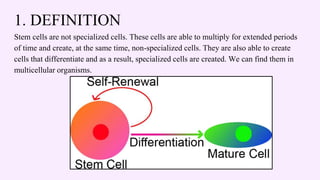
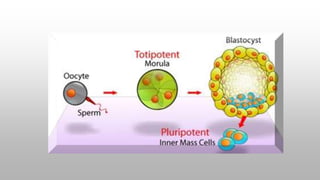
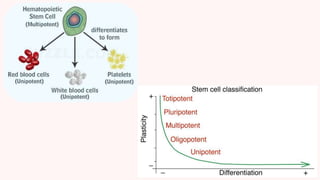
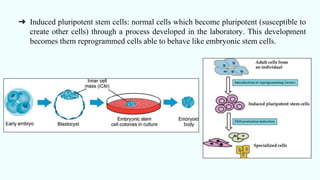
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that can differentiate into specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells. There are several types of stem cells including totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent cells. Stem cells also come from different sources such as embryonic stem cells obtained from blastocysts, adult or somatic stem cells found in tissues, and induced pluripotent stem cells created in the laboratory. Stem cell research offers potential benefits for treating diseases through regenerative medicine, immune therapies, and gene therapies. However, the use of embryonic stem cells remains controversial due to ethical concerns regarding the destruction of embryos.