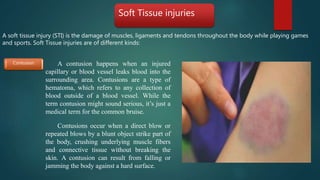
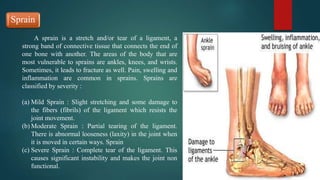
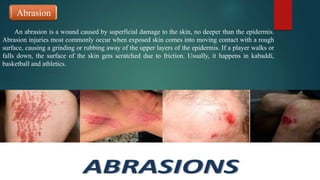
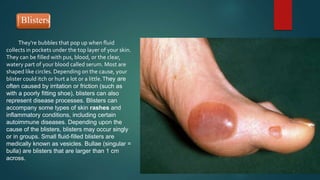
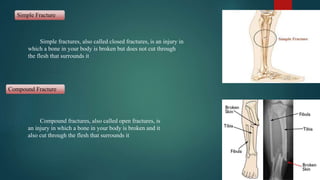
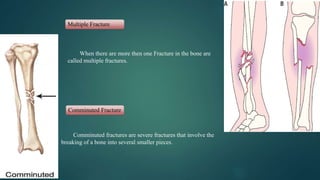
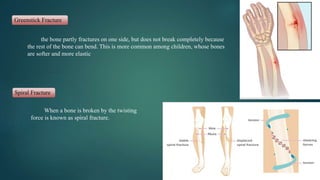
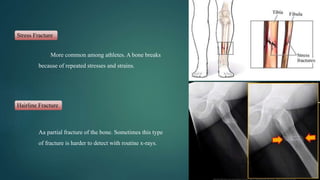
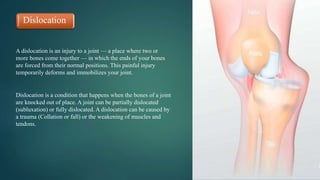
The document discusses sports injuries, providing definitions and examples of common types of injuries. It explains that sports injuries can be soft tissue injuries, like strains, sprains, bruises and blisters, which damage muscles, ligaments or tendons, or hard tissue injuries like fractures and dislocations, which damage bones or joints. The document emphasizes the importance of studying sports injuries in physical education, as they are common in sports and knowing how to diagnose, treat and prevent injuries is crucial for coaches and trainers. Proper warm-ups, rest, ice, compression and elevation are recommended treatments for many minor soft tissue injuries.