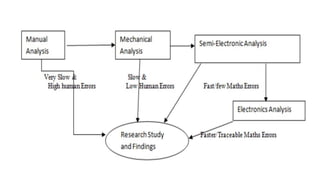
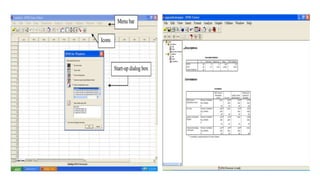
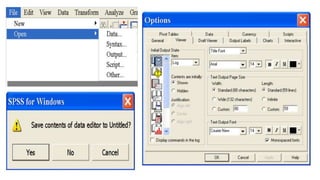
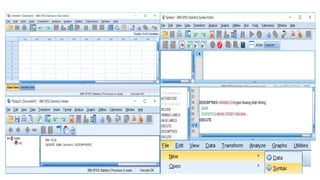
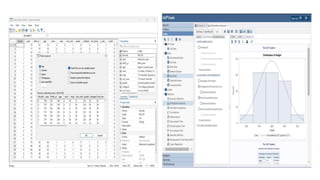
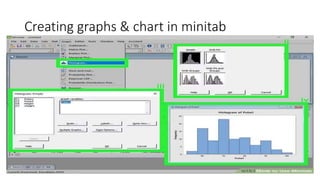
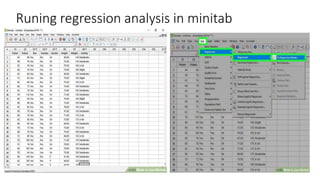
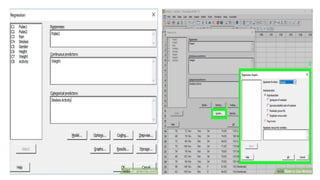
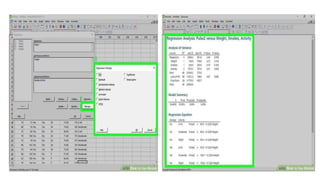
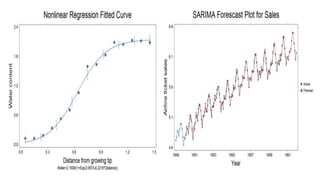
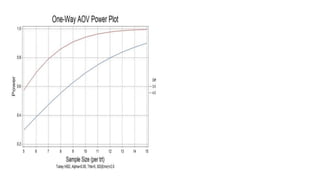
This document provides an overview of statistical software packages including their common features, advantages, types, and most common packages used in social science. It discusses features of Microsoft Excel, SPSS, SAS, Stata, R, Minitab, and GraphPad Prism. These software packages vary in their ease of use, available statistical analyses, programming capabilities, and cost. Excel is best for basic statistics while SAS and Stata provide more advanced analyses but are harder to use. SPSS and Minitab offer a good balance of capabilities and usability.