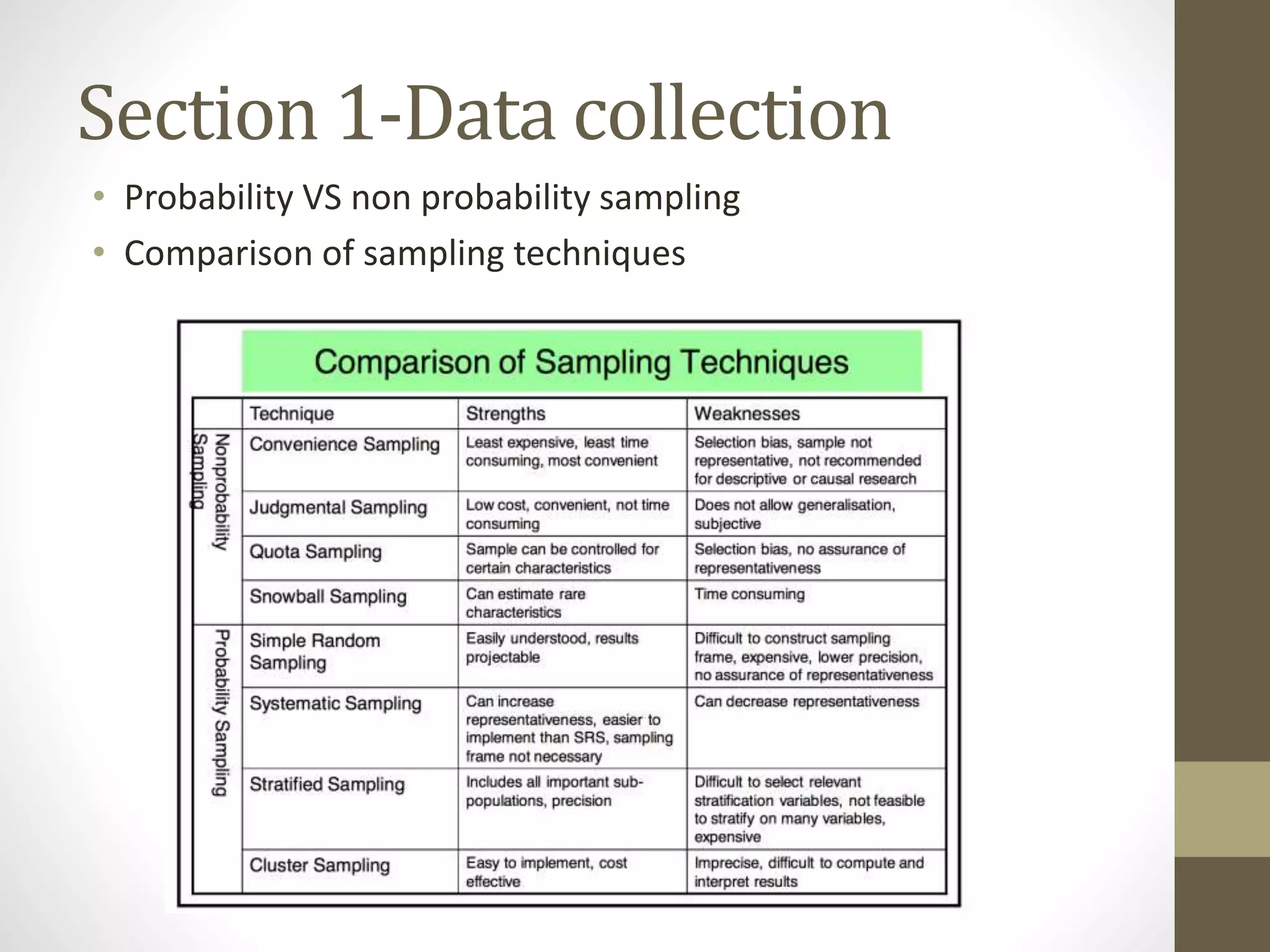
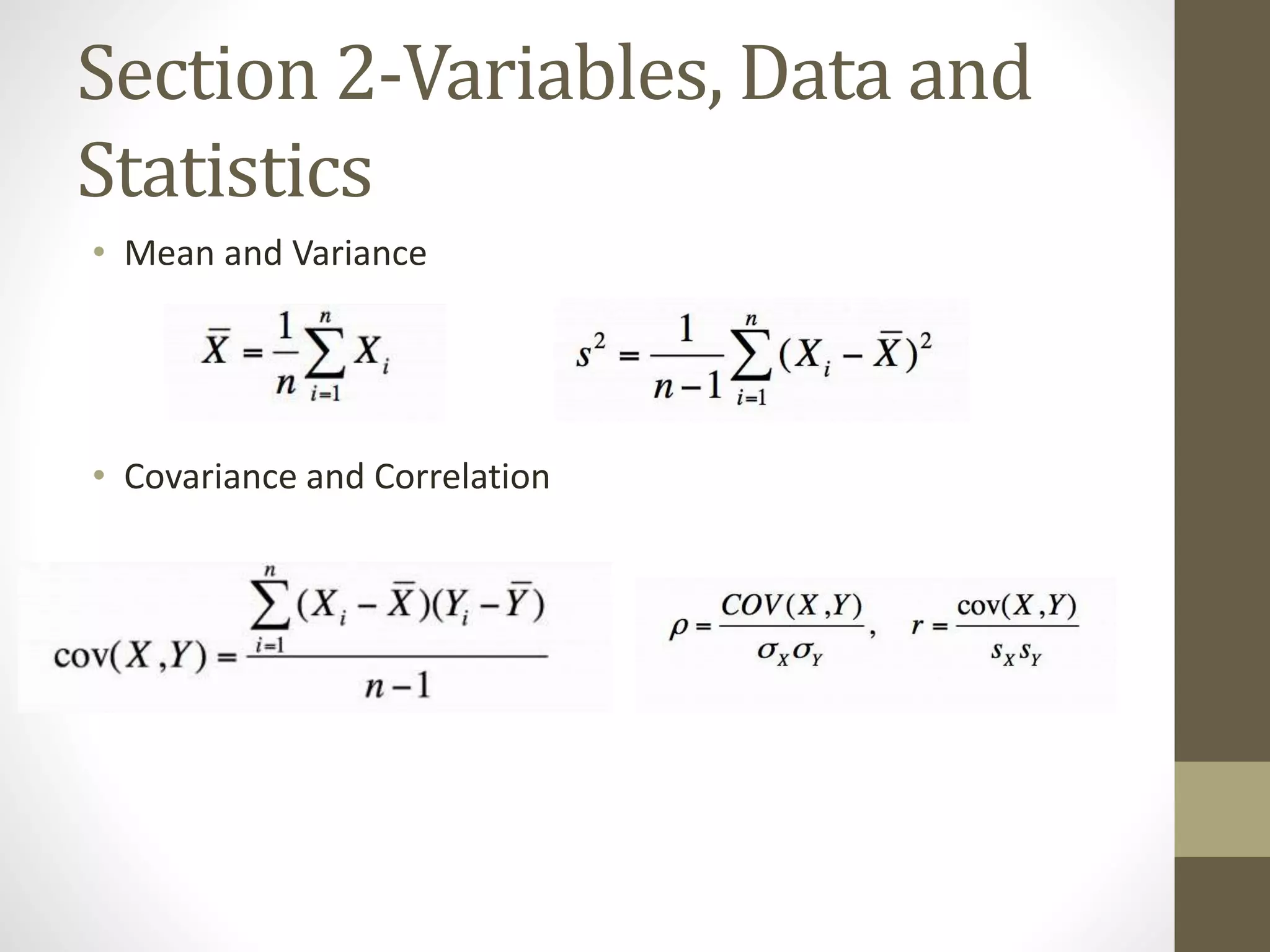
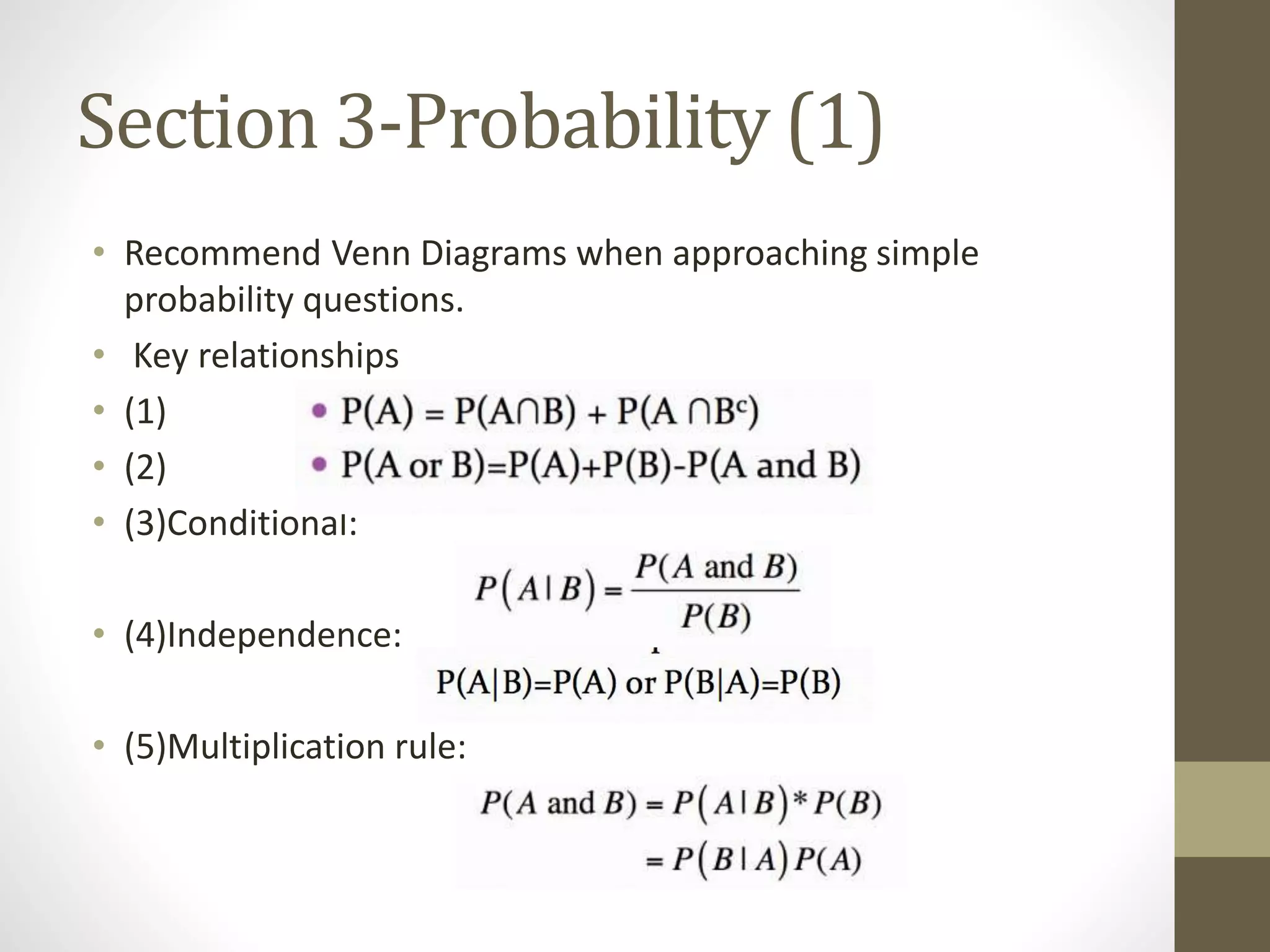
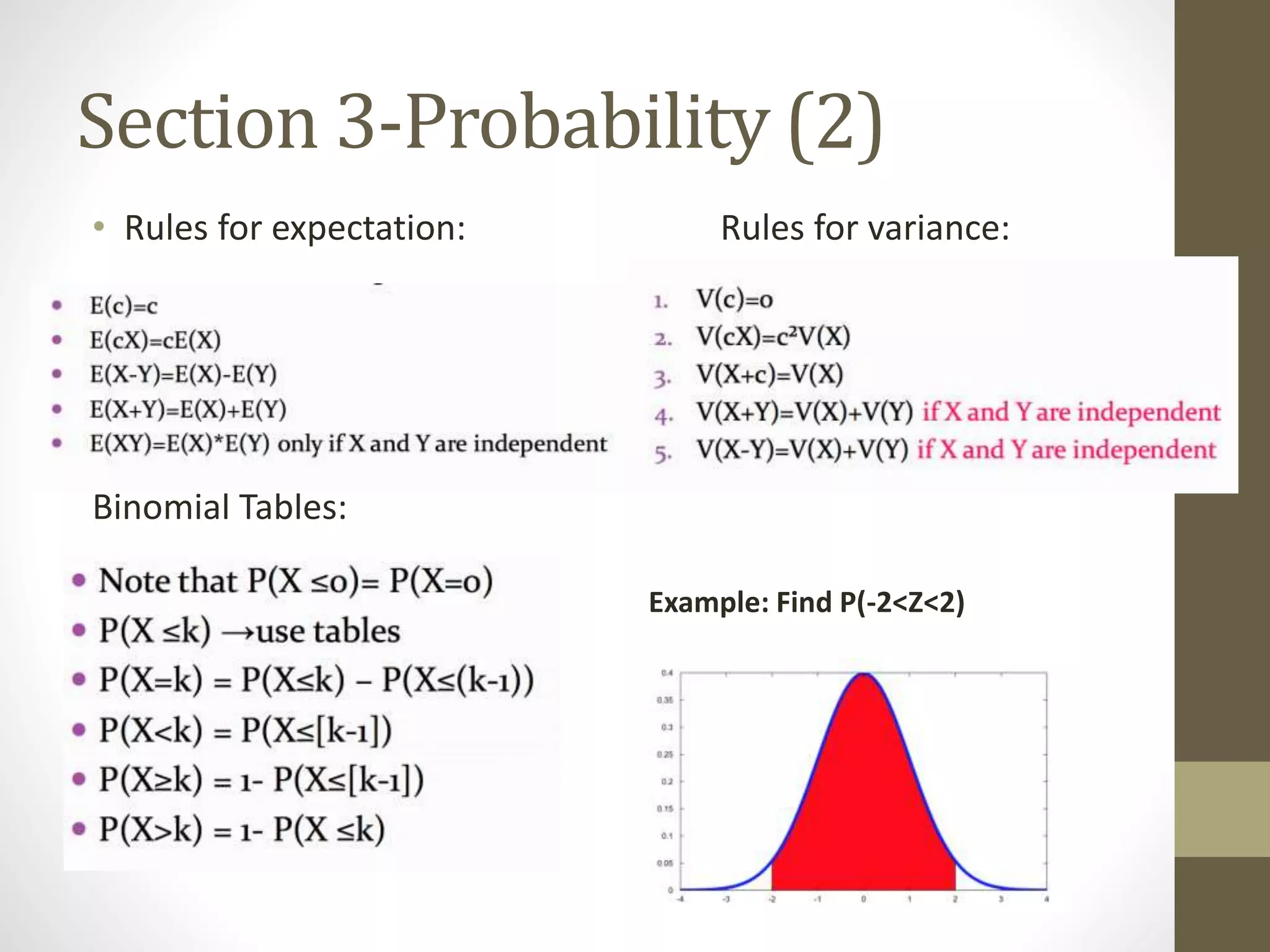
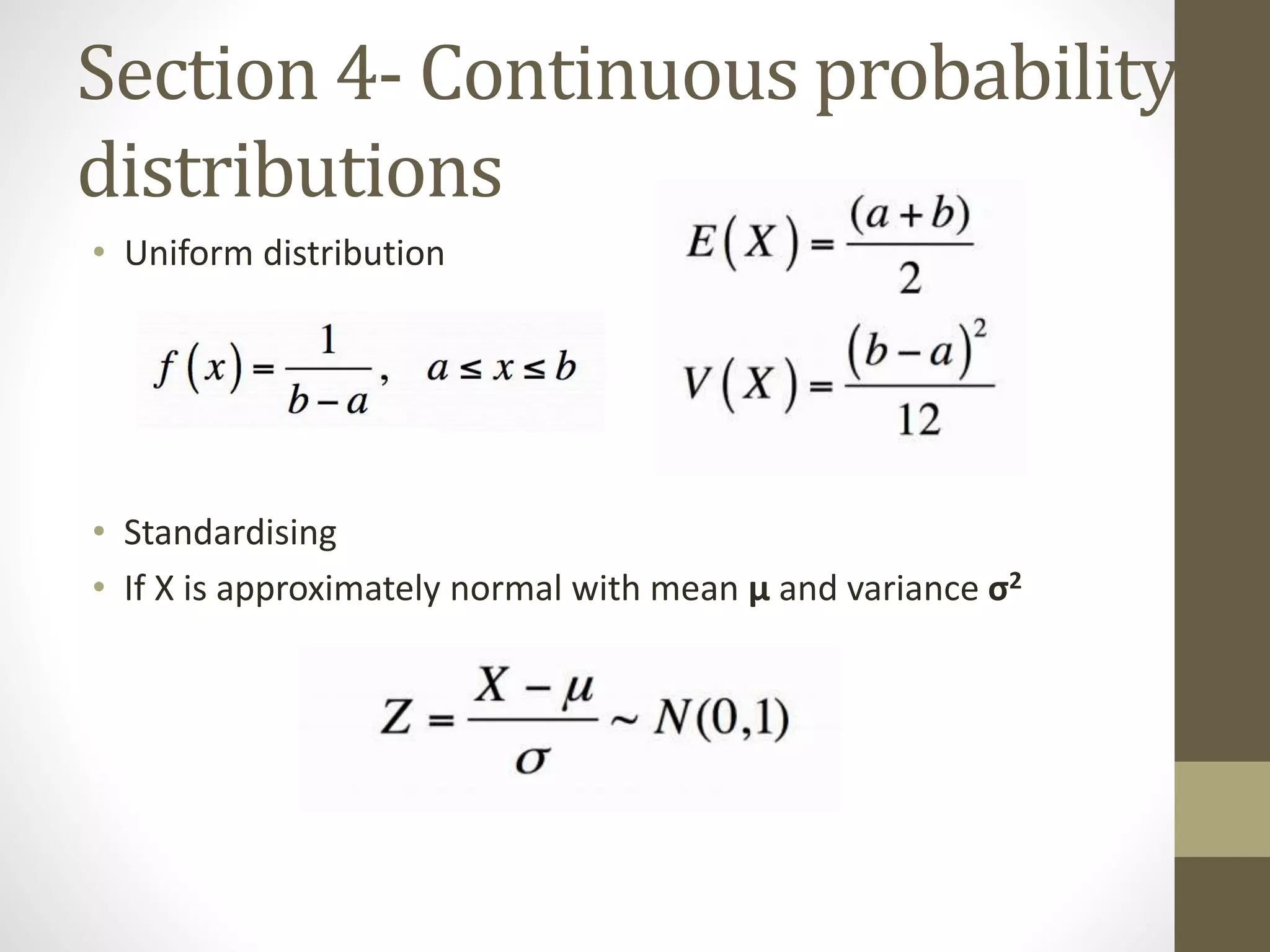
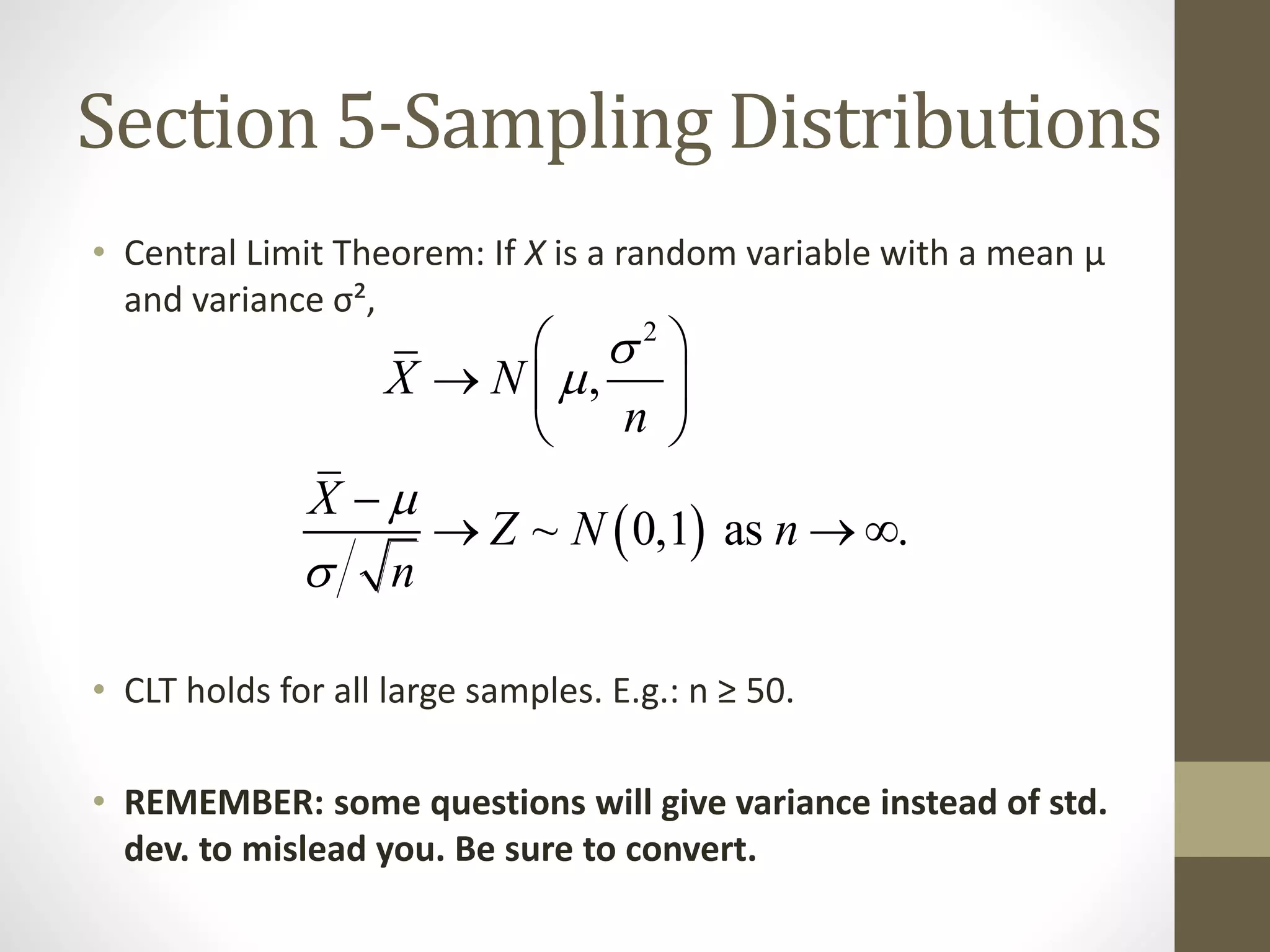
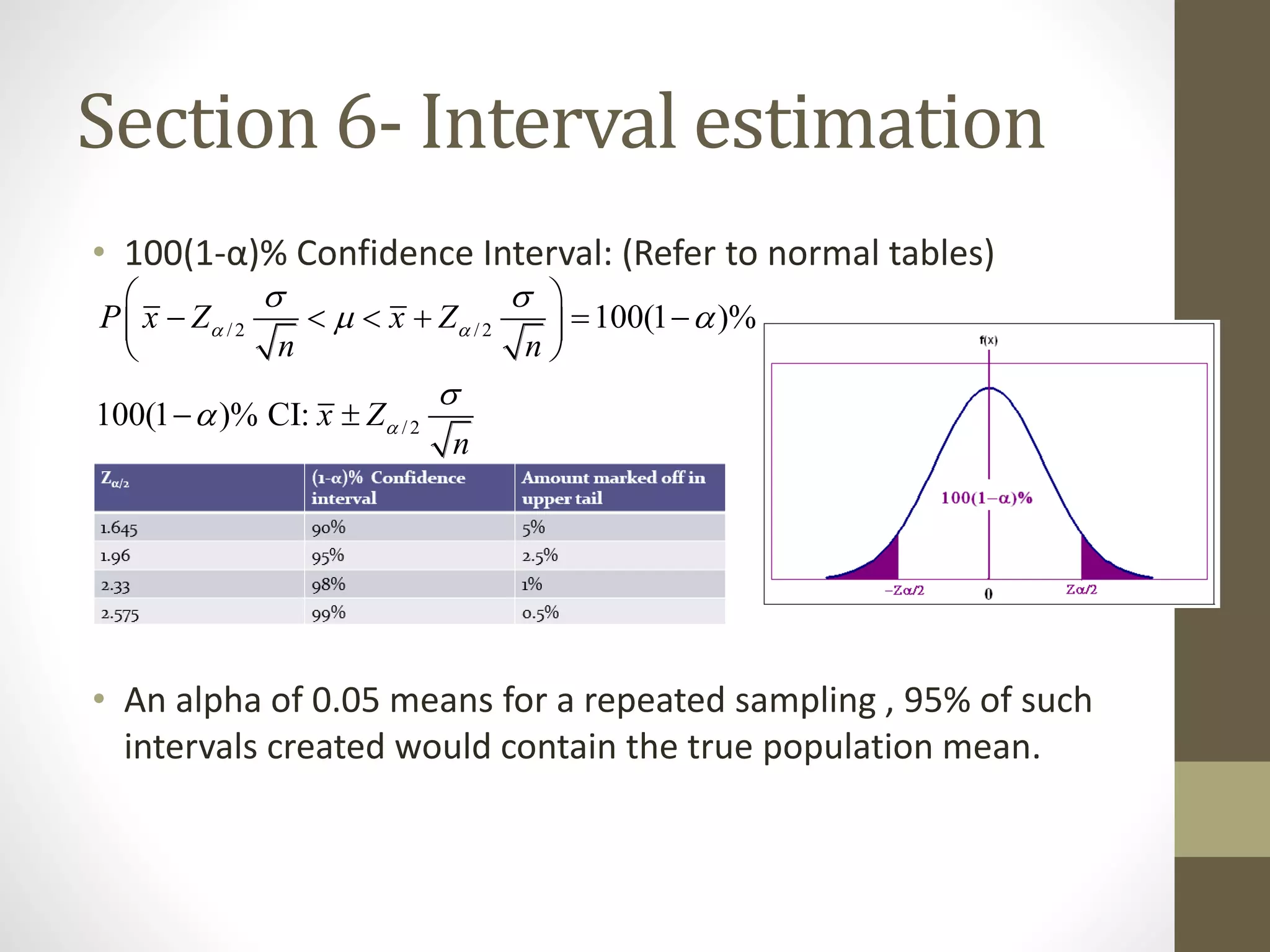
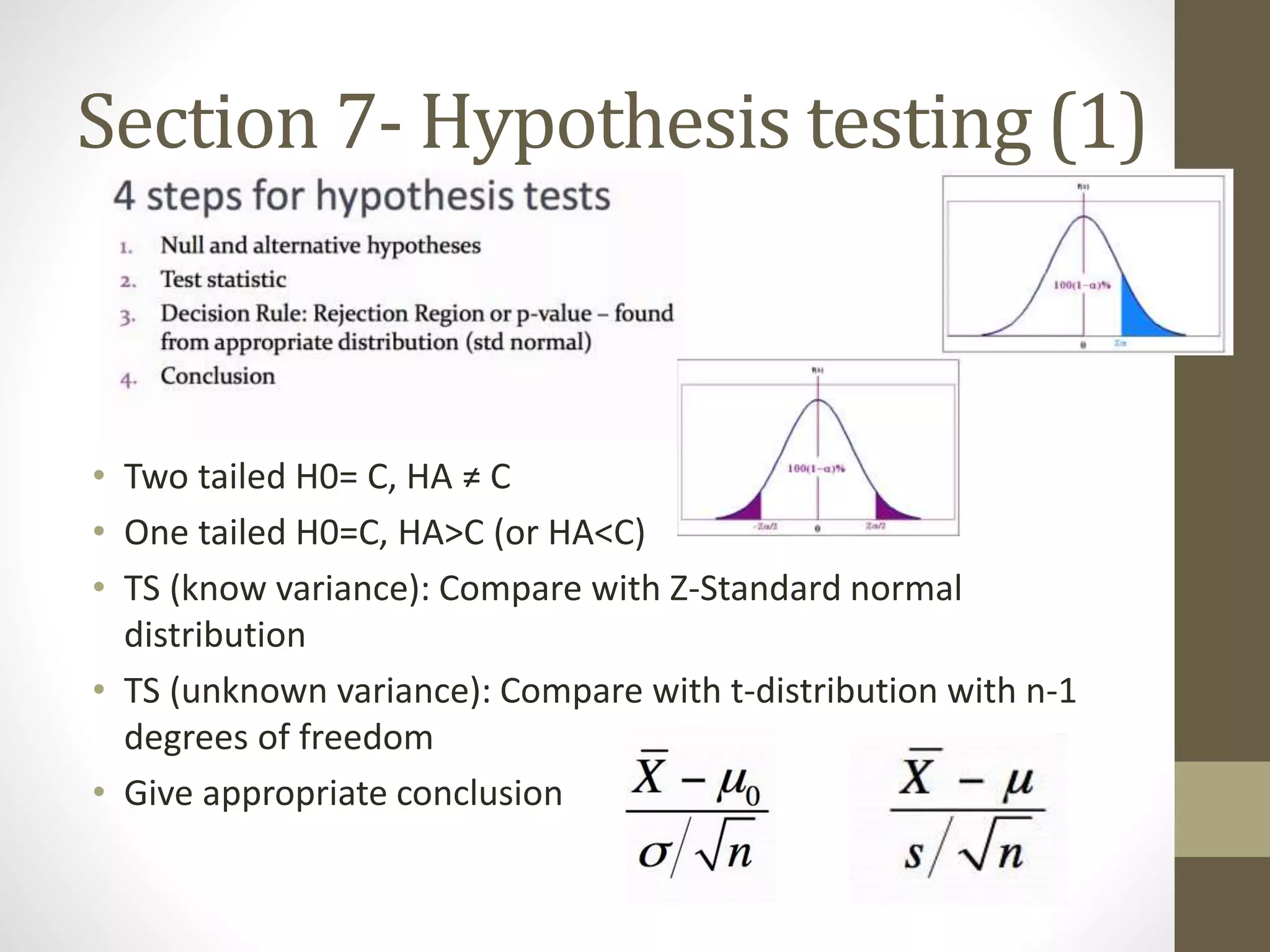
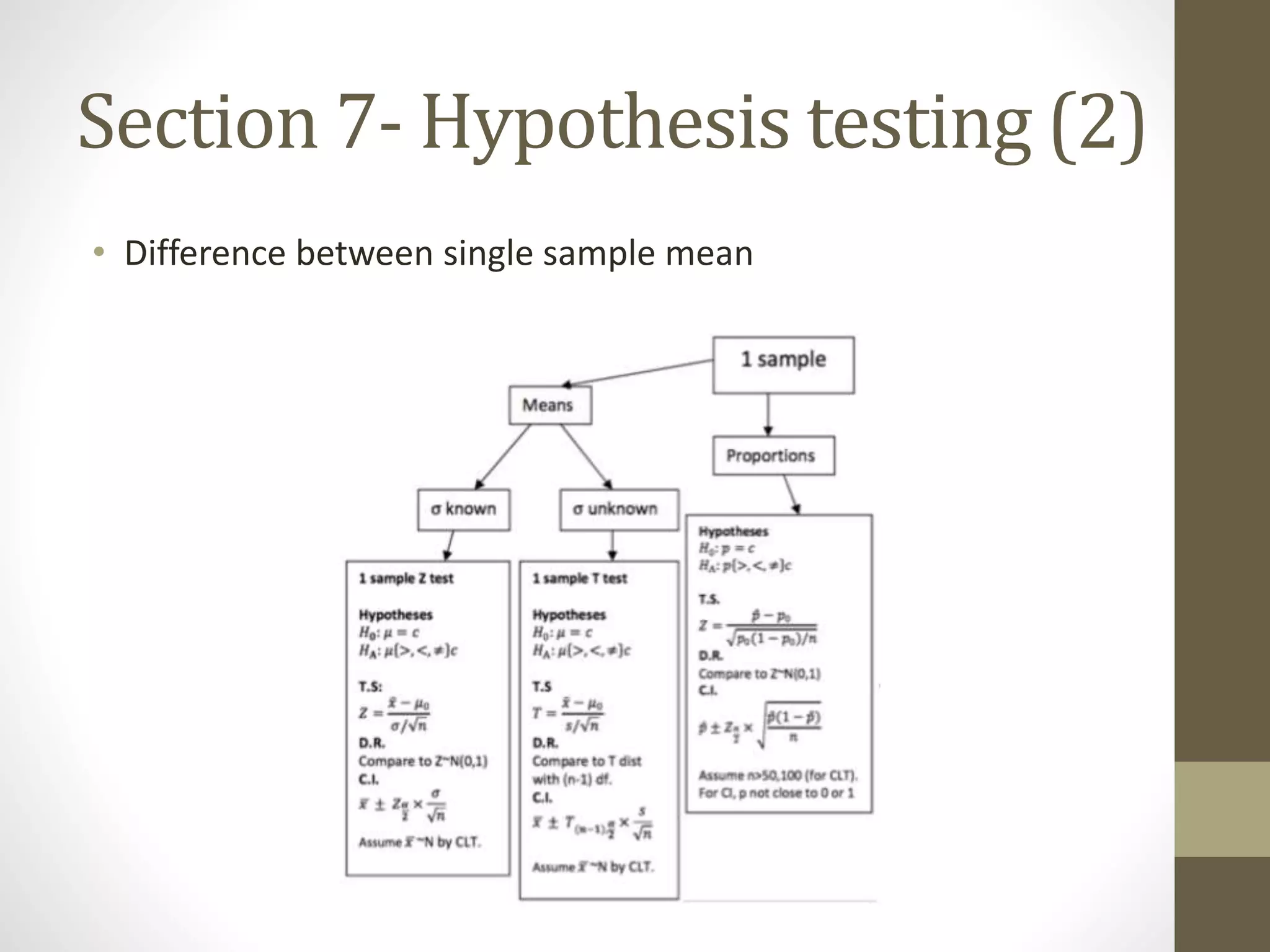
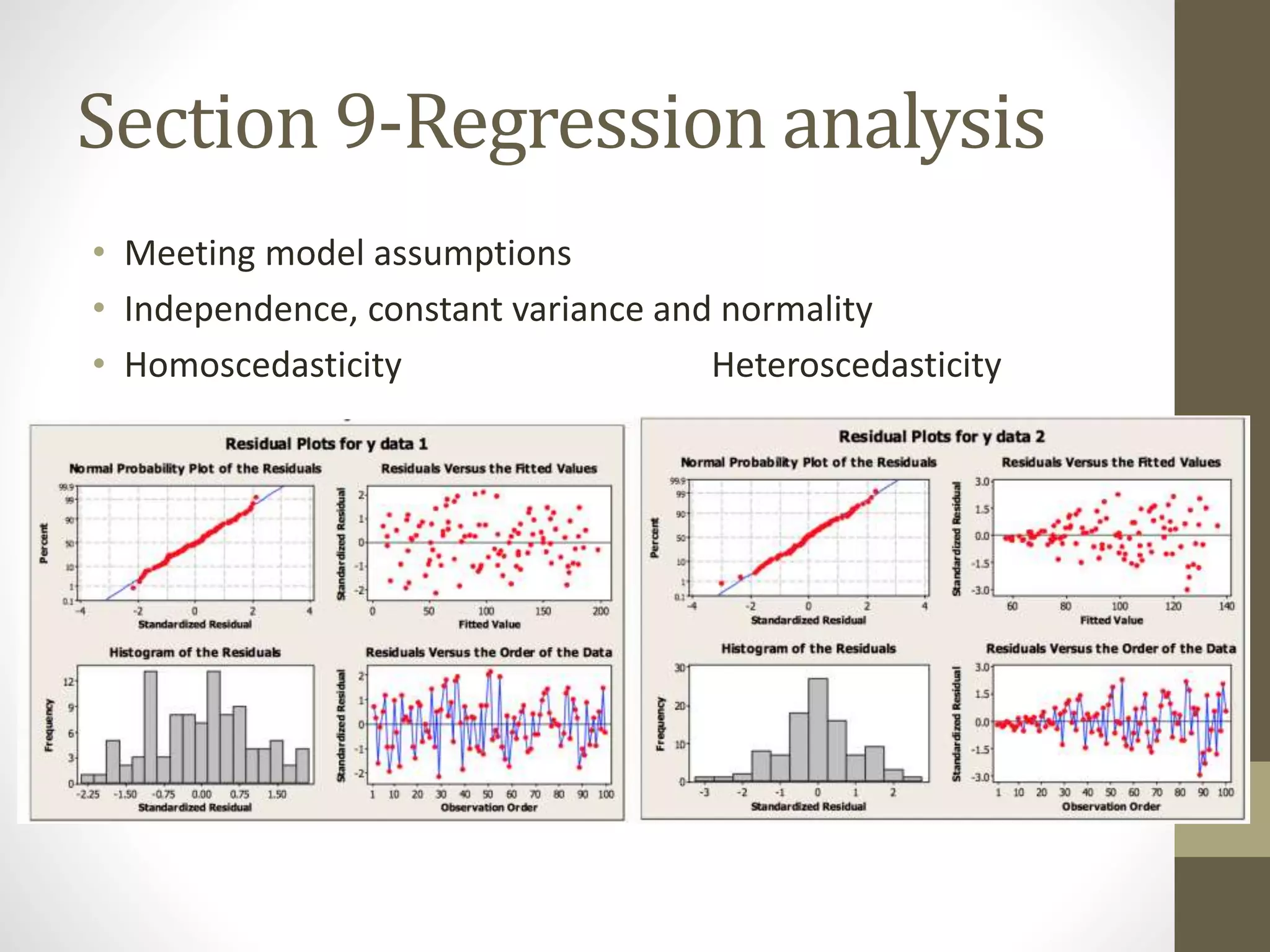
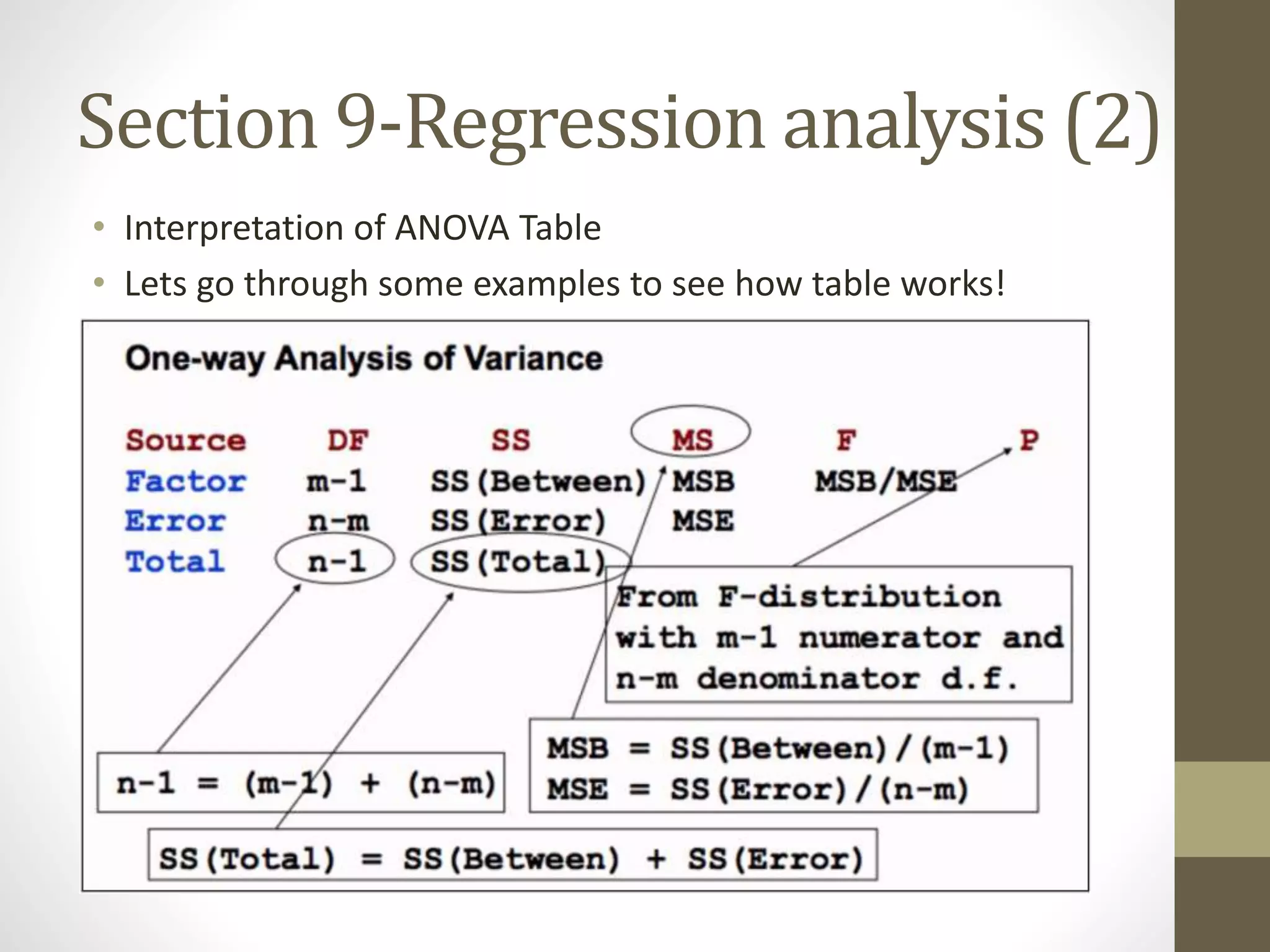
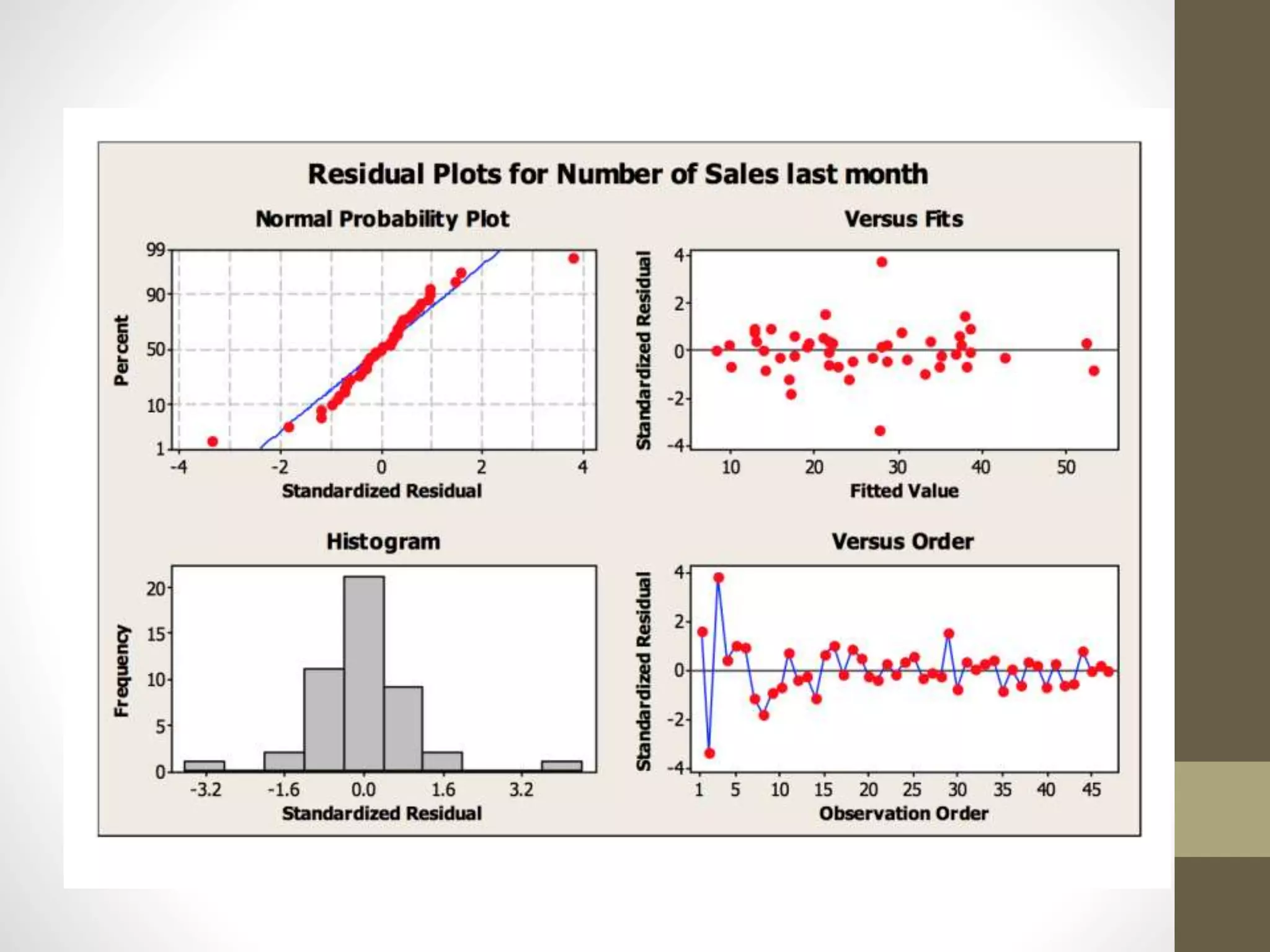
This document provides an overview and examples for a STAT1008 tutorial covering 9 sections: 1) data collection, 2) variables and statistics, 3) probability, 4) continuous probability distributions, 5) sampling distributions, 6) interval estimation, 7) hypothesis testing, 8) hypothesis tests for variances, and 9) regression analysis. Key concepts are explained for each section along with examples from past exams. The tutorial aims to cover the key points needed to understand the material and do well on exams through challenging questions and general hints.