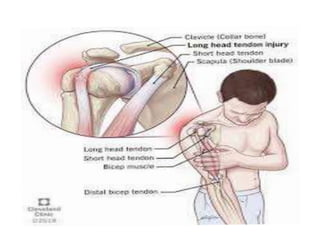
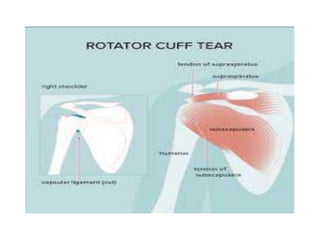
A sprain involves the stretching or tearing of a ligament supporting a joint, while a strain is the stretching or tearing of a muscle or tendon. Sprains and strains are commonly caused by overuse or a single injury event and most often affect athletes. Common sites are the ankle, knee, quadriceps, hamstrings, and Achilles tendon. Treatment focuses on the PRICE method - protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation - along with exercises to regain range of motion and strength under medical supervision. More severe grade 3 injuries may require surgery followed by physical therapy. Prevention emphasizes warming up muscles before exercise or strenuous activity.