The document discusses in-built functions in C++, command line parameters, and function pointers. It provides examples of commonly used string functions like strcpy, strcat, and strlen as well as numeric functions like abs, ceil, and sqrt. It explains that command line parameters allow passing values to programs during execution and are accessed through argc and argv. Function pointers are variables that store the address of a function and can be initialized with a function name.


![More About Functions
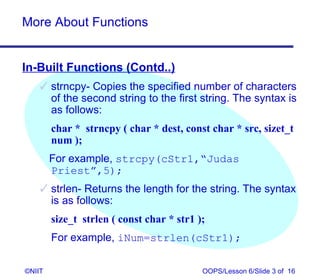
In-Built Functions (Contd..)
strstr- Scans string1 for the first occurrence of
string2. The syntax is as follows:
Char * strstr (char * string1, const char * string2 );
For example, char str1[]=”Hello World”;
char str2[]=”or”;
char * sFound=strstr(str1,str2);
coutsFound-str1+1;
strcmp- compares two strings (supplied as its
parameters) and returns an integer value.
©NIIT OOPS/Lesson 6/Slide 4 of 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaeoopxp06-120502155906-phpapp02/85/Aae-oop-xp_06-4-320.jpg)



![More About Functions
In-Built Functions (Contd..)
atoi- Returns the integer value stored as a string.
The syntax is as follows:
int atoi (const char * string)
For example, char str[]=”345A”;
result=atoi(str);
©NIIT OOPS/Lesson 6/Slide 8 of 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaeoopxp06-120502155906-phpapp02/85/Aae-oop-xp_06-8-320.jpg)

![More About Functions
Declaration of Functions
The syntax to declare a function is as follows:
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
}
©NIIT OOPS/Lesson 6/Slide 10 of 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaeoopxp06-120502155906-phpapp02/85/Aae-oop-xp_06-10-320.jpg)

![More About Functions
Just a Minute…
int argc gives ________________
char *argv[] gives ________________.
©NIIT OOPS/Lesson 6/Slide 12 of 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaeoopxp06-120502155906-phpapp02/85/Aae-oop-xp_06-12-320.jpg)

![More About Functions
Pointer to Function
Function pointers are pointers, i.e. variables, which
point to the address of a function.
The addresses that the function pointers contain
reside in the code segment itself
The syntax to declare to declare a function pointer is
as follows:
[return_type] (*pointer_name)[(list_of_parameters)]
A pointer to a function can be initialized with the name
of a function, within the declaration of the pointer. For
example,
long max(const long* array,int cnt); pFun=max;
©NIIT OOPS/Lesson 6/Slide 14 of 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aaeoopxp06-120502155906-phpapp02/85/Aae-oop-xp_06-14-320.jpg)

