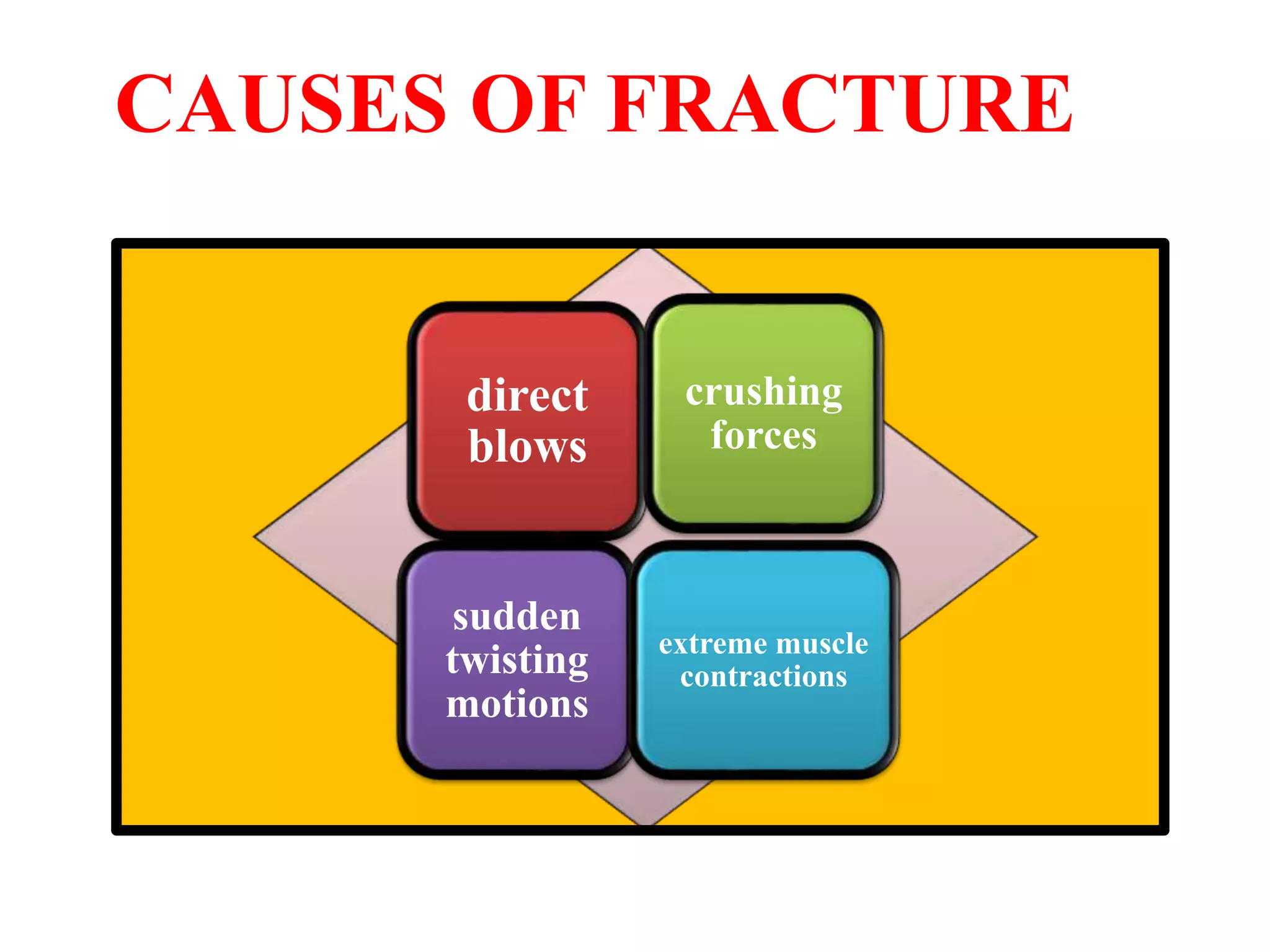
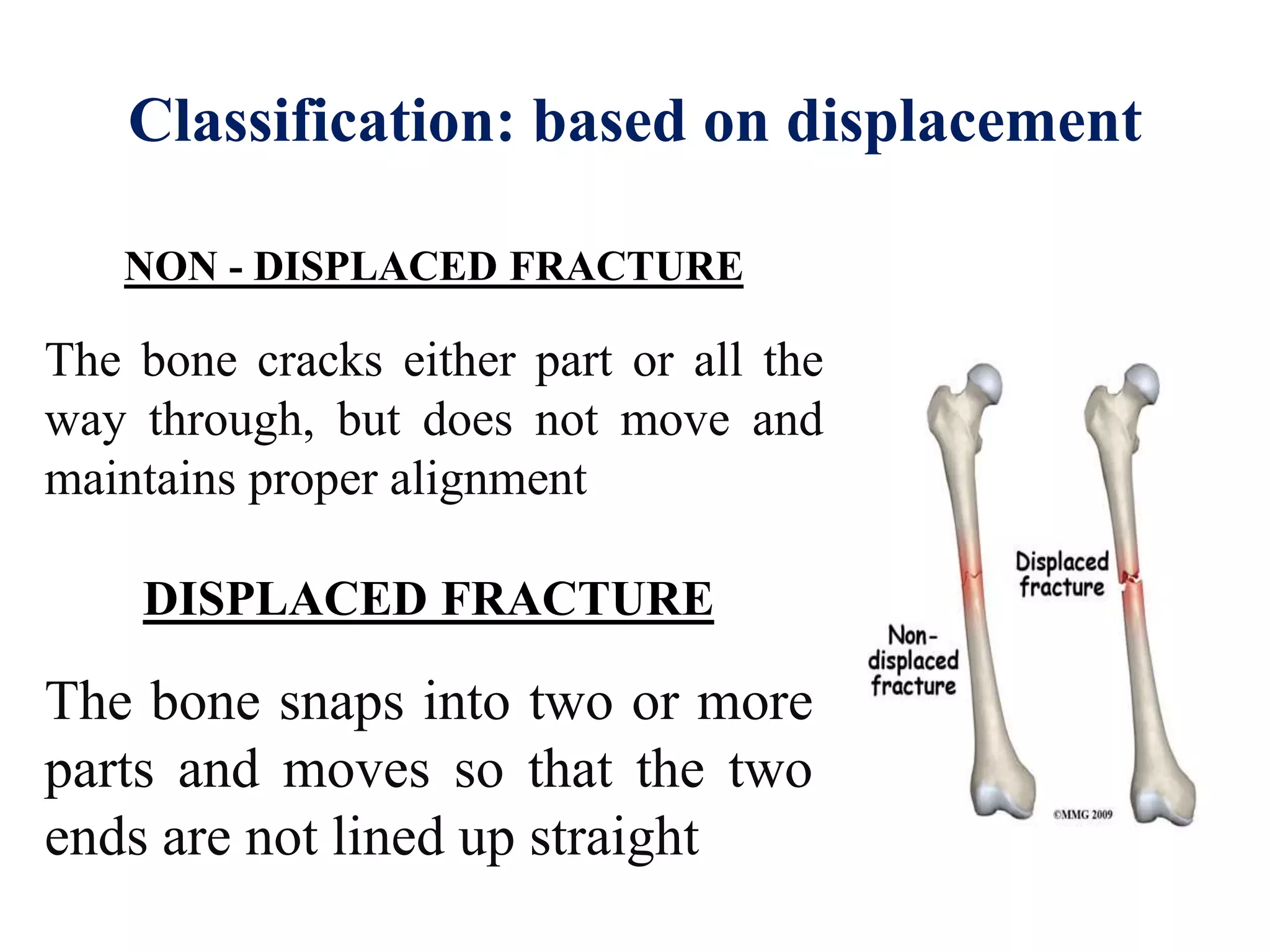
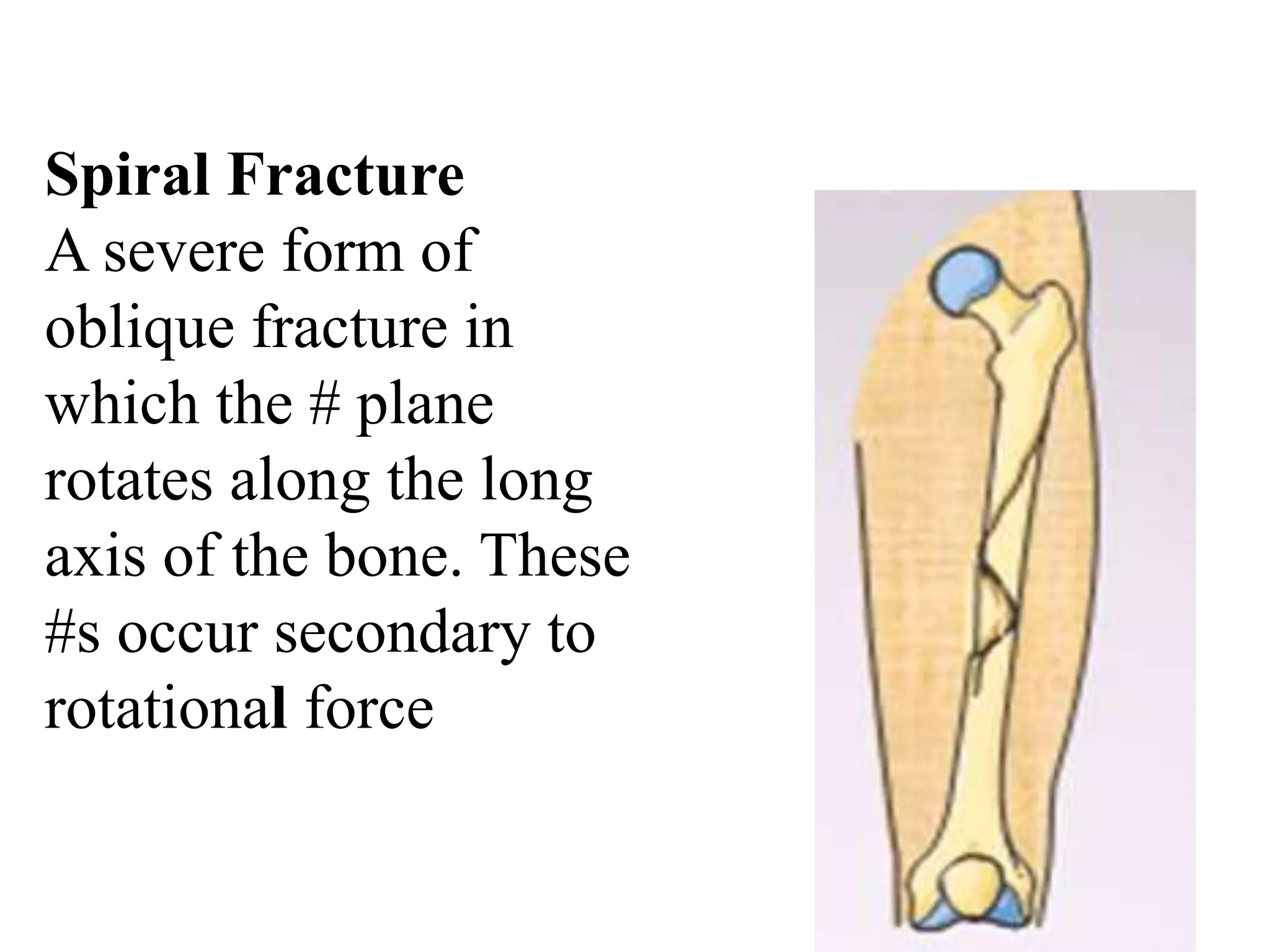
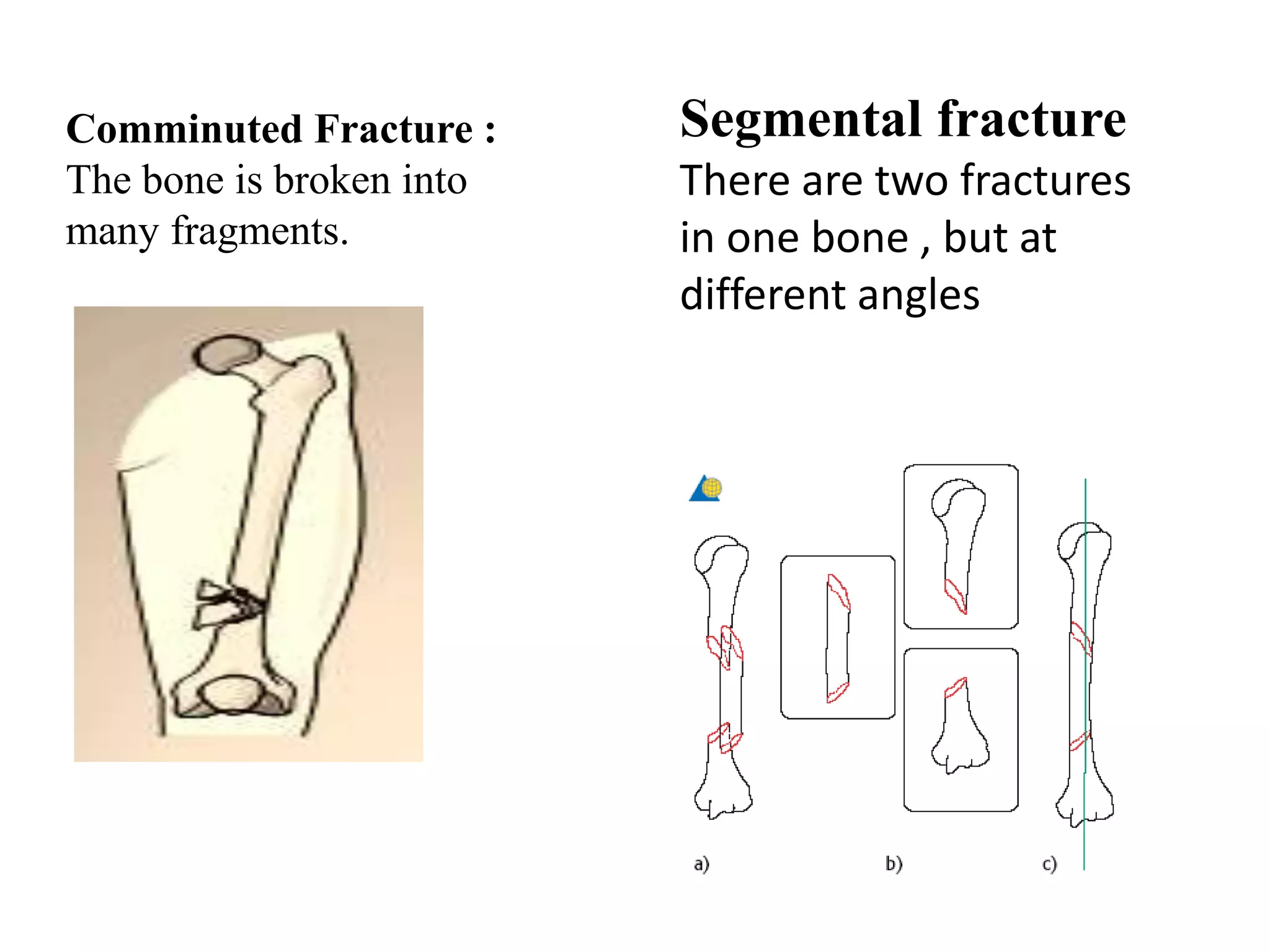
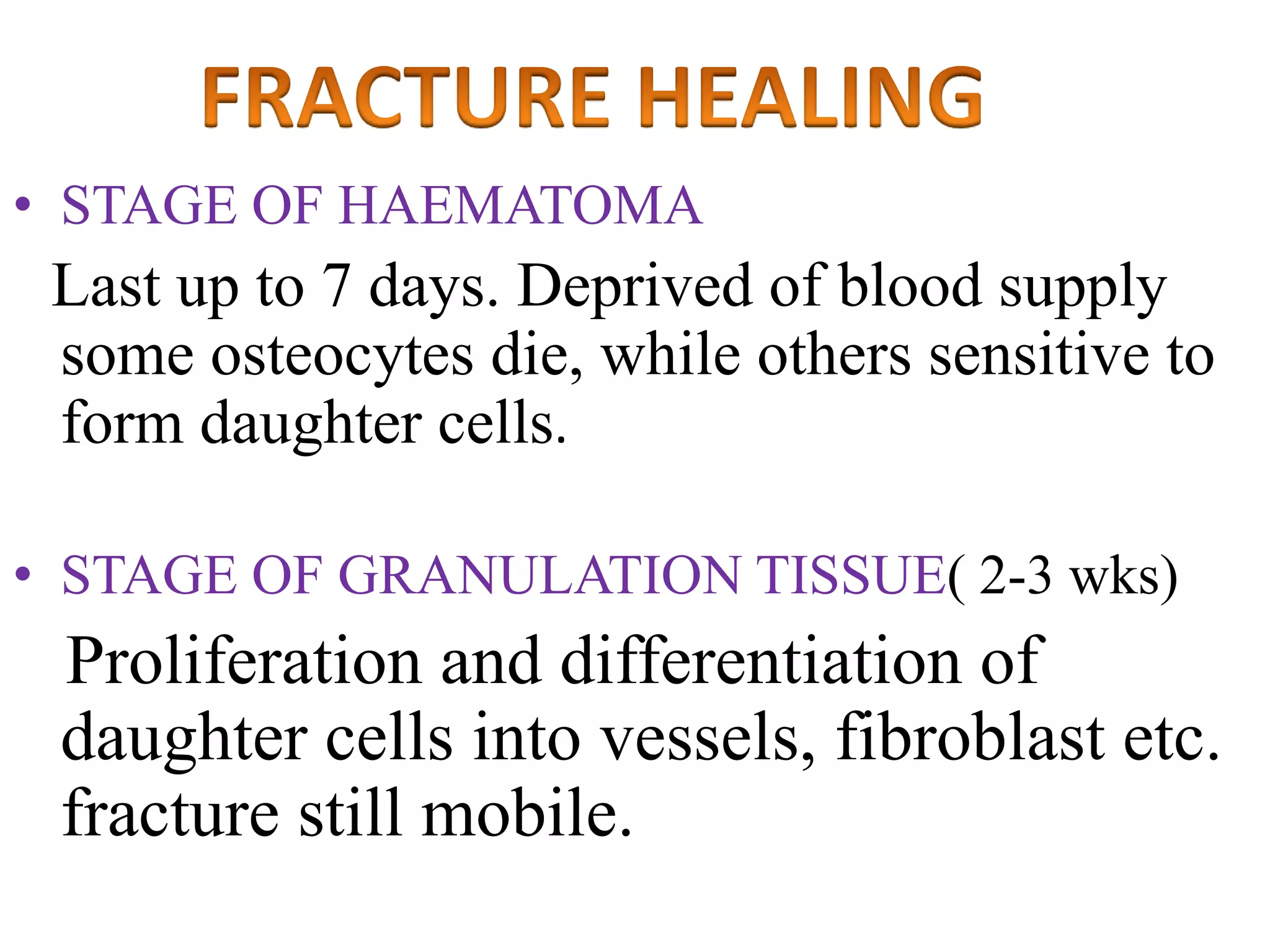
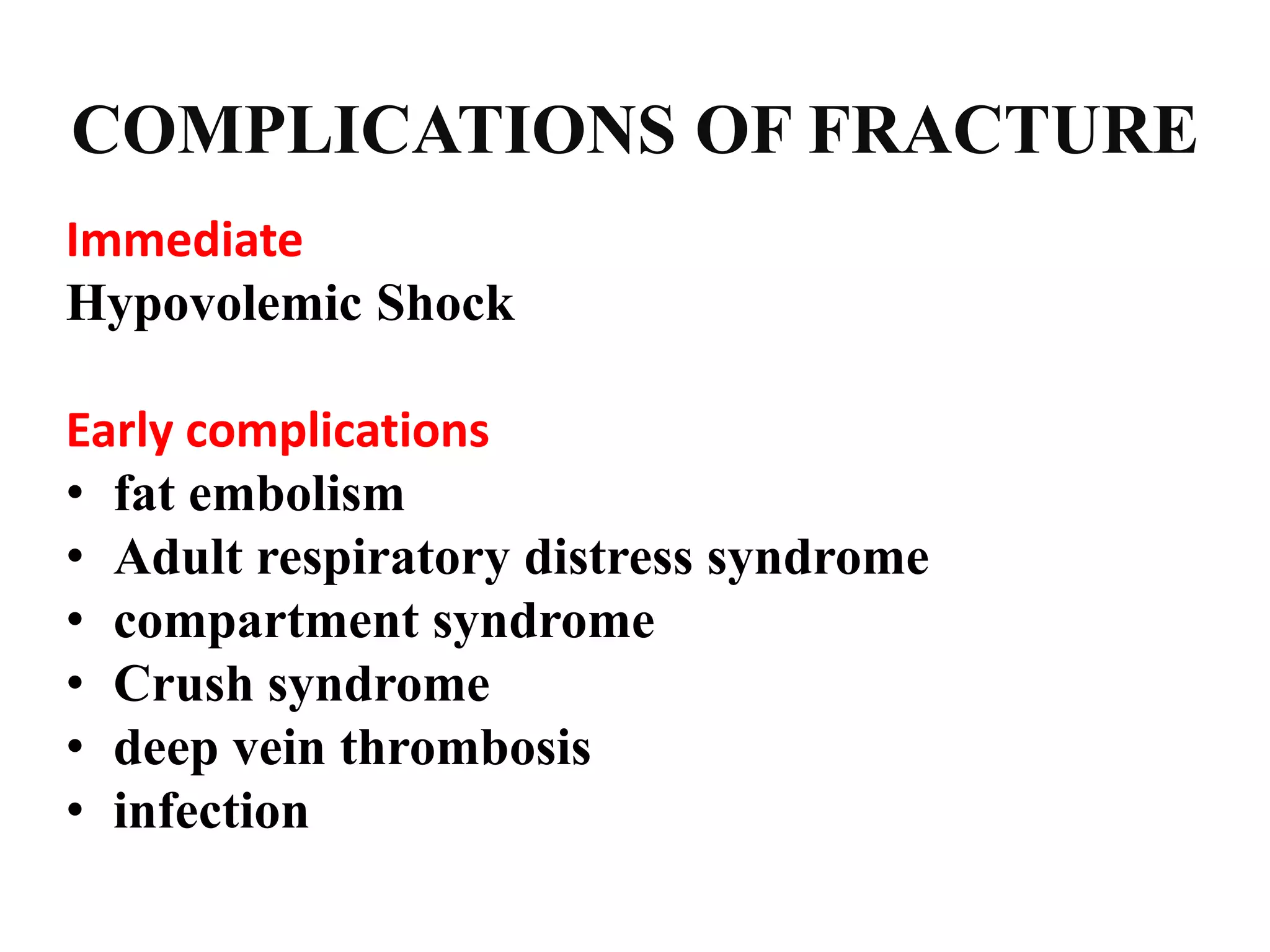
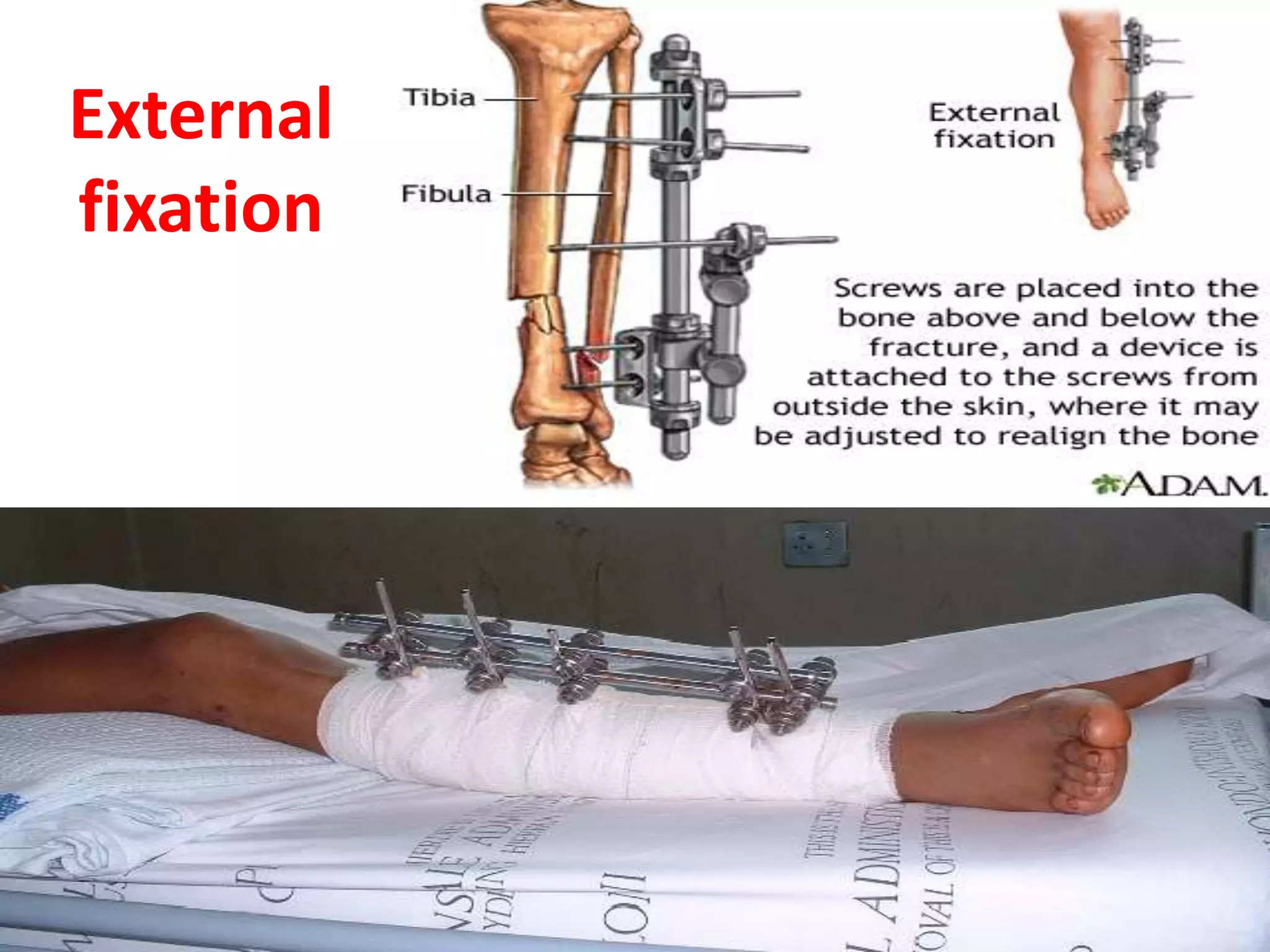
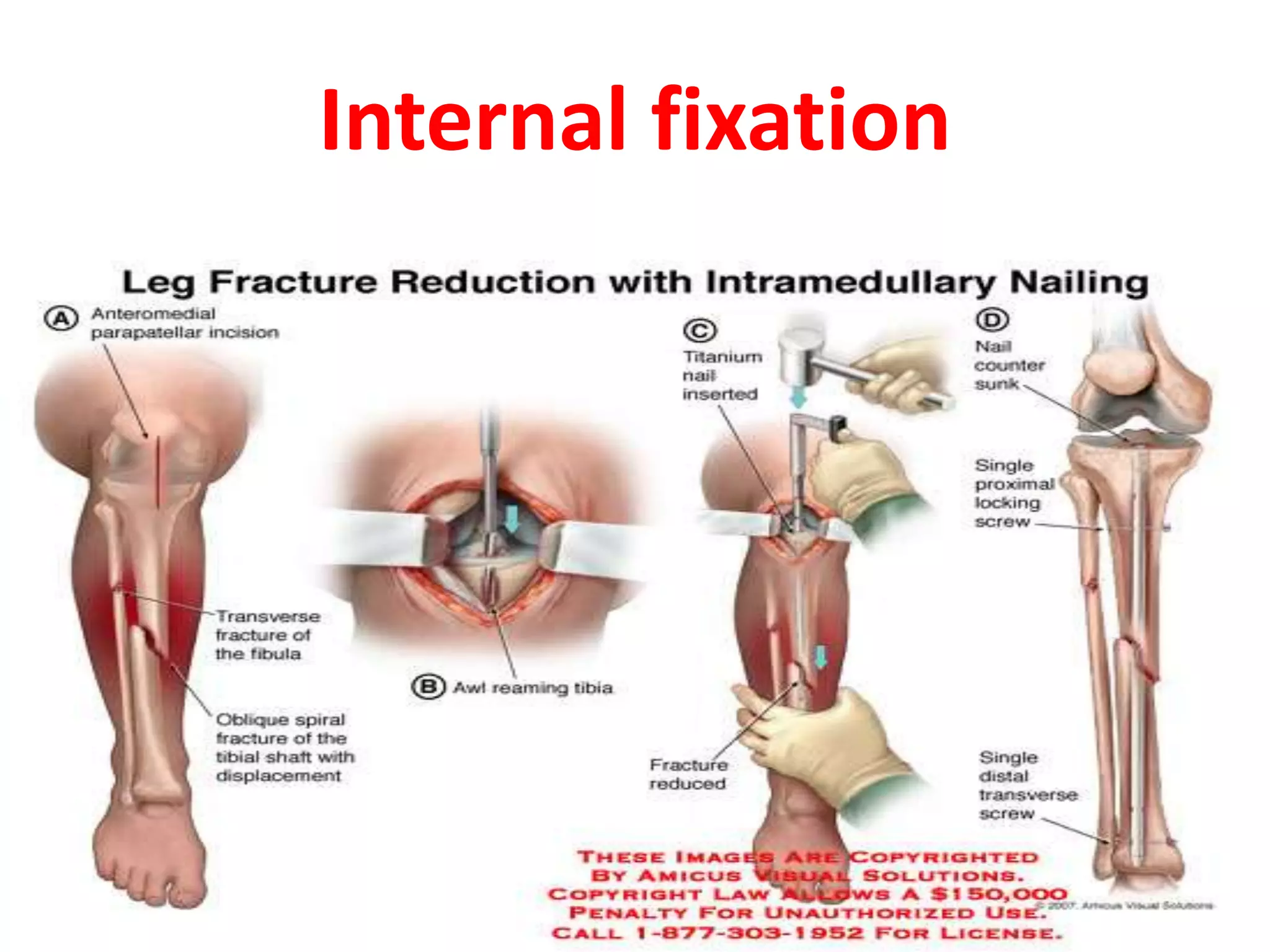
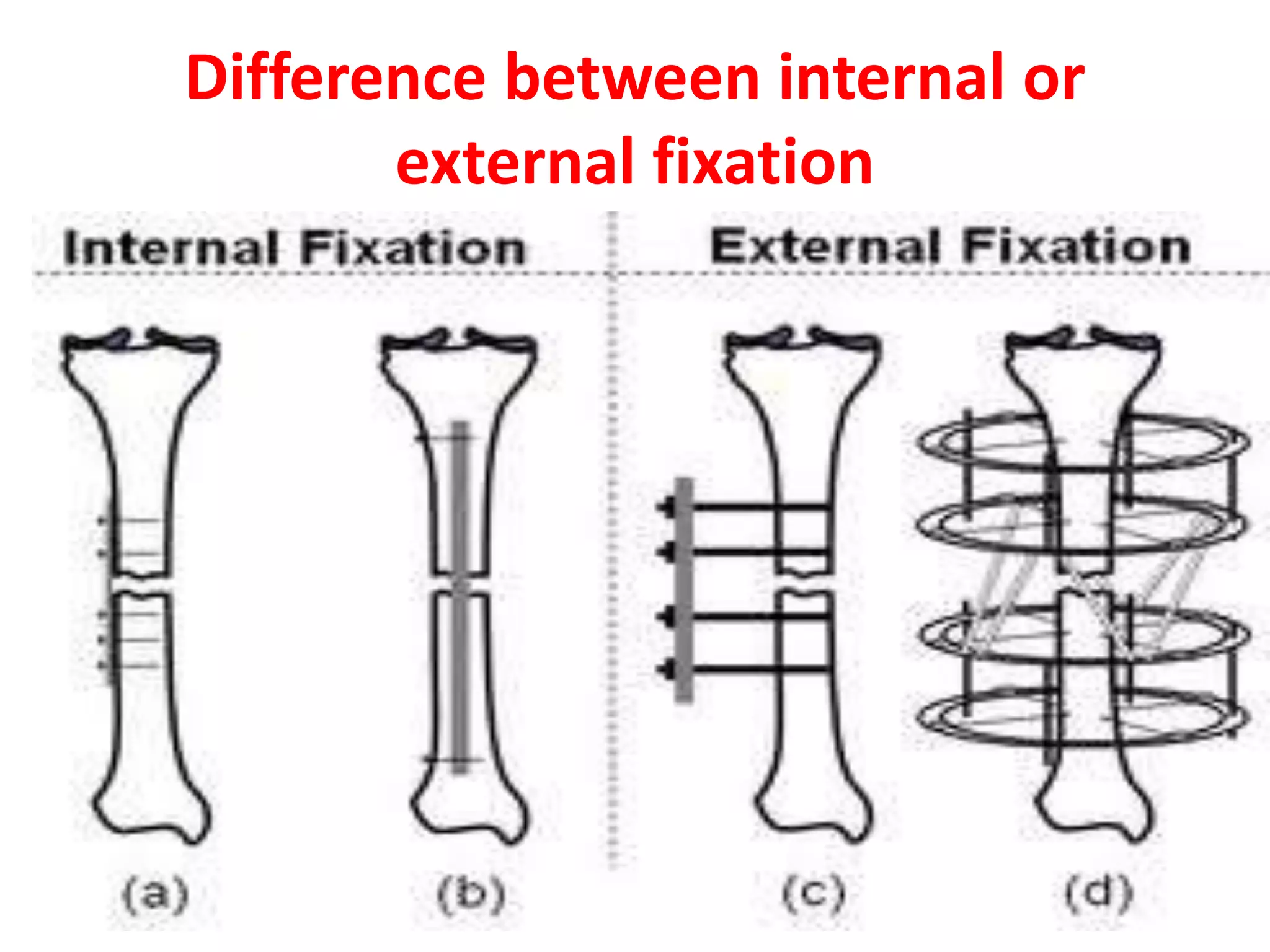
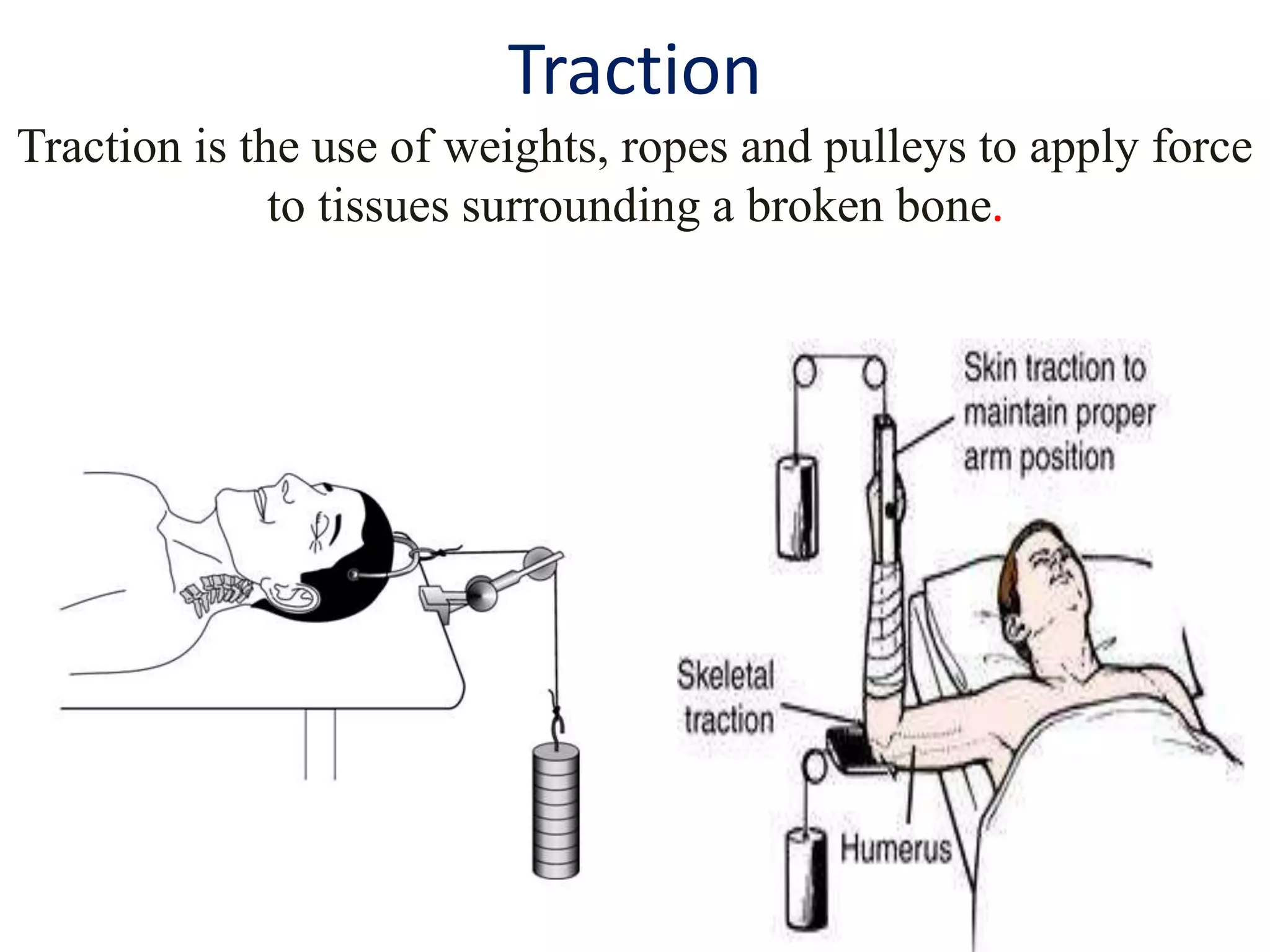
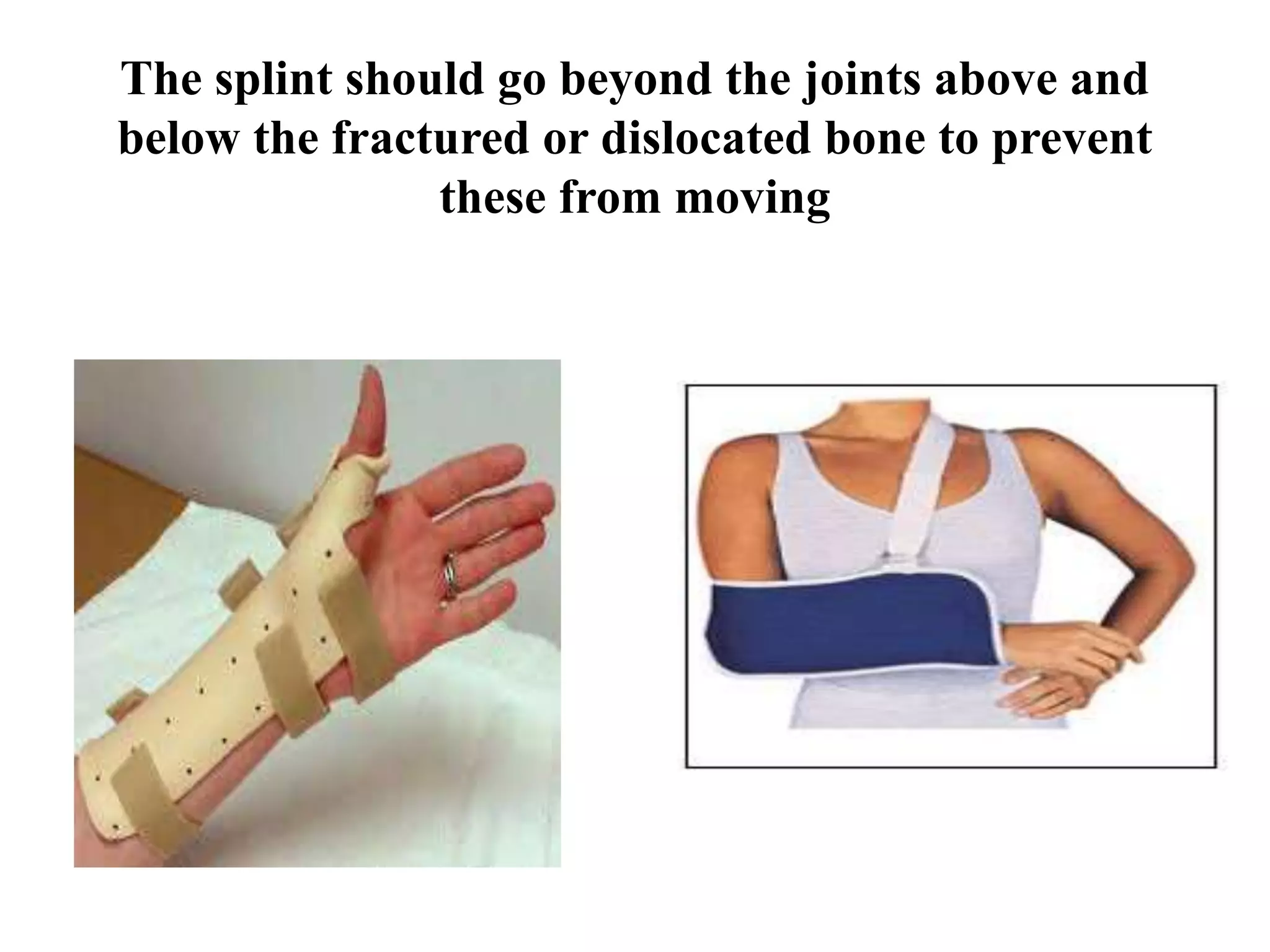
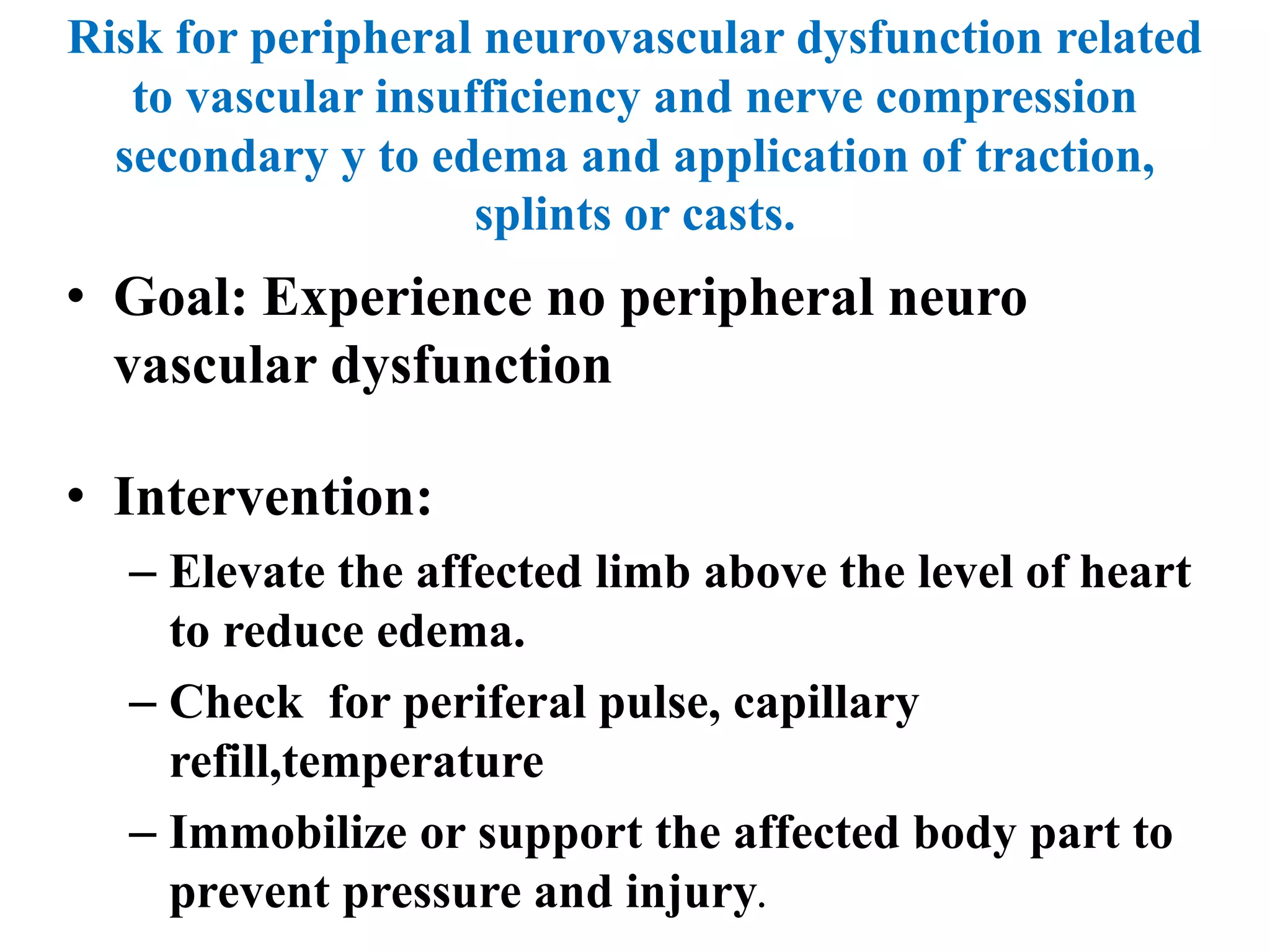
This seminar discusses fractures, including their definition, causes, classification, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, complications, and medical and nursing management. Fractures are breaks in bone continuity and can be caused by direct blows, twisting motions, or muscle contractions. They are classified based on their relationship to the environment (closed vs open), degree of displacement, fracture pattern (transverse, oblique, etc.), and etiology (traumatic vs pathological). Treatment involves reduction, immobilization using devices like casts, splints, or traction, and restoring function through exercises. Nursing care focuses on pain management, preventing complications like infection or neurovascular issues, and promoting mobility and independence.