The document discusses new C++11 features including:
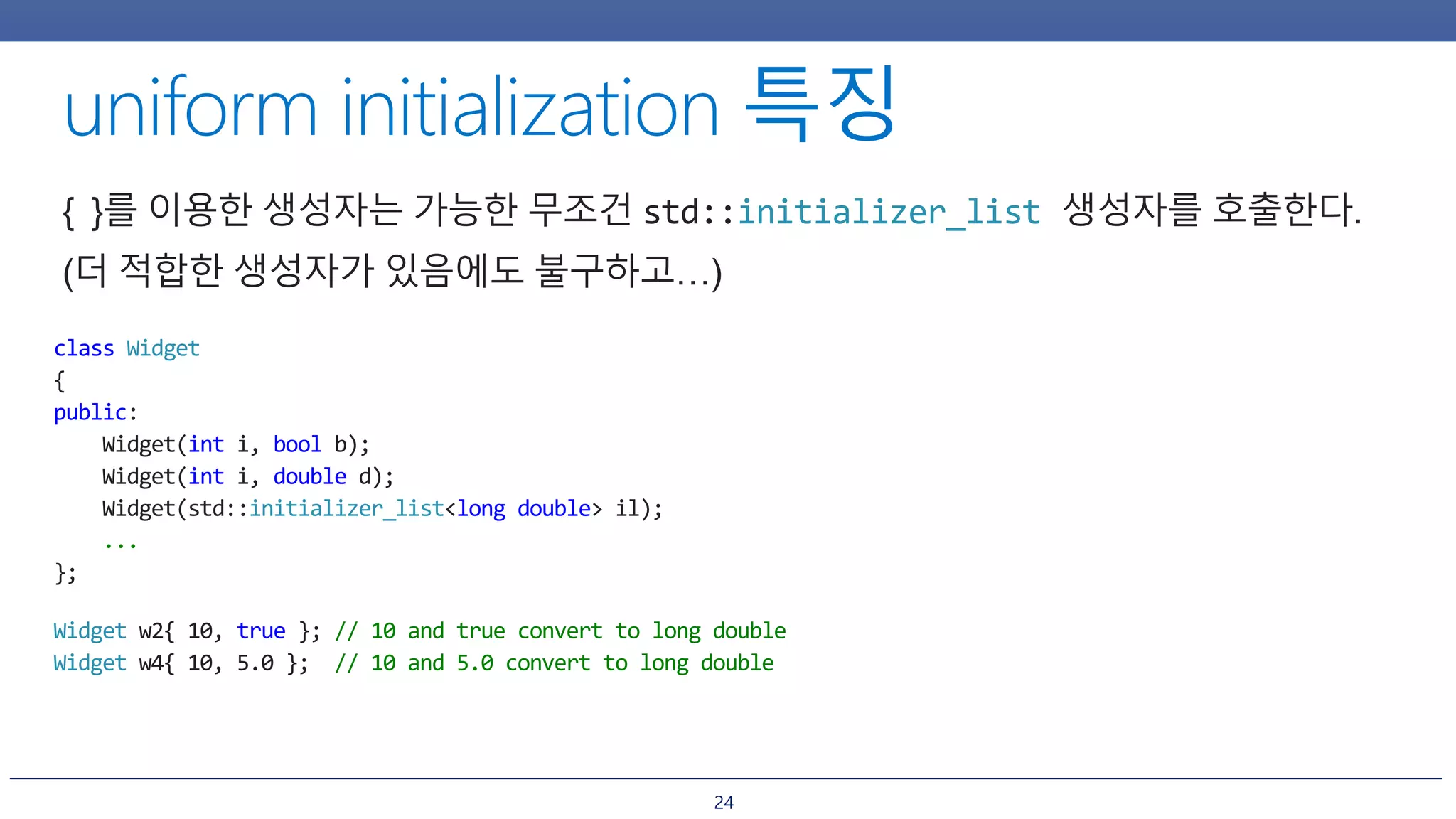
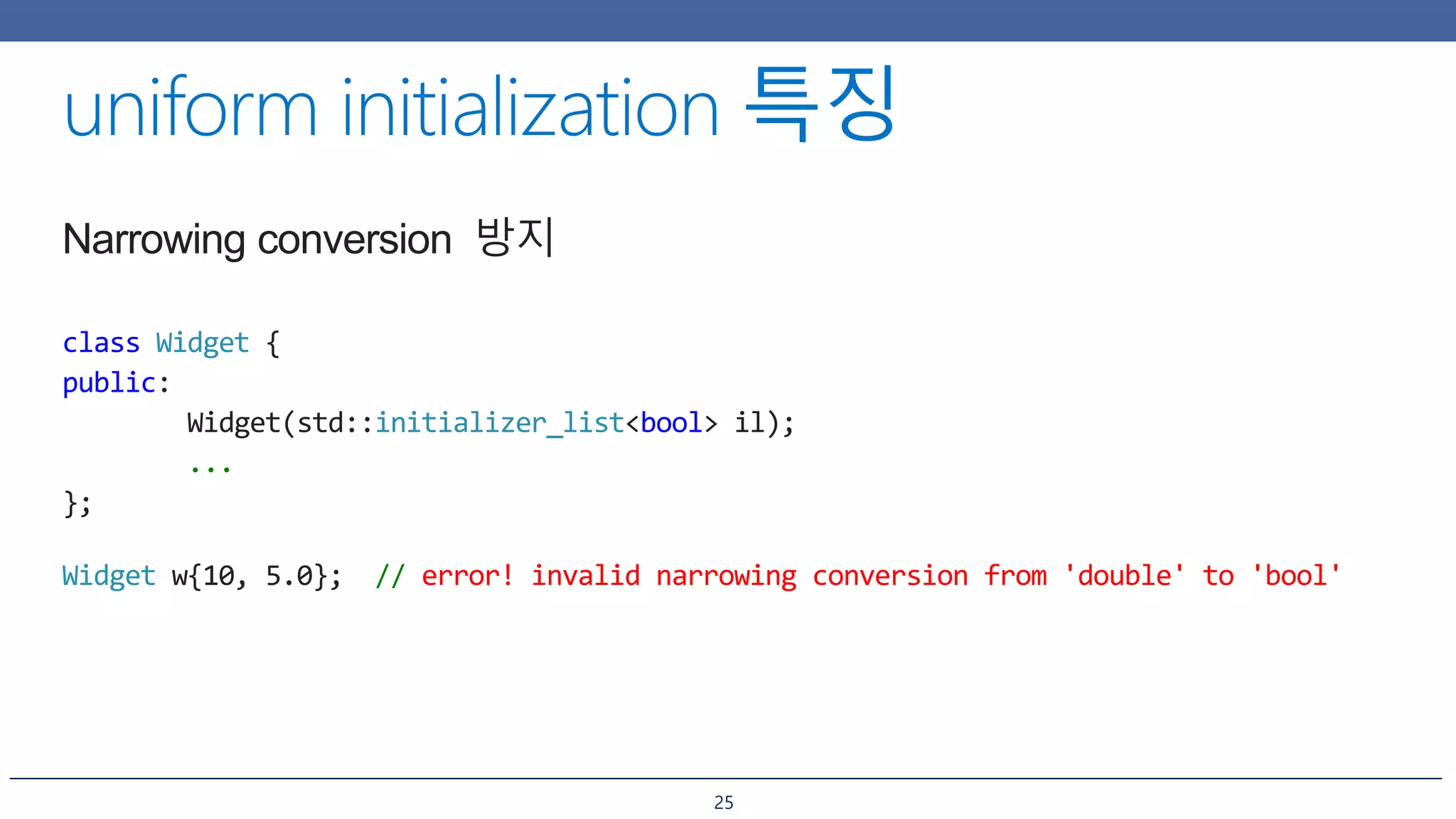
1. Uniform initialization syntax using curly braces {} which can initialize objects in a clear and consistent way compared to parentheses () or equals =.
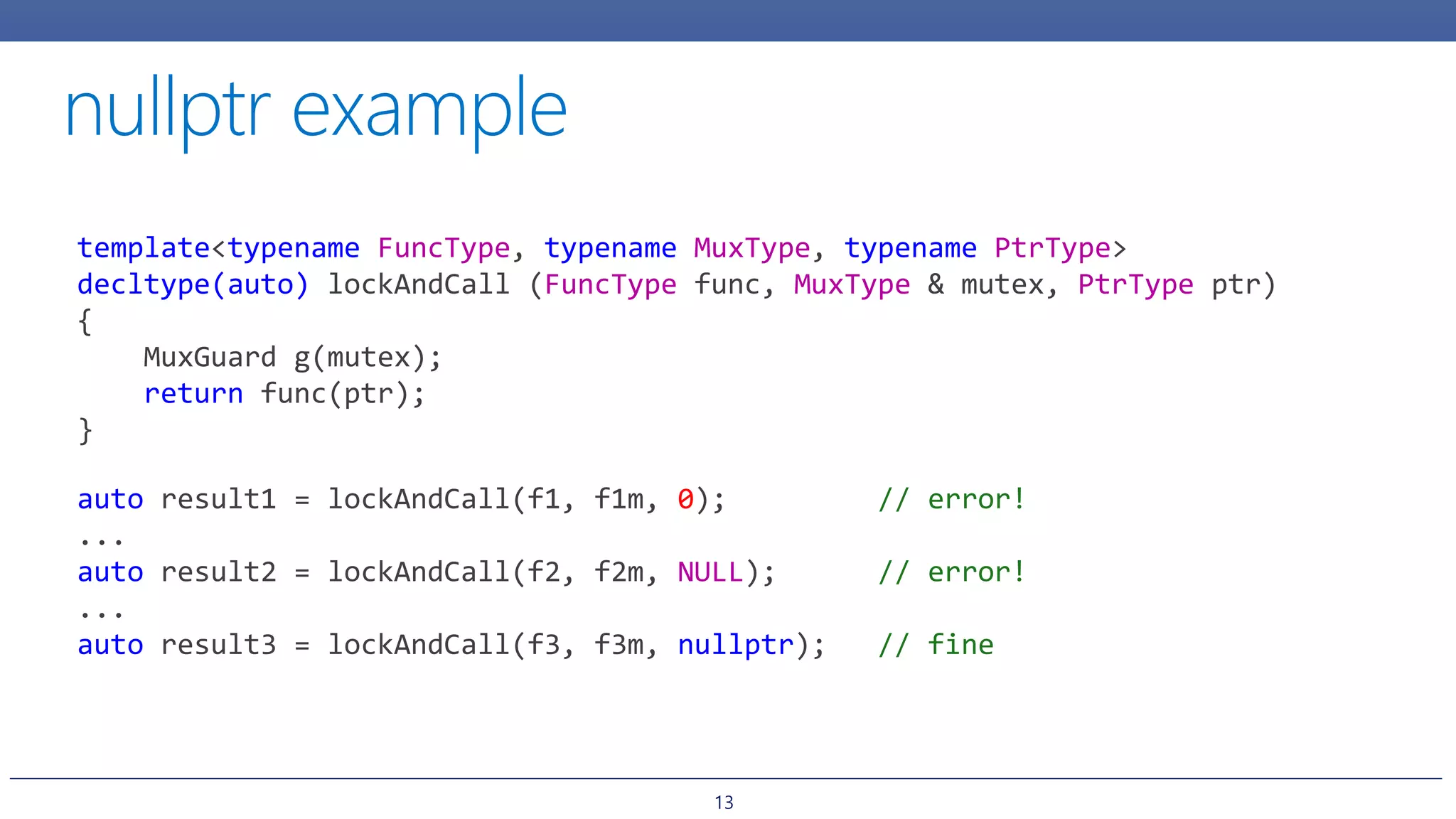
2. Initializer lists and how they allow initializing objects from a list of values. However, initializer lists may prefer certain constructors unintuitively.
3. How uniform initialization helps prevent narrowing conversions and most vexing parse issues that could occur in C++98 code.

![Overview
vector<vector<int>>
user-defined
literals thread_local
=default, =delete
atomic<T> auto f() -> int
array<T, N>
decltype
vector<LocalType>
noexcept
regex
initializer lists
constexpr
extern template
unordered_map<int, string>raw string literals
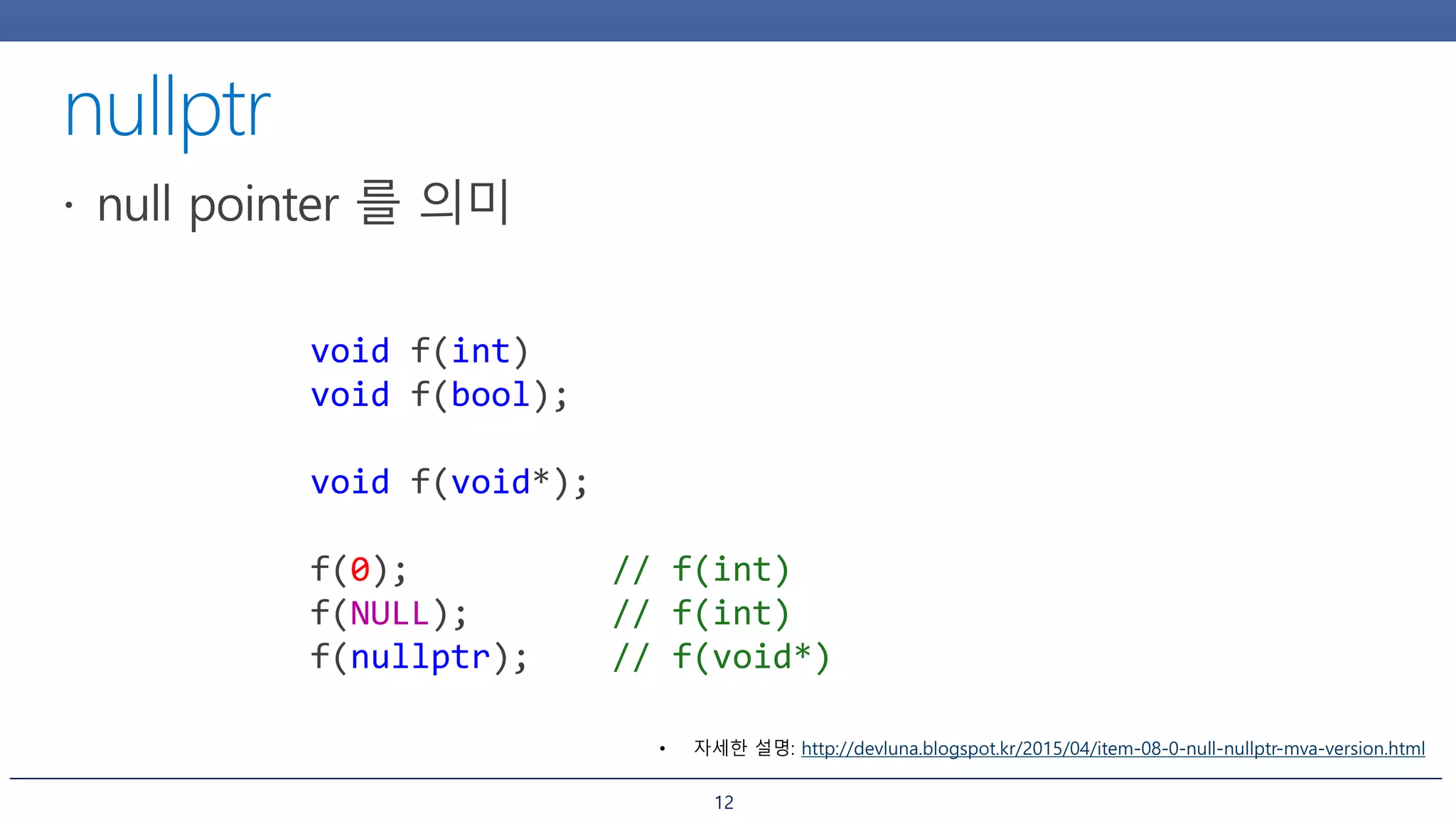
nullptr auto i = v.begin();
async
lambdas
[]{ foo(); }
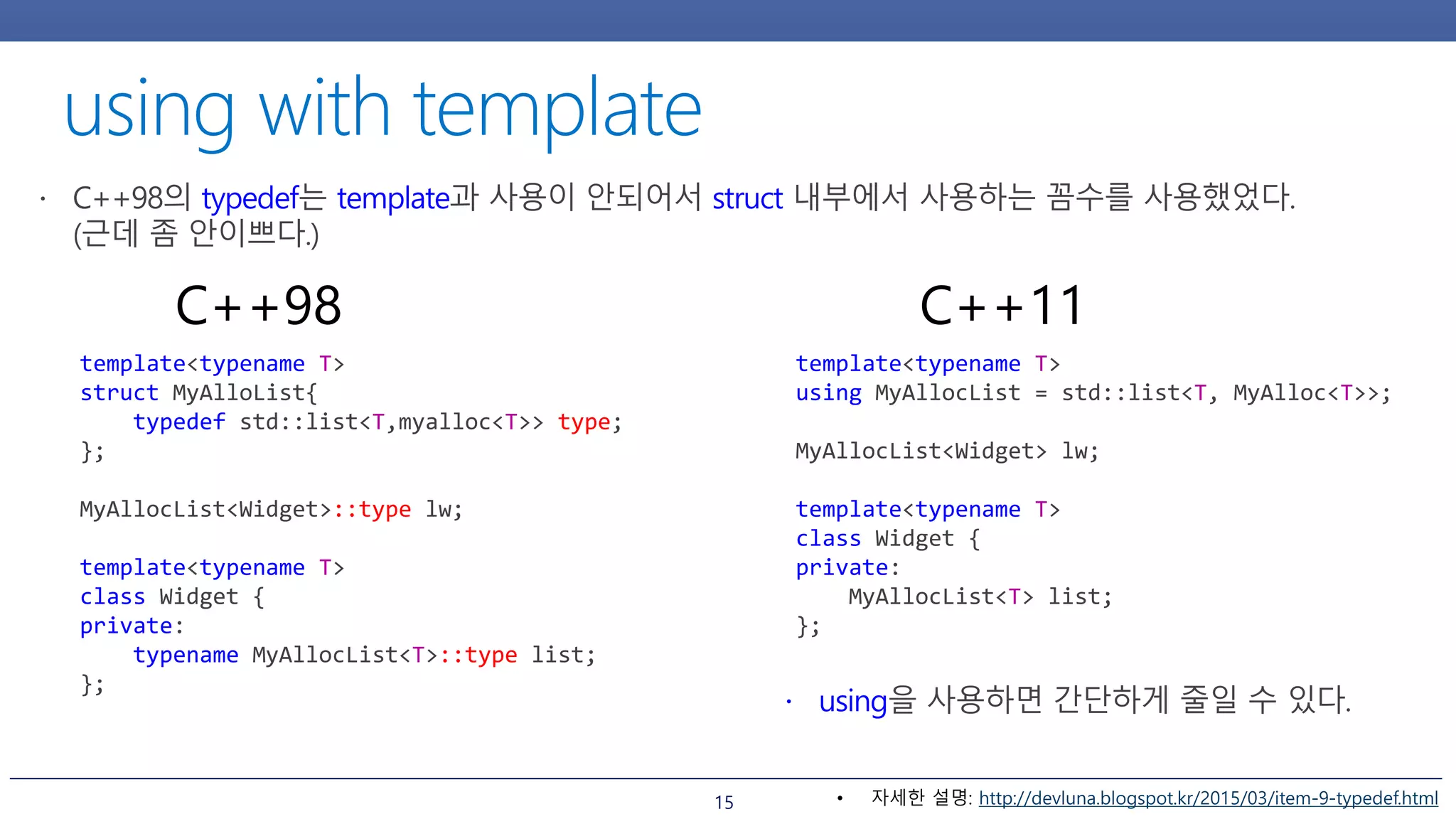
template
aliases
unique_ptr<T>
shared_ptr<T>
weak_ptr<T>
thread, mutex
for (x : coll)
override,
final
variadic templates
template <typename T…>
function<>
promise<T>/future<T>
tuple<int, float, string>
strongly-typed enums
enum class E {…};
static_assert(x)
rvalue references
(move semantics)
delegating constructors
packaged_task<T>
Decucing Type
Concurrency
Performance
Smart Pointer
lambda expression
range-based for
initializer list
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/welcometomodernc-151020055652-lva1-app6892/75/Welcome-to-Modern-C-2-2048.jpg)



![8
template<typename Container, typename Index>
decltype(auto) authAndAccess(Container& c, Index i)
{
authenticateUser();
return c[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/welcometomodernc-151020055652-lva1-app6892/75/Welcome-to-Modern-C-8-2048.jpg)


![11
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
std::cout << arr[i] << std::endl;
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
for (auto& i : arr)
std::cout << i << std::endl;
C++98 C++11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/welcometomodernc-151020055652-lva1-app6892/75/Welcome-to-Modern-C-11-2048.jpg)