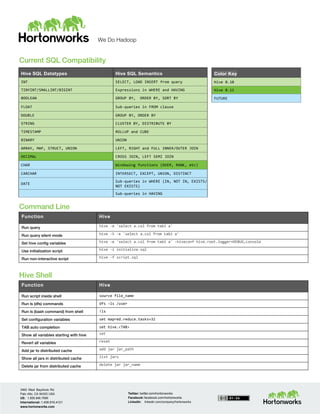
The document is a comprehensive guide for SQL users transitioning to Hadoop with Apache Hive, which is a data warehouse infrastructure built on Hadoop. It includes a cheat sheet for HiveQL (Hive Query Language) with SQL syntax equivalents for various operations, alongside additional resources for learning Hive. Users can access tutorials and services related to Hadoop and Hive through provided links.