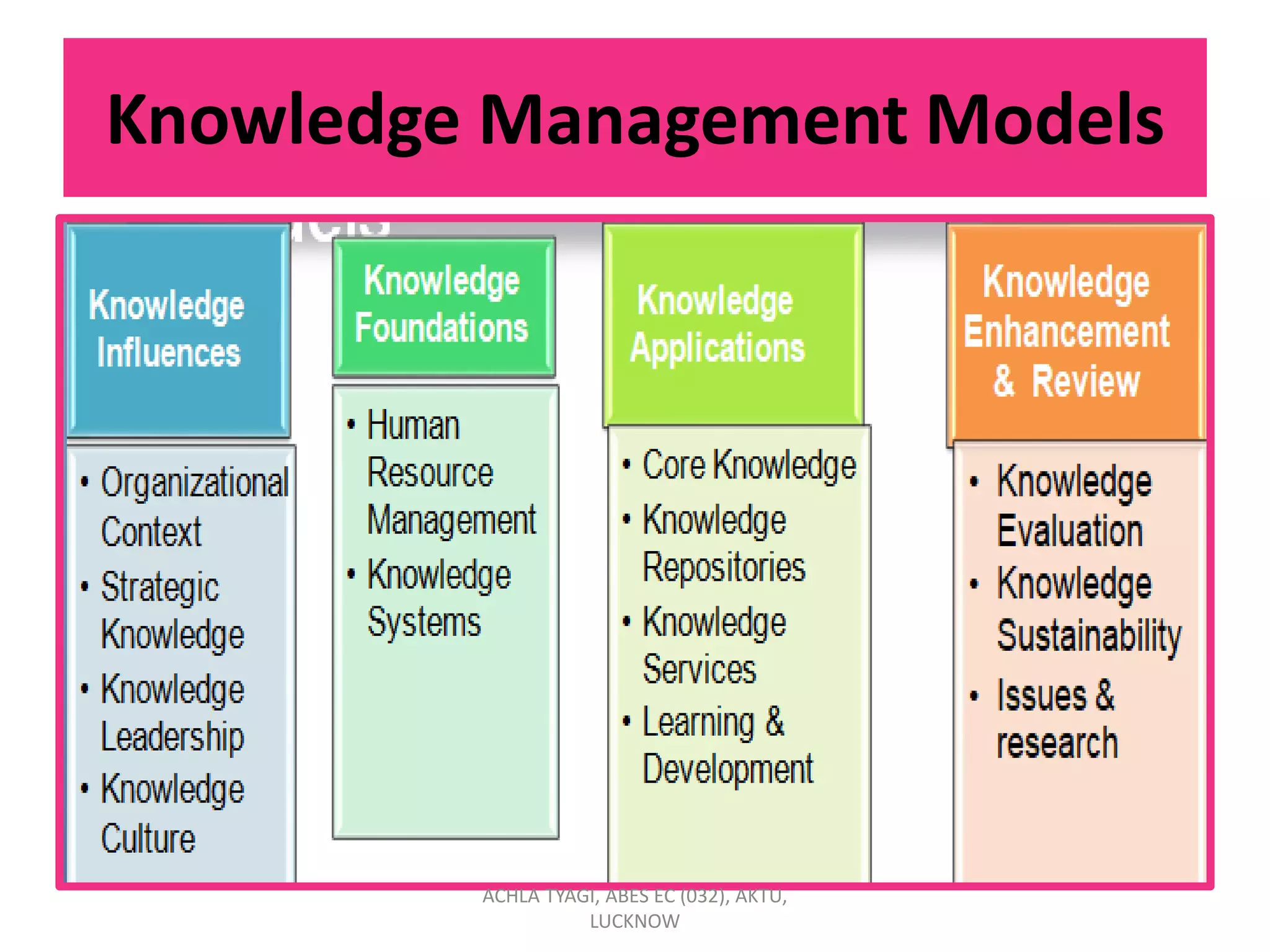
Knowledge management (KM) involves enabling individuals and organizations to systematically create, share, and apply knowledge to better achieve objectives. KM focuses on acquiring, creating, and sharing knowledge through processes and cultural and technical foundations. The purpose of KM is to provide the right information to the right people at the right time to enable informed decision-making. KM can benefit organizations by reducing time-to-market, increasing revenue, retaining market share, and expanding profit margins. Strategic KM involves developing, implementing, and maintaining an effective KM system with attention to planning, people, processes, products, and performance.