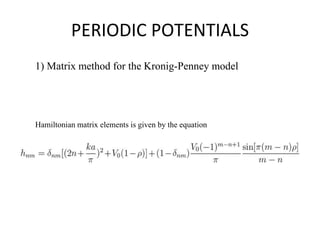
This document extends the Kronig-Penney model for modeling electron interactions with atomic lattices in semiconductors to arbitrary periodic potentials using numerical matrix mechanics. It introduces the Kronig-Penney model and represents periodic potentials using matrix representations in different basis sets. Numerical solutions are obtained and band structures are compared for different periodic potentials, including the Kronig-Penney, harmonic oscillator, and inverted harmonic oscillator potentials. Effective mass is also calculated from the band structure curvature.