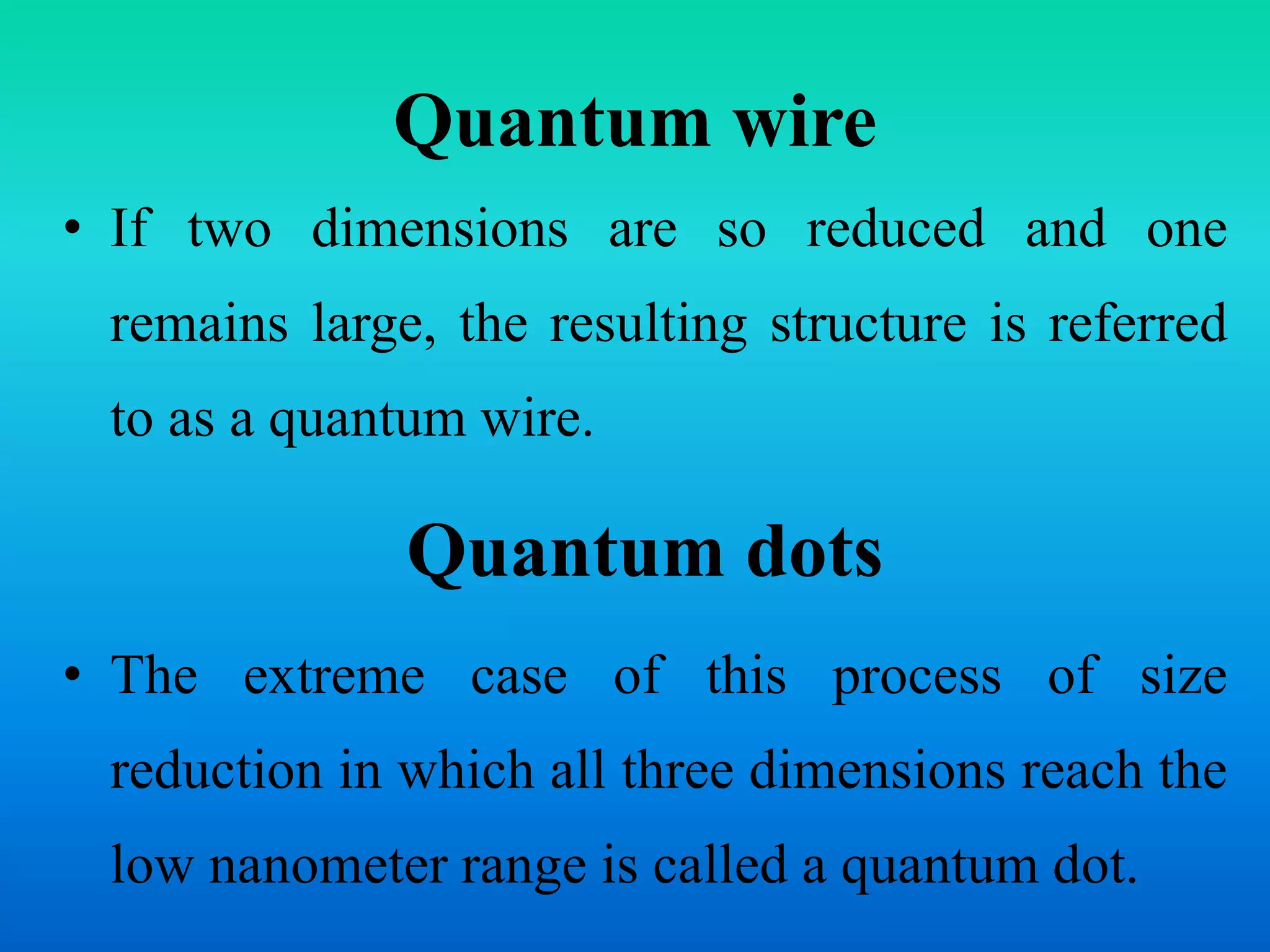
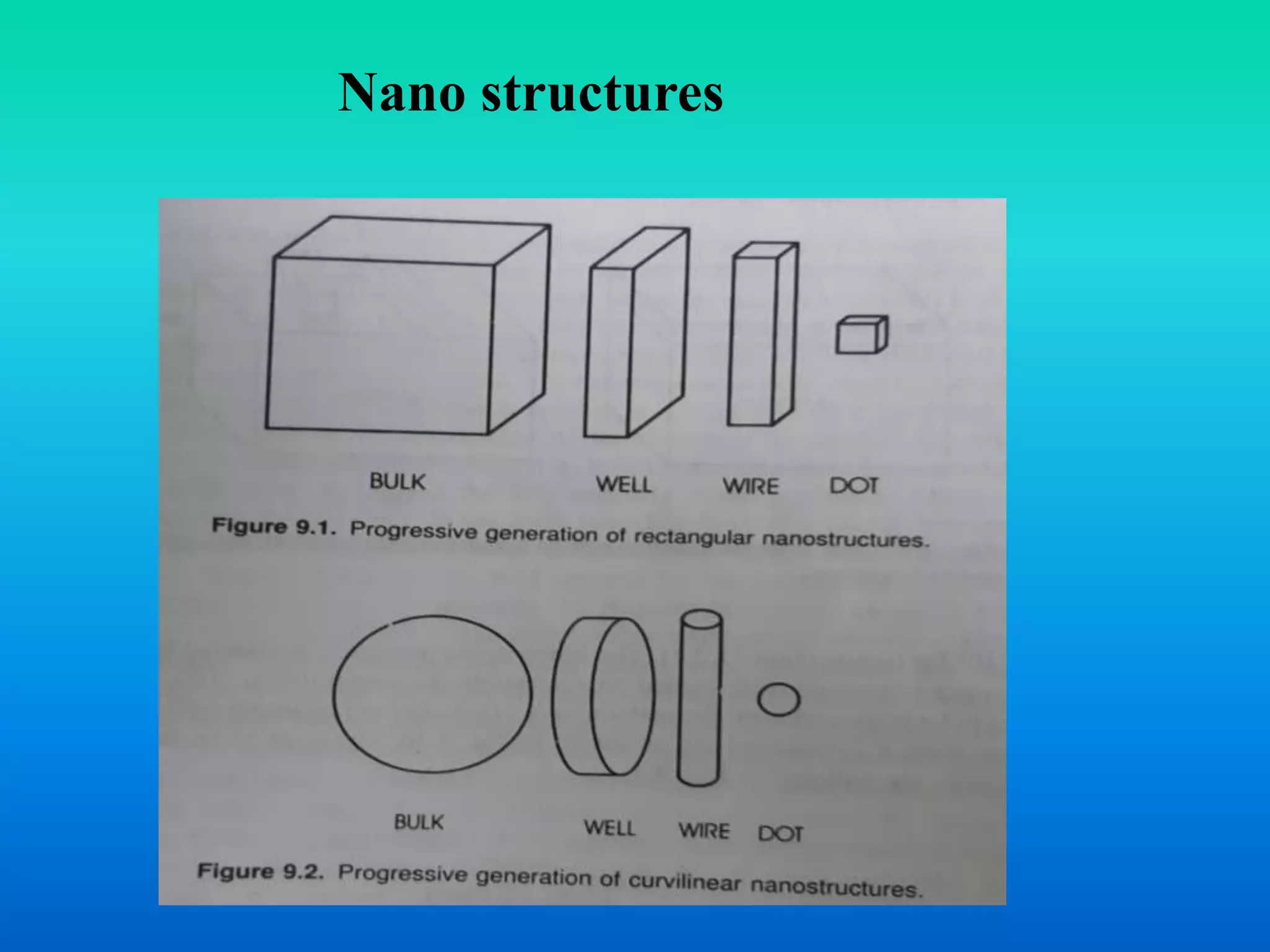
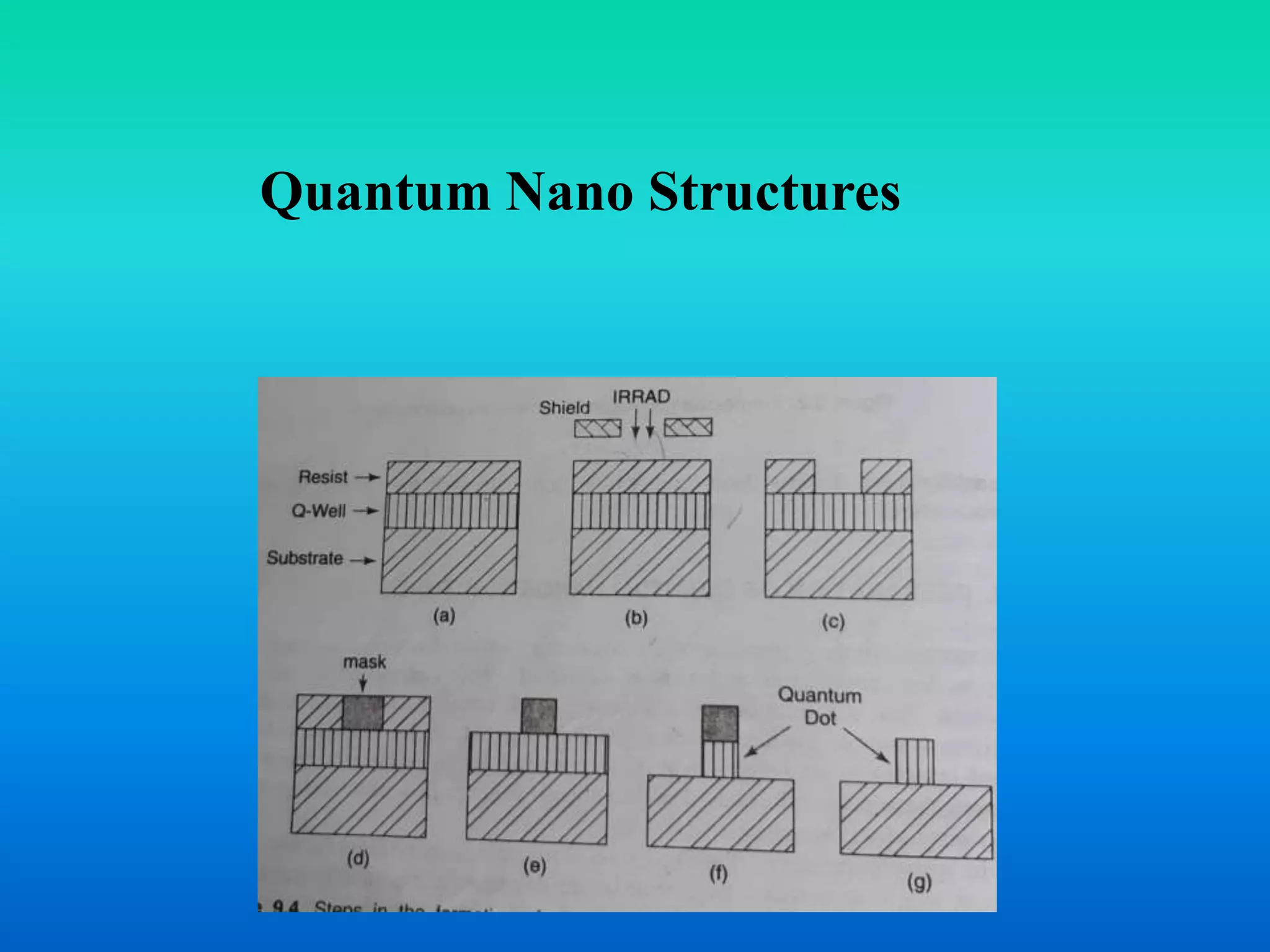
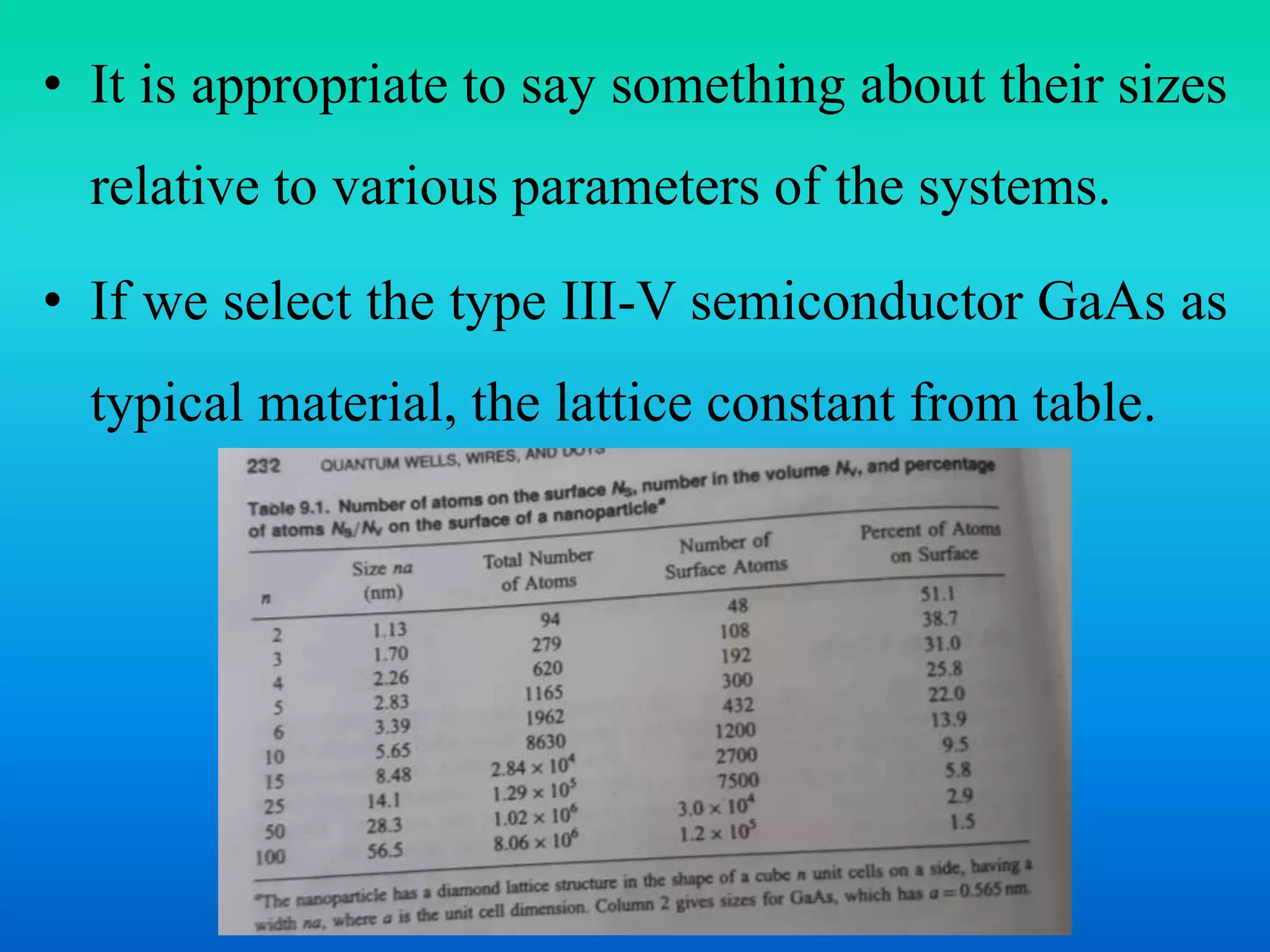
This document discusses various quantum nanostructures including quantum wells, wires, and dots. It explains that a quantum well is formed when one dimension is reduced to the nanoscale, a quantum wire results from reducing two dimensions, and a quantum dot occurs when all three dimensions are reduced. The document also discusses approaches for preparing these structures using a bottom-up method involving chemical reactions. It describes how properties change with size reduction and provides examples using semiconductors like GaAs. References are provided at the end.