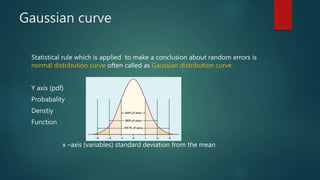
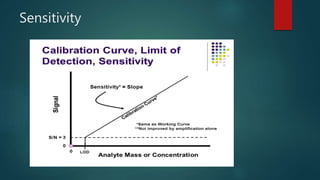
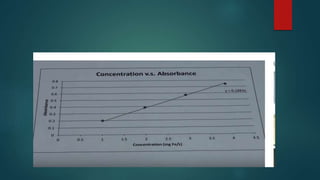
This document discusses statistical analysis and errors in measurement. It defines statistical analysis as dealing with numerical data using probability theory. Measurement errors can be divided into determinate (systematic) errors and indeterminate (random) errors. Determinate errors can be avoided or corrected, while indeterminate errors cannot be determined precisely but their probability can be estimated using statistical distributions like the Gaussian curve. The document also discusses concepts like significant figures, rounding off data, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), standard deviation, tests like F-test and T-test, quality control/quality assurance, good laboratory practices, validation of analytical methods and their parameters.