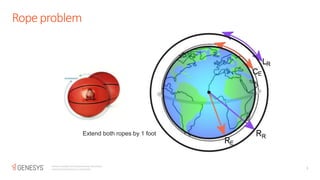
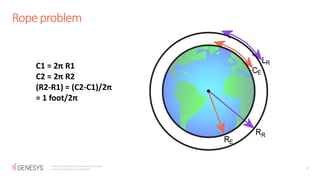
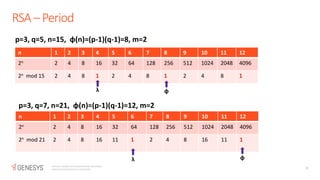
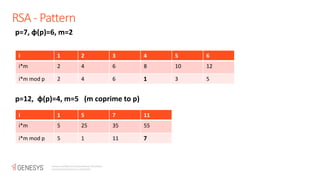
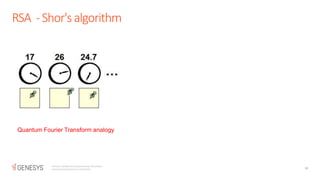
The document discusses the RSA encryption algorithm. It begins by explaining how to generate the public and private keys, including choosing two prime numbers p and q, computing phi(n) as (p-1)(q-1), and selecting the public and private exponents e and d. It then explains how RSA encryption and decryption work using these keys. The document also discusses some ways RSA can be broken, such as with a quantum computer using Shor's algorithm to find the prime factors of n through periodicity. It provides examples to illustrate RSA key generation and encryption/decryption.