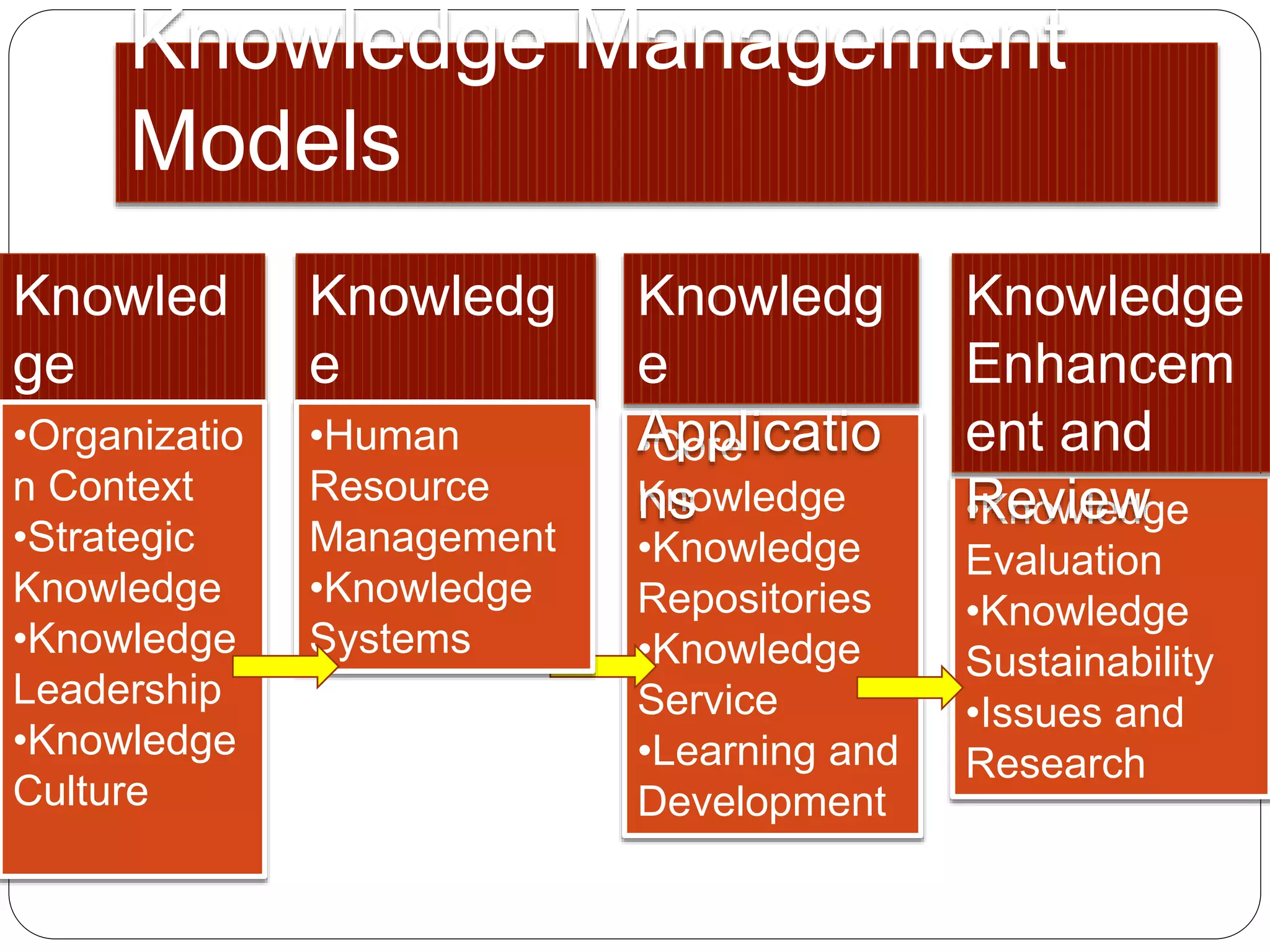
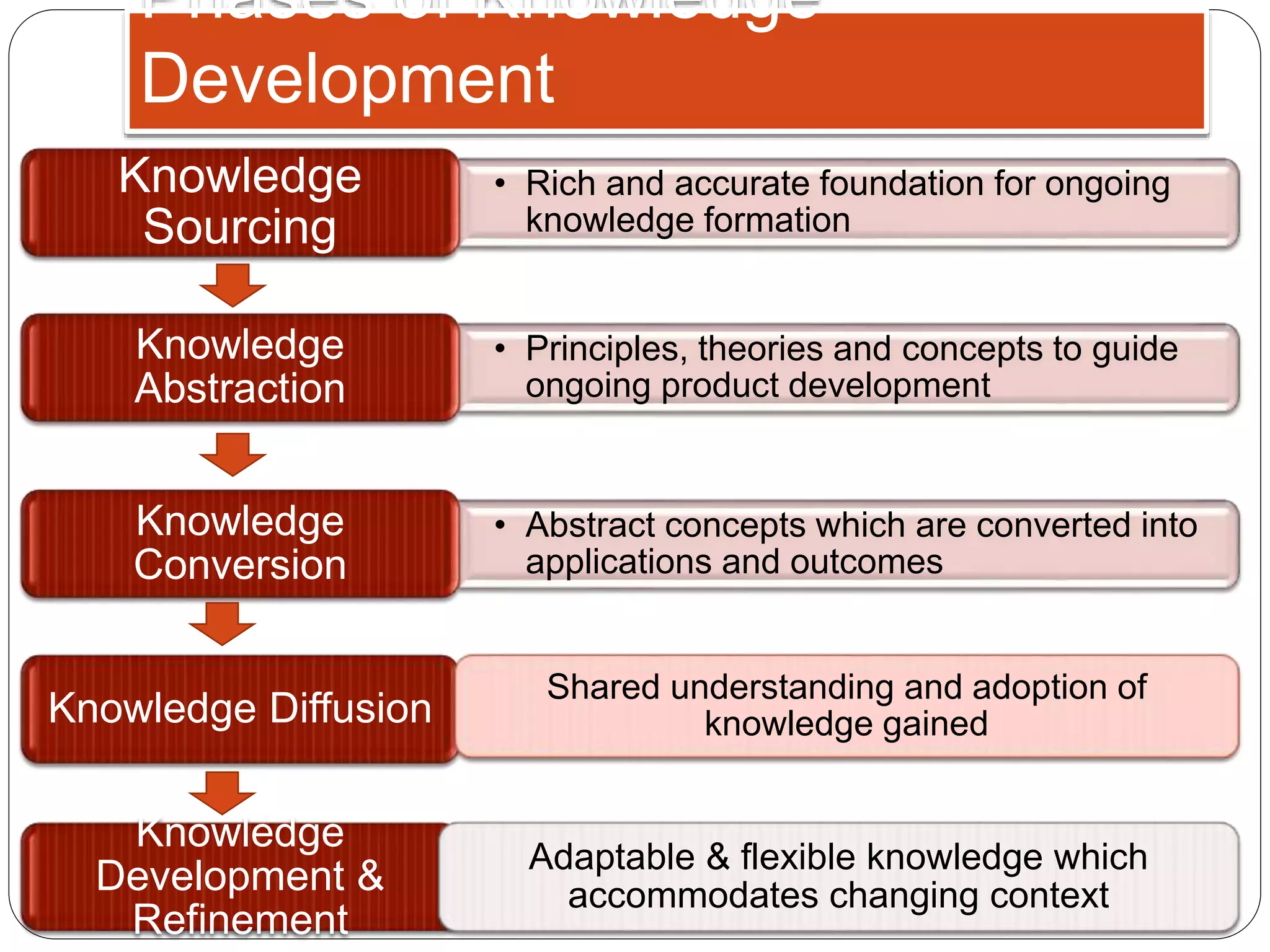
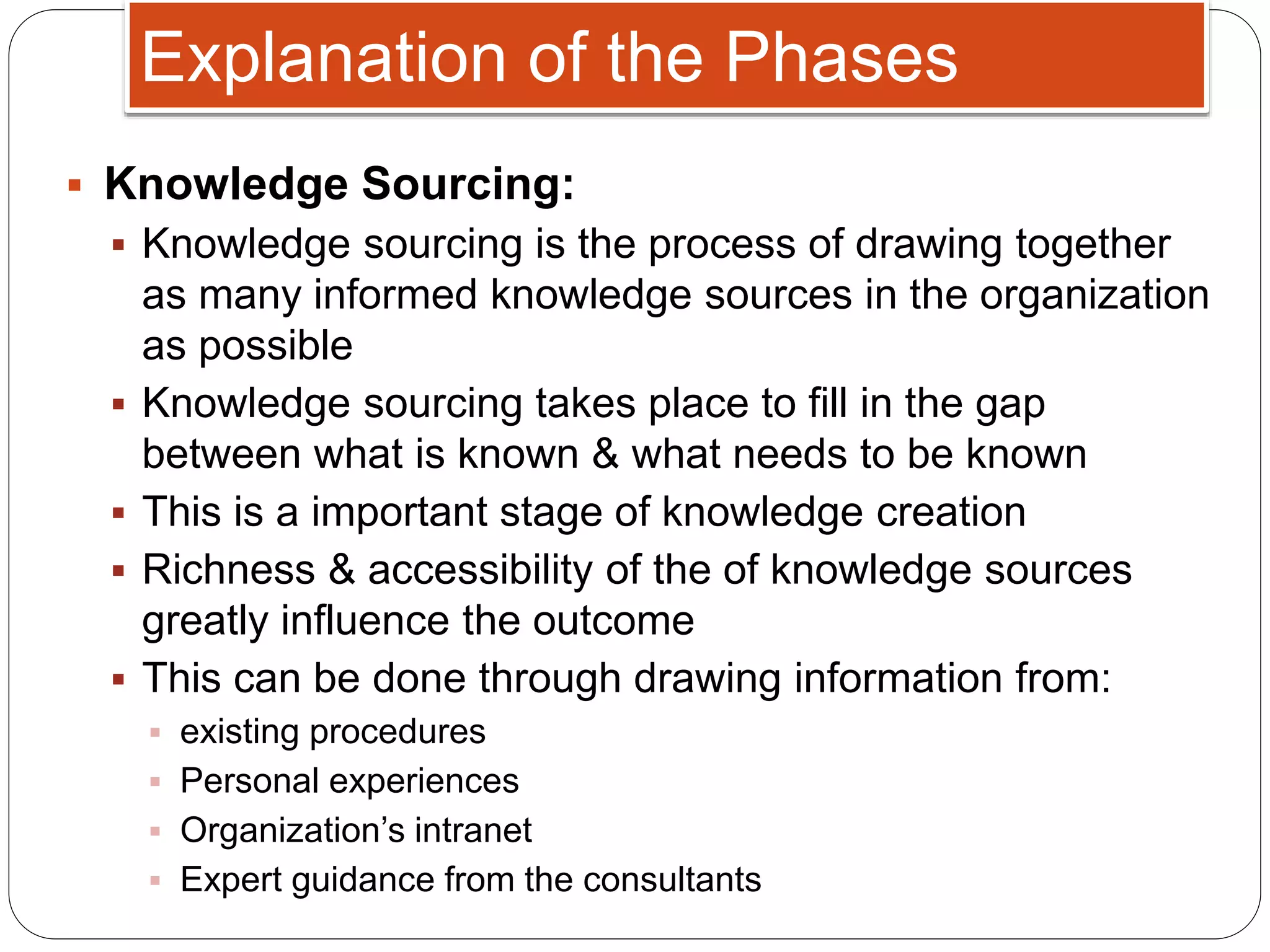
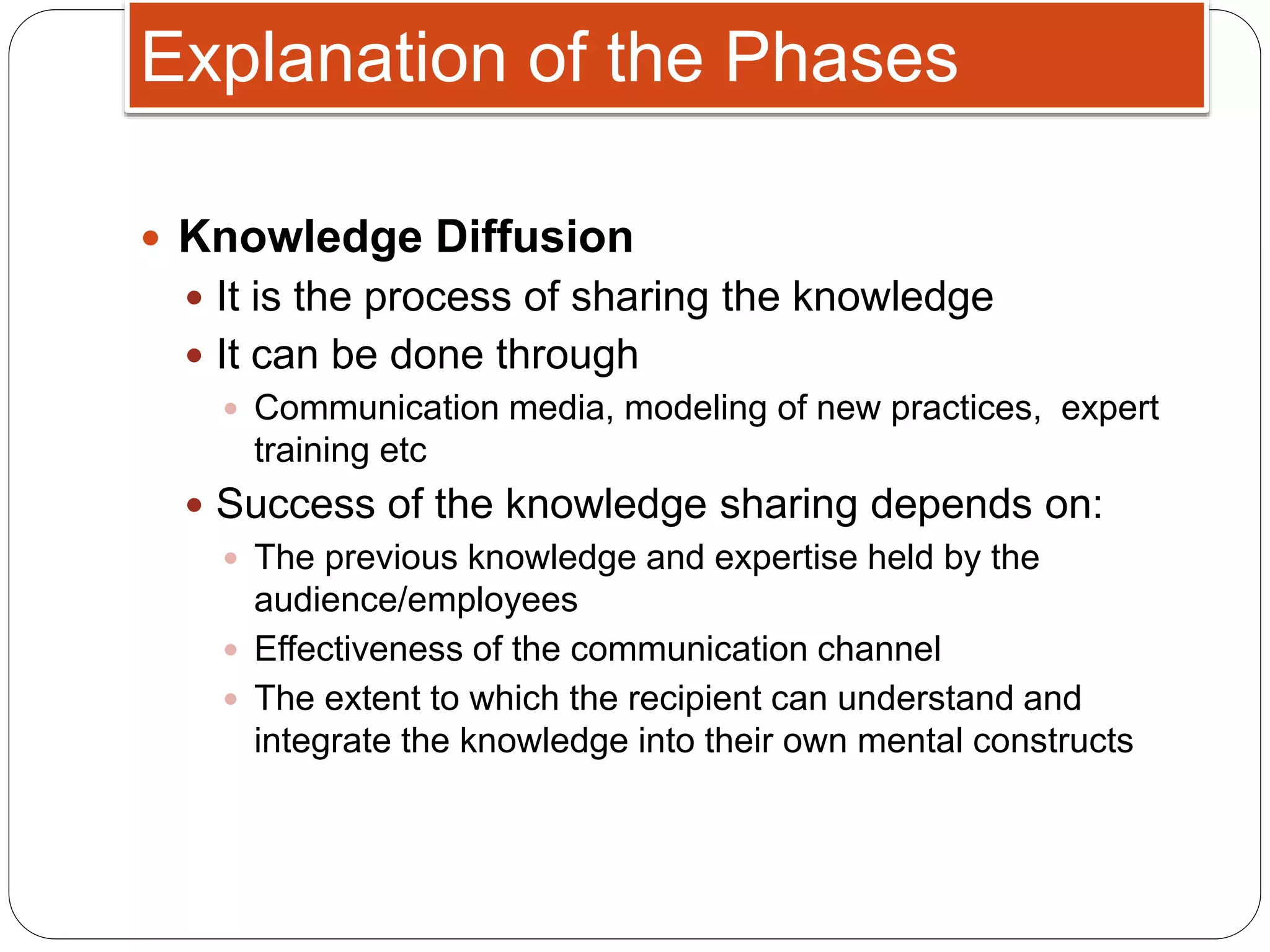
This document discusses strategic knowledge management. It explains that strategic knowledge management involves developing, implementing, and maintaining an effective organizational knowledge management system. It requires attention to five areas: planning, people, processes, products, and performance. The document also outlines phases of knowledge development including sourcing, abstraction, conversion, diffusion, and refinement. It describes how knowledge management infrastructure, knowledge workers, knowledge objects, and intellectual property play roles in strategic knowledge management.