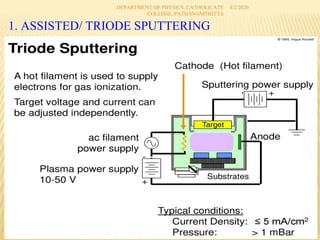
Cathodic sputtering is a thin film deposition technique where a target material is bombarded with energetic ions, ejecting atoms from the surface that are then deposited on a substrate. There are two main types: glow discharge sputtering and low pressure sputtering. Glow discharge sputtering uses a glow discharge to generate ions from a gas to sputter the target material and works best at pressures between 25-75 mTorr. Low pressure sputtering reduces collisions of sputtered atoms with gas to improve directionality and energy, including triode sputtering which uses an auxiliary electrode to increase ion generation efficiency.





![8/2/2020
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS,
CATHOLICATE COLLEGE,
PATHANAMTHITTA
7
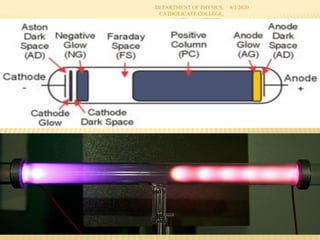
Cathode Dark Space: A fairly well defined region of
relatively low luminosity. A region where most of the
applied voltage is dropped[cathode fall]
Negative Glow region: Region followed by cathode dark
space where ions and electrons created in breakdown
region are accelerated and can collide with the gas
Positive Column: Due to collision of gas atoms in
negative glow region with energetic ions can create
secondary electrons to sustain glow and hit the anode to
give sputtering](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msppt-2-221030113835-151c6051/85/sputtering-process-7-320.jpg)