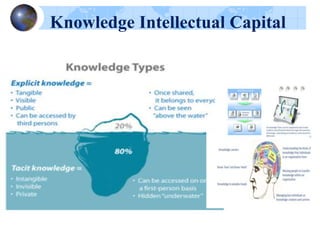
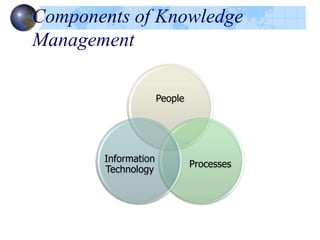
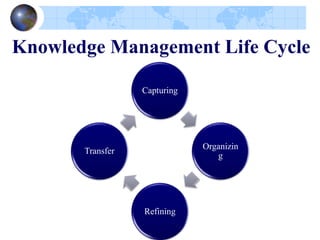
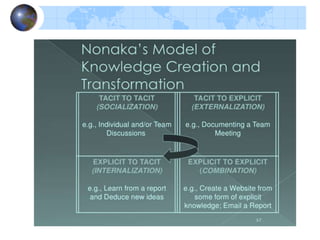
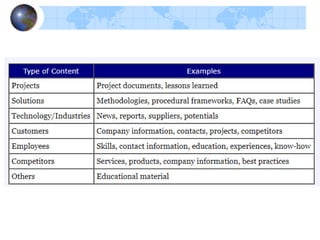
Knowledge management refers to systematically managing an organization's knowledge assets to create value and meet tactical and strategic goals. It involves initiatives, processes, strategies, and systems to store, assess, share, refine, and create knowledge. Key components of knowledge management include people, processes, information, and technology. The knowledge management life cycle includes capturing, organizing, refining, and transferring knowledge. Knowledge management systems support knowledge dissemination and application, while tools include knowledge portals, intranets, groupware, and data mining software. Knowledge professionals organize and distribute knowledge through repositories, search, and collaboration applications to enhance knowledge accessibility and quality.