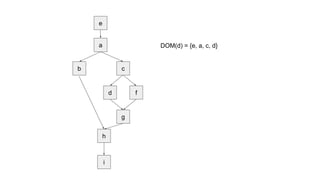
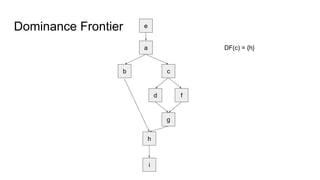
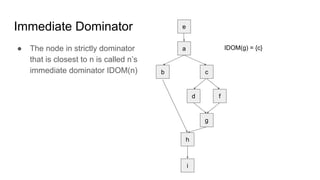
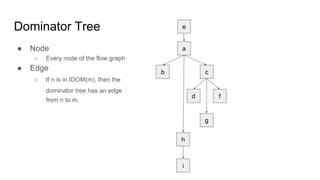
The document discusses the process of converting a program into static single assignment (SSA) form. It involves inserting phi-functions at join points to rename variables and ensure each variable has a single definition. Phi-functions are inserted at nodes in the dominance frontier of a definition, which contains predecessors that are not strictly dominated. The dominance frontier and dominator tree properties are used to determine where to place phi-functions to construct the SSA form.