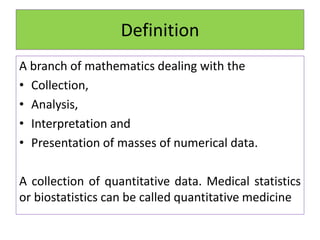
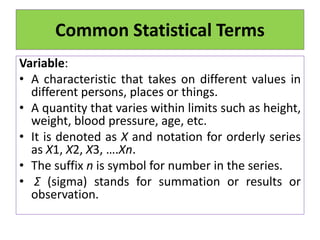
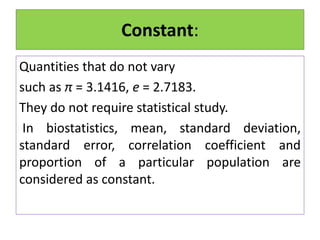
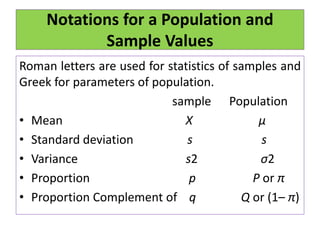
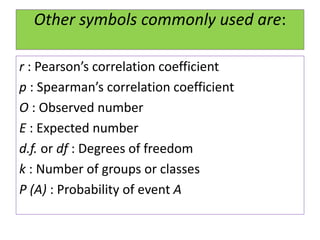
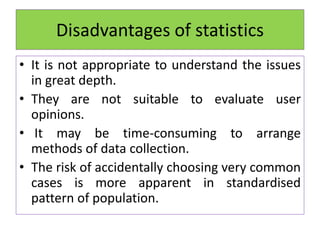
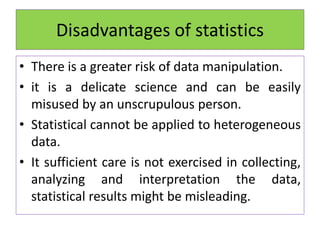
This document defines statistics as the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of quantitative data. It discusses key statistical terms like variables, constants, observations, data, populations, samples, parametric and nonparametric tests. Notations for populations and samples are also covered. The document outlines the scope of statistics in fields like planning, economics, business, industry, mathematics, science, psychology, education, war, banking, astronomy, and sociology. It describes the functions and advantages of statistics, as well as some disadvantages.