Embed presentation
Downloaded 51 times

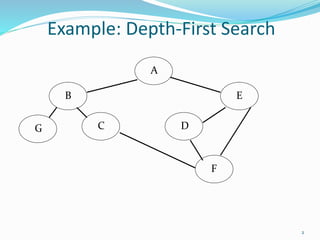
![DFS(Algorithm)
1. Initialize all nodes to the ready state(STATUS=1).
2. Push the starting node A onto STACK and change its
status to the waiting state(STATUS=2).
3. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until STACK is empty:
4. Pop the top node N of STACK. Process N and change
the status of N to the processed state (STATUS=3).
5. Push onto STACK all the neighbors of N that are still
in the ready state (STATUS=1), and change their
status to the waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Step 3 loop]
6. Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds16-graphtraversal-180827163420/85/Data-Structure-and-Algorithms-Graph-Traversal-3-320.jpg)
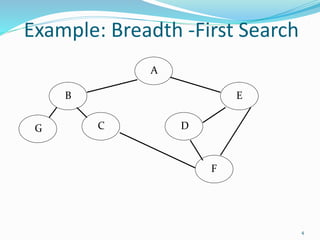
![BFS(Algorithm)
5
1. Initialize all nodes to the ready state(STATUS=1).
2. Put the starting node A in QUEUE and change its
status to the waiting state(STATUS=2).
3. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until QUEUE is empty:
4. Remove the front node N of QUEUE. Process N
and change the status of N to the processed state
(STATUS=3).
5. Add to the rear of QUEUE all the neighbors of N
that are in the steady state (STATUS=1), and change
their status to the waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Step 3 loop]
6. Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds16-graphtraversal-180827163420/85/Data-Structure-and-Algorithms-Graph-Traversal-5-320.jpg)

The document describes depth-first search (DFS) and breadth-first search (BFS) graph traversal algorithms. DFS uses a stack and processes each node by first exploring all of its neighbor nodes before backtracking, while BFS uses a queue and processes nodes level-by-level from the starting node outwards. Both algorithms initialize all nodes as ready, process nodes by changing their status, and add neighboring ready nodes to the stack/queue to change their status to waiting.


![DFS(Algorithm)
1. Initialize all nodes to the ready state(STATUS=1).
2. Push the starting node A onto STACK and change its
status to the waiting state(STATUS=2).
3. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until STACK is empty:
4. Pop the top node N of STACK. Process N and change
the status of N to the processed state (STATUS=3).
5. Push onto STACK all the neighbors of N that are still
in the ready state (STATUS=1), and change their
status to the waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Step 3 loop]
6. Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds16-graphtraversal-180827163420/85/Data-Structure-and-Algorithms-Graph-Traversal-3-320.jpg)

![BFS(Algorithm)
5
1. Initialize all nodes to the ready state(STATUS=1).
2. Put the starting node A in QUEUE and change its
status to the waiting state(STATUS=2).
3. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until QUEUE is empty:
4. Remove the front node N of QUEUE. Process N
and change the status of N to the processed state
(STATUS=3).
5. Add to the rear of QUEUE all the neighbors of N
that are in the steady state (STATUS=1), and change
their status to the waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Step 3 loop]
6. Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ds16-graphtraversal-180827163420/85/Data-Structure-and-Algorithms-Graph-Traversal-5-320.jpg)
