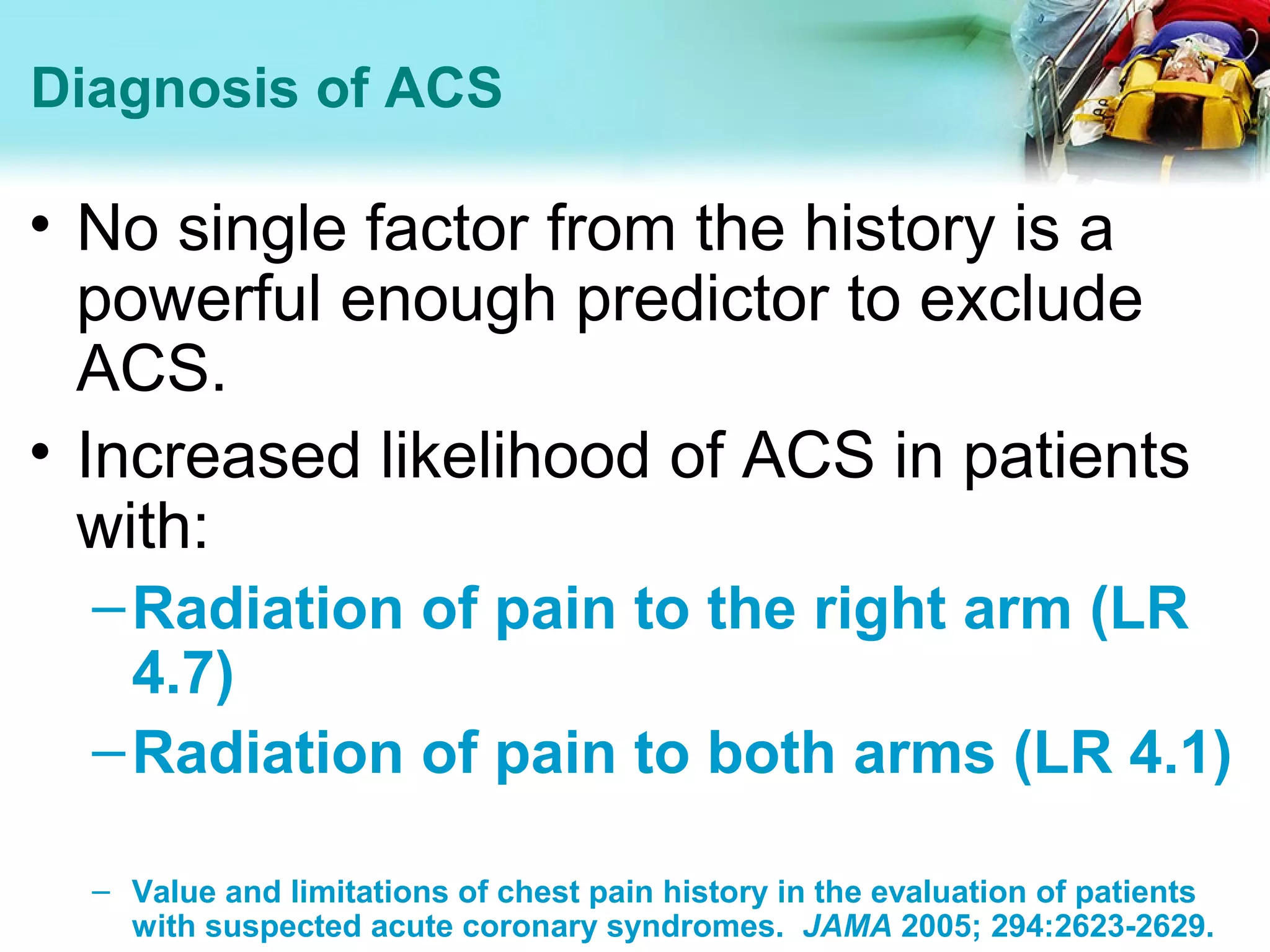
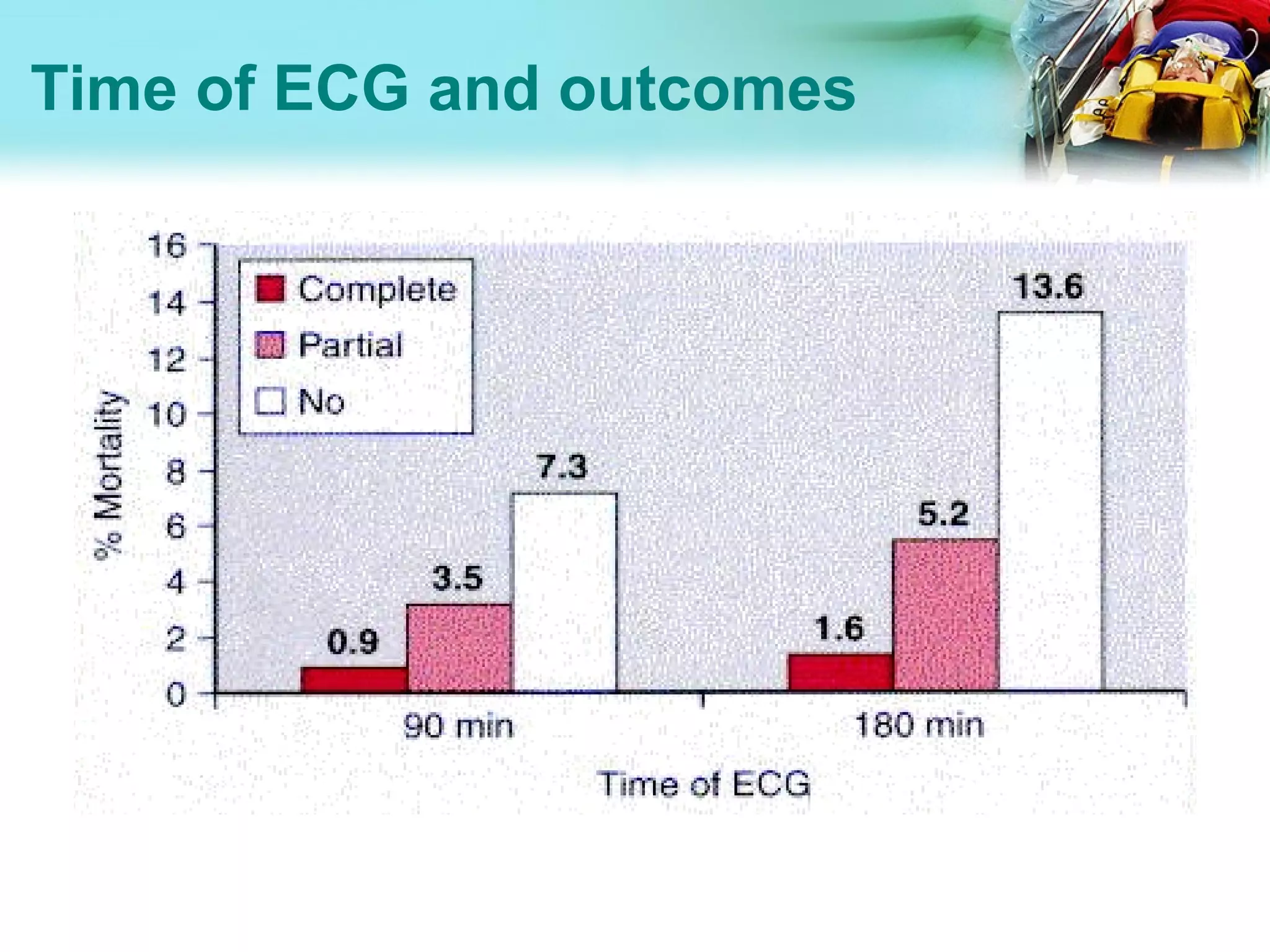
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) encompasses a spectrum of conditions caused by reduced blood flow in the coronary arteries, including unstable angina and myocardial infarction (MI). It is typically diagnosed through a patient's symptoms, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and cardiac biomarker levels. For ACS patients presenting within 12 hours of symptoms, guidelines recommend obtaining an ECG within 10 minutes and starting reperfusion therapies like thrombolysis within 30 minutes to minimize heart muscle damage. Diagnosis is based on criteria including typical chest pain, ECG changes, and elevated troponin levels. Outcomes are generally worse in elderly patients and those with atypical presentations and longer treatment delays.





![Process of care in emergency : 4 D’s
• Timed 0: onset of symptoms
• ED time 1: Door [arrival at ED]
• ED time 2: Data
[initial ECG]
• ED time 3: Decision
[to administer thrombolytics]
• ED time 4: Drug
[infusion of thrombolytic started
Time interval 1
Time interval 2
Time interval 3
Door
To
Drug
time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecoronarysyndrome-100813200221-phpapp02/75/Acute-coronary-syndrome-7-2048.jpg)






![Ischemic Chest Discomfort
ST Elevation
or New LBBB
ECG s/o Ischemia
ST dep, T inversion
Non-diagnostic
or Normal ECG
Assess initial ECG
Aspirin
Baseline CK, CK-MB
Assess C/I to thrombolysis
Anti-ischemic therapy
Reperfusion therapy
thrombolyse or Primary PTCA ]
Admit
Anti-ischemic therapy
Serial cardiac markers
2D Echo
E/o ischemia / MI
NoYes
DischargeAdmit
Goal 10 minutes
Goal
< 30 min for STK or
< 60 min for arrival in Cath Lab for PTCA
Triage of ACS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecoronarysyndrome-100813200221-phpapp02/75/Acute-coronary-syndrome-15-2048.jpg)



![No pain ; No gain
• In a lot of cases with proven acute MI, chest
pain was absent at initial presentation [33%]
• These pts
– were at least 70 years older;
– Higher proportion were women[49% vs 38%];
diabetics; had h/o prior heart failure
– Had longer delay before hospital admission;
– Were less likely to receive thrombolysis or
primary PTCA; b-blockers, aspirin or heparin
– Had higher in-hospital mortality [23.3% vs 9.3%]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecoronarysyndrome-100813200221-phpapp02/75/Acute-coronary-syndrome-19-2048.jpg)

















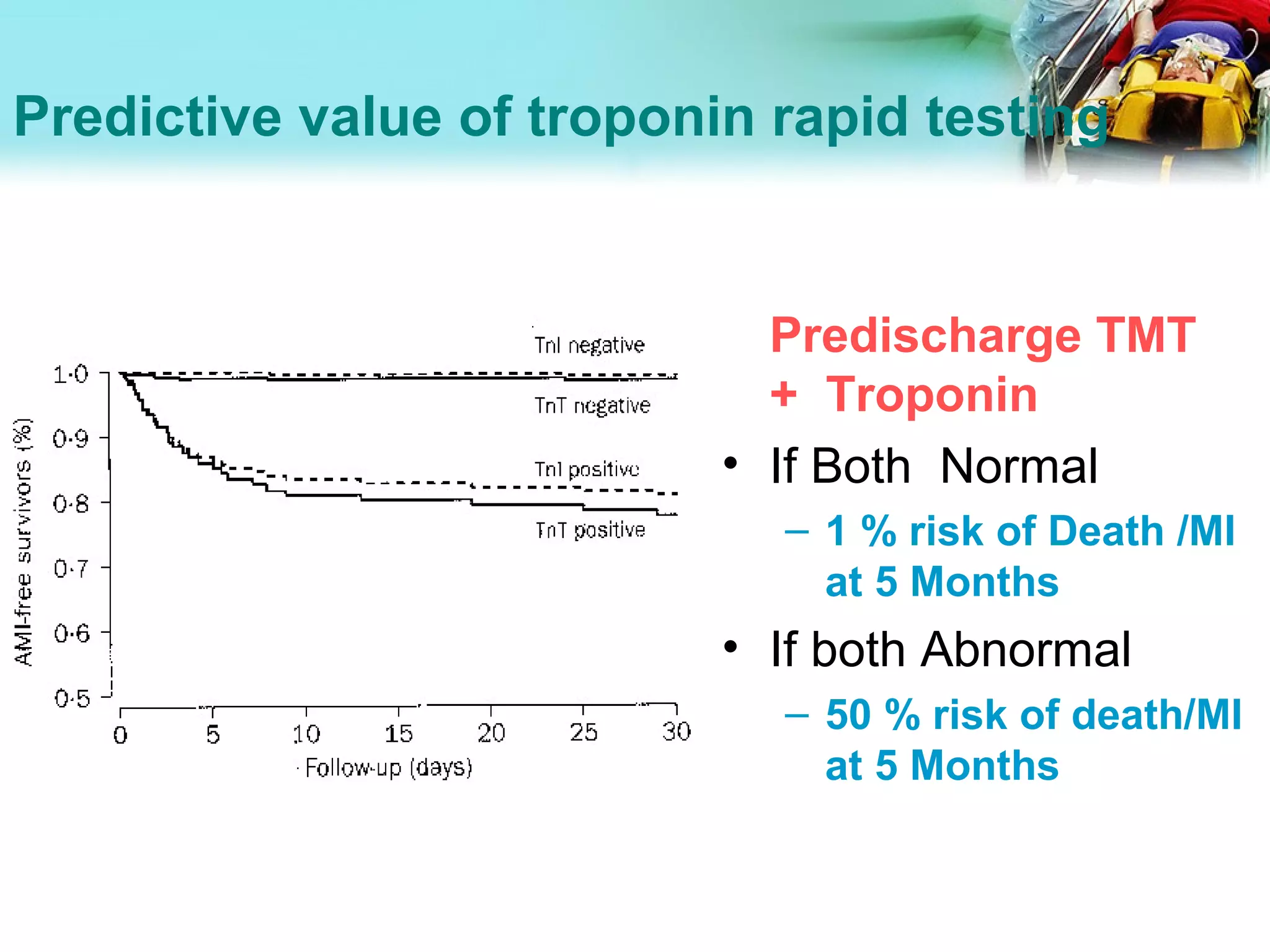

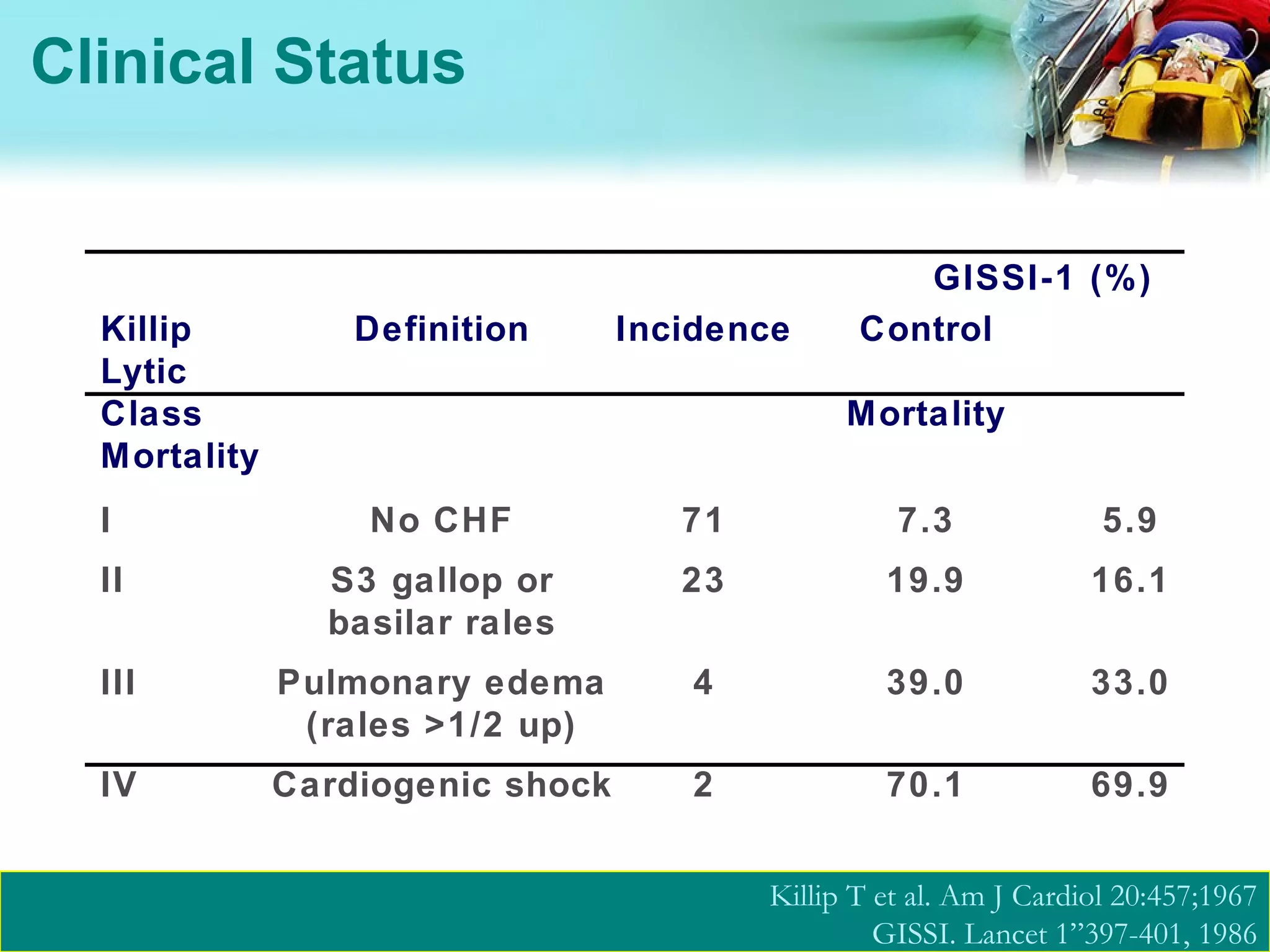


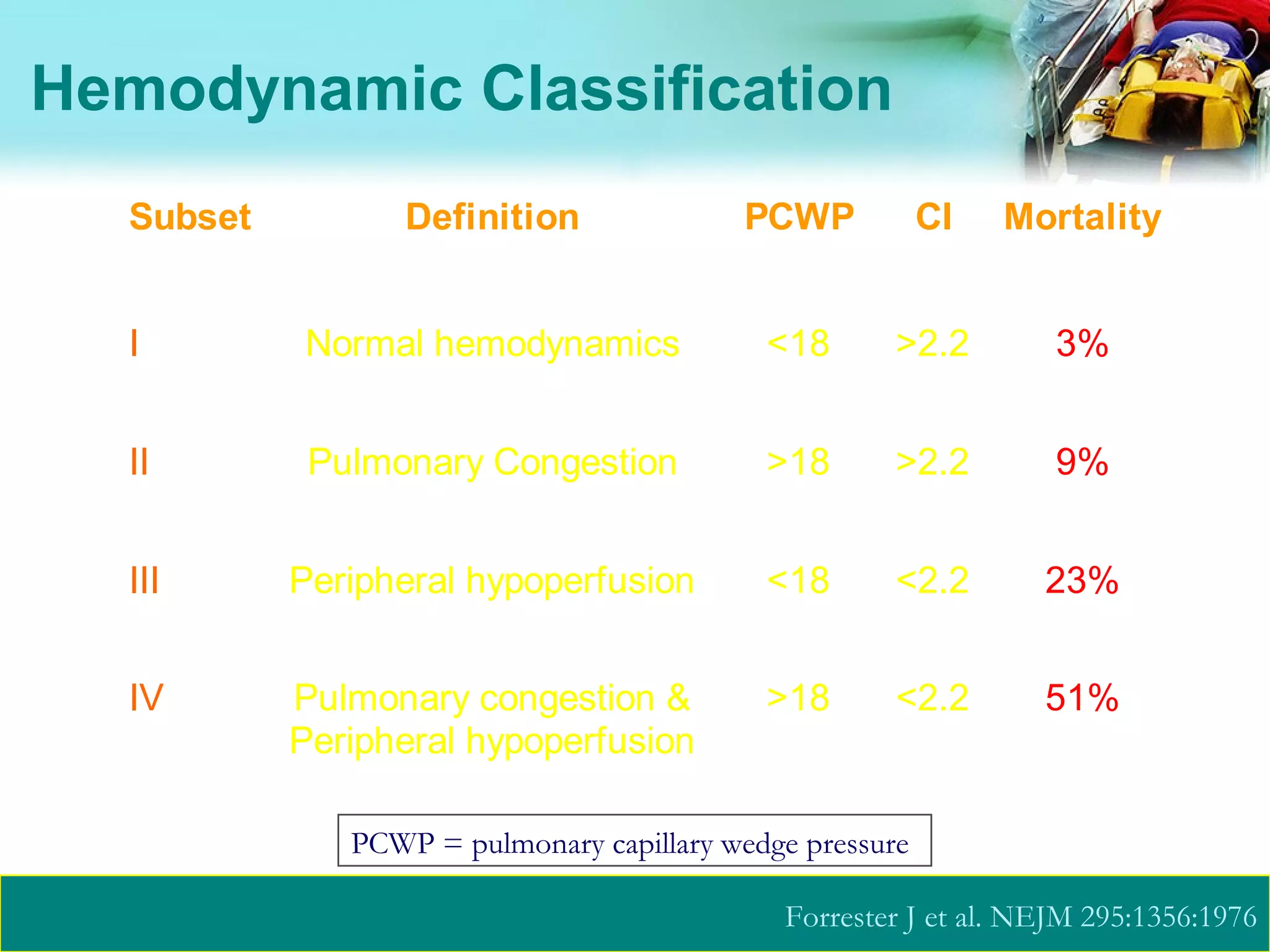



![Echocardiography
• Greater number of WMA
[wall motion
abnormalities] correlated
with
– Higher Killip class,
– Lower pO2,
– Higher CPK levels and
– Larger number of Q
waves on ECG
• Romano et al
• 30 day mortality
– WMA < 3 segments=
3.5%
– WMA 4-6 segments=
12.9%
– WMA 7-9 segments=
18.3%
– WMA > 9 segments=
37.8%
Am J Cardiol 81(12A):13G-16G;1998](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecoronarysyndrome-100813200221-phpapp02/75/Acute-coronary-syndrome-47-2048.jpg)




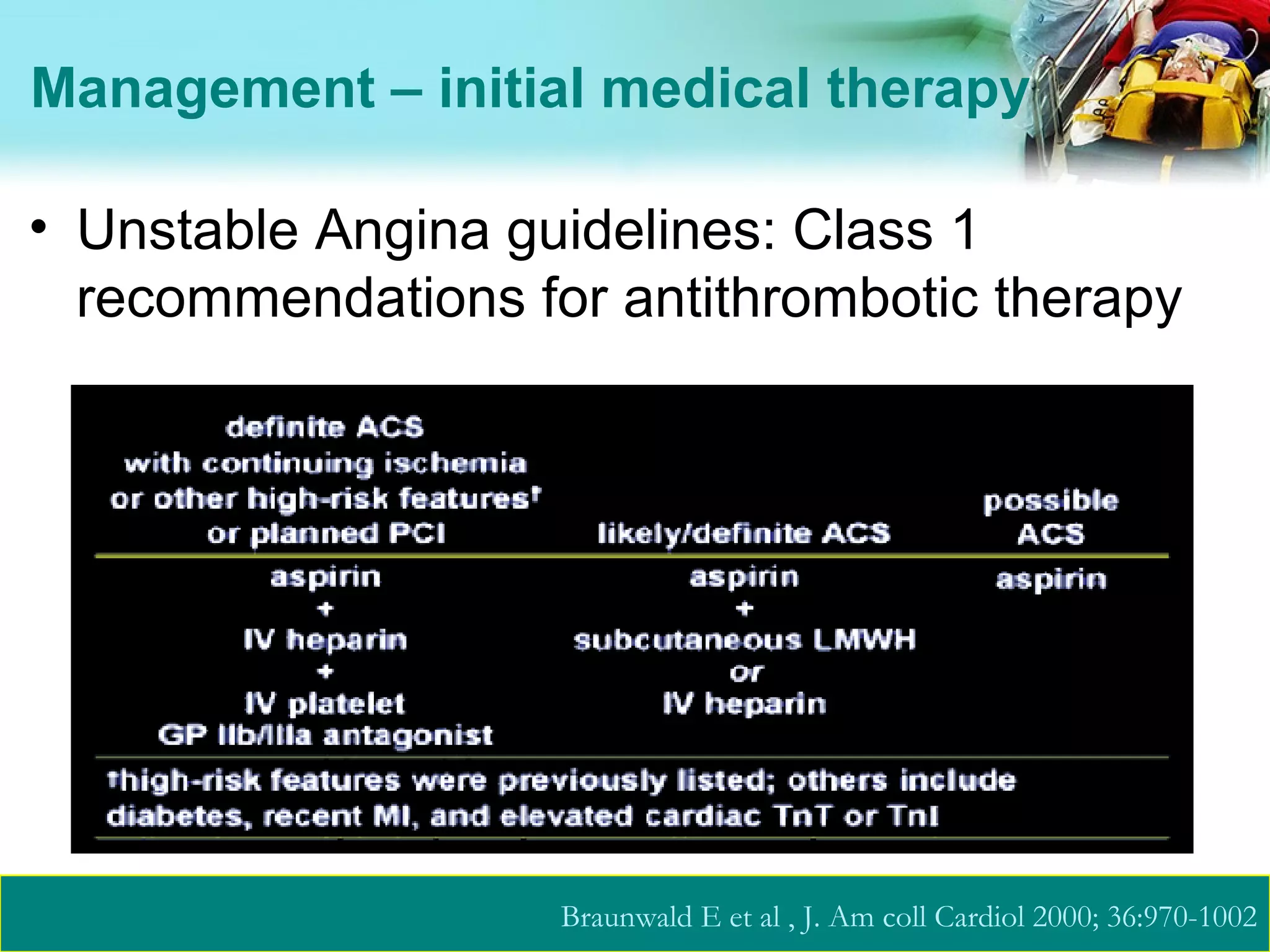






![Role of Anticoagulants in ACS
Mortality %Study Yr N
Tt c
UFH
[Meta-analysis]
1994 1353 6.5 6.9
LMWH
[FRISC 1]
1996 1506 1.8 3.8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutecoronarysyndrome-100813200221-phpapp02/75/Acute-coronary-syndrome-60-2048.jpg)