Hydro geology slides 21 to 30
•
2 likes•538 views
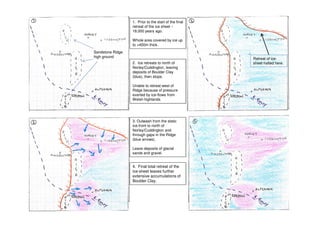
1. Prior to 18,000 years ago, the entire area was covered by an ice sheet up to 400 meters thick. 2. As the ice sheet retreated north of Norley/Cuddington, it deposited boulder clay and then stopped, unable to retreat further west due to pressure from ice flows from the Welsh highlands. 3. Outwash from the static ice front deposited glacial sands and gravels north of Norley/Cuddington and through gaps in the sandstone ridge. 4. Final retreat of the ice sheet left further extensive deposits of boulder clay across the area.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Groundwater occurrence, Rock properties affecting groundwater, Soil classific...

Groundwater occurrence, Rock properties affecting groundwater, Soil classific...
Similar to Hydro geology slides 21 to 30
Similar to Hydro geology slides 21 to 30 (20)
GEOG 100 lecture 10--Water Resources (ground water and ice)

GEOG 100 lecture 10--Water Resources (ground water and ice)
Physical Geography Lecture 09 - Water Resources (Ground water and ice) 110716

Physical Geography Lecture 09 - Water Resources (Ground water and ice) 110716
Chapter4groundwaterhydrology 130630055824-phpapp02

Chapter4groundwaterhydrology 130630055824-phpapp02
More from The Sandstone Ridge Trust Ltd
More from The Sandstone Ridge Trust Ltd (10)
Ridge, Rocks and Springs Project presentation September 2014

Ridge, Rocks and Springs Project presentation September 2014
Recently uploaded
This slide is prepared for master's students (MIFB & MIBS) UUM. May it be useful to all.Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx

Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptxMohd Adib Abd Muin, Senior Lecturer at Universiti Utara Malaysia
https://app.box.com/s/tkvuef7ygq0mecwlj72eucr4g9d3ljcs50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...

50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
MARUTI SUZUKI- A Successful Joint Venture in India.pptx

MARUTI SUZUKI- A Successful Joint Venture in India.pptx
Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx

Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx
Industrial Training Report- AKTU Industrial Training Report

Industrial Training Report- AKTU Industrial Training Report
50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...

50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...
Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf

Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf
Danh sách HSG Bộ môn cấp trường - Cấp THPT.pdf

Danh sách HSG Bộ môn cấp trường - Cấp THPT.pdf
Home assignment II on Spectroscopy 2024 Answers.pdf

Home assignment II on Spectroscopy 2024 Answers.pdf
Basic Civil Engineering Notes of Chapter-6, Topic- Ecosystem, Biodiversity G...

Basic Civil Engineering Notes of Chapter-6, Topic- Ecosystem, Biodiversity G...
Salient features of Environment protection Act 1986.pptx

Salient features of Environment protection Act 1986.pptx
Solid waste management & Types of Basic civil Engineering notes by DJ Sir.pptx

Solid waste management & Types of Basic civil Engineering notes by DJ Sir.pptx
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa

aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Matatag-Curriculum and the 21st Century Skills Presentation.pptx

Matatag-Curriculum and the 21st Century Skills Presentation.pptx
INU_CAPSTONEDESIGN_비밀번호486_업로드용 발표자료.pdf

INU_CAPSTONEDESIGN_비밀번호486_업로드용 발표자료.pdf
Hydro geology slides 21 to 30
- 1. 1. Prior to the start of the final retreat of the ice sheet ~ 18,000 years ago. Whole area covered by ice up to >400m thick. 2. Ice retreats to north of Norley/Cuddington, leaving deposits of Boulder Clay (blue), then stops. Unable to retreat west of Ridge because of pressure exerted by ice-flows from Welsh highlands. Retreat of ice- sheet halted here. 3. Outwash from the static ice-front to north of Norley/Cuddington and through gaps in the Ridge (blue arrows). Leave deposits of glacial sands and gravel. 4. Final total retreat of the ice-sheet leaves further extensive accumulations of Boulder Clay. Sandstone Ridge high ground
- 2. Hydrogeology Workshop Present Geology (1) • And it has all resulted in this: Go to British Geological Survey (BGS) ‘Geology of Britain Viewer’ @ http://www.bgs.ac.uk/discoveringGeology/geologyOfBritain/viewer.html (Follow instructions at rear of handout)
- 3. Hydrogeology Workshop Present Geology (2) Note: Relative thickness of the Glacial Clay, Sands and Gravel and Alluvium is greatly exaggerated
- 4. Hydrogeology Workshop Part 2 Introduction to Hydrogeology
- 5. Hydrogeology Workshop Introduction to Hydrogeology (1) What is groundwater and its place in the hydrological cycle? Ocean Evaporation Heat/Radiation Clouds form Circulation in the atmosphere Precipitation Runoff Transpiration and evaporation Recharge Water table Groundwater flow Discharges Groundwater discharges: •River/lakes springs/wetlands; •Sea/estuaries •Abstractions (wells/boreholes) Saline water
- 6. Hydrogeology Workshop Introduction to Hydrogeology (2) Some basic terminology Aquifer: • Rock which allows water to flow in ‘significant’ quantities (Ridge area examples: Terrace/Glacial Sands and Gravel, Sherwood Sandstones) Aquiclude: • Rock through which virtually no water flows. (Ridge area examples rare strictly speaking but could include Mercia Mudstones, Halite formations, Glacial Boulder Clay) • Can be a layer above a ‘confined’ aquifer. Aquitard: • Rock which allows ‘small’ amounts of water to flow through it. (Ridge area examples Mercia Mudstones, Halite formations, Glacial Boulder Clay) • Can be a layer above a ‘semi-confined’ aquifer. Porosity; Void space, expressed as % of rock volume. • Primary porosity – intergranular; • Secondary porosity – fractures/fissures; • Effective porosity – space in which groundwater flow is ‘active’ (also related to ‘storage’). Permeability (Hydraulic Conductivity) • Property which allows fluid (water) to move through rock/soil.
- 7. Hydrogeology Workshop Introduction to Hydrogeology (3) Some basic terminology • Water table: – Surface of groundwater, interface between the saturated aquifer and the unsaturated zone. • Piezometric Level: – ‘Pressure’ (head) of water in a confined or semi-confined aquifer. Effectively where the water level will be in a borehole drilled into the aquifer. • Aquifer conditions: – Unconfined: Aquifer which contains the water table. Water can enter it from recharge. – Confined: Fully saturated aquifer with piezometric surface (e.g. level of water in a borehole) above its top. Sometimes known as ‘artesian’. Strictly speaking, no water enters as recharge from above. – Semi-confined: Fully saturated aquifer with piezometric surface (e.g. level ,of water in a borehole) above its top. BUT water can leak into it from above. – Perched aquifer: An upper unconfined aquifer (i.e. It contains a water table) which is separated from a lower one , with an intervening unsaturated zone. Based on Brassington, R. (1988) Field Hydrogeology, Geological Society Handbook, Open University Press, Milton Keynes/Halstead Press, New York – Toronto, P.4, fig. 1.2 Confined or semi-confined Unconfined
- 8. Hydrogeology Workshop Introduction to Hydrogeology (4) Groundwater Flow Bath Tubs and Black Boxes Where does it want to go? • In at the top (recharge/leakage) and out at the bottom (discharge to rivers, lakes, sea etc). • From high groundwater level/pressure (higher ground) to low level/pressure (lower ground/lower pressure).
- 9. Hydrogeology Workshop Introduction to Hydrogeology (5) Groundwater Flow Bath Tubs and Black Boxes How does it get there? • Driven by hydraulic gradients – Lateral hydraulic gradients – Vertical hydraulic gradients • Downwards • Upwards – How do they work (e.g from recharge to discharge at rivers, springs etc). • ‘Controlled’ by Permeability • Primary – intergranular – flow tends to be fairly slow • Secondary - fractures/fissures/bedding planes and geological faults – flow can be very fast. Sherwood Sandstone aquifers benefit from Primary AND Secondary porosity/permeability: – Lots of water ‘stored’ in intergranular primary pores; – Rapid flow of groundwater through fractures/fissures; – (very good for water supplies) And...........
- 10. Photographs from CCTV down a public water supply borehole in the Sherwood Sandstone. • Primary porosity in the rock-mass; •Clear fissures showing secondary porosity; •Nice clear water under these ‘static’ conditions.
