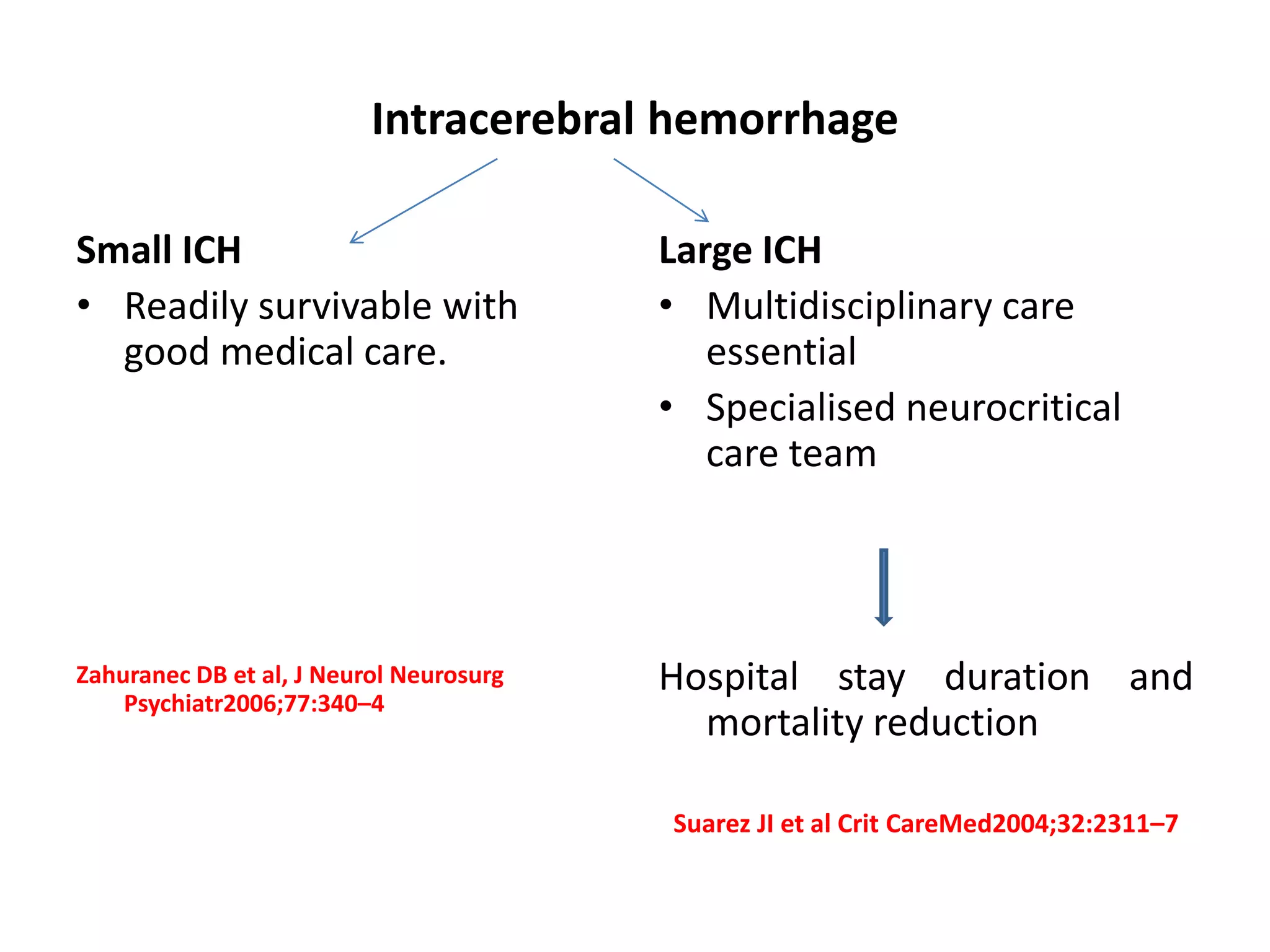
This document provides an overview of the management of hypertensive intracerebral bleed (ICH). Key points include:
1) Uncontrolled hypertension is the leading risk factor for ICH. Early diagnosis with non-contrast CT is important for appropriate care and outcomes.
2) Acute management focuses on preventing hematoma expansion through aggressive blood pressure control to SBP 140 mmHg, reversing anticoagulants, and considering platelet transfusion.
3) Other priorities are treating increased intracranial pressure through measures like head elevation, osmotic therapies, and CSF drainage if hydrocephalus is present. Salvage therapies like induced coma and neuromuscular blockade are reserved for refract