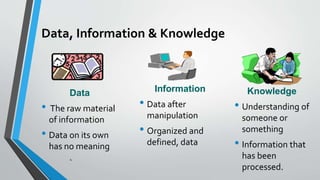
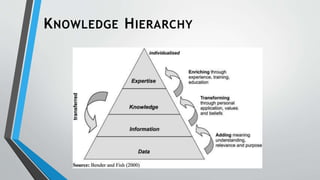
This document provides an overview of knowledge management. It defines key terms like data, information, and knowledge. It also describes different types of explicit and tacit knowledge. Several knowledge management models are introduced, including the Nonaka/Takeuchi knowledge spiral model and the Choo sense-making KM model. The document also discusses why organizations invest in knowledge management, such as enabling better decision making and avoiding duplicating mistakes.