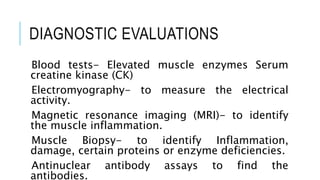
Polymyositis is a type of inflammatory myopathy that causes muscle weakness and pain often on both sides of the body. It is characterized by symmetrical proximal muscle weakness, elevated muscle enzymes, and abnormal electromyography and muscle biopsy findings. Polymyositis most commonly affects adults aged 30-50 and has an unknown cause but is considered an autoimmune disorder. Treatment focuses on corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and physical therapy to improve muscle strength and function while managing complications like trouble swallowing or breathing problems.