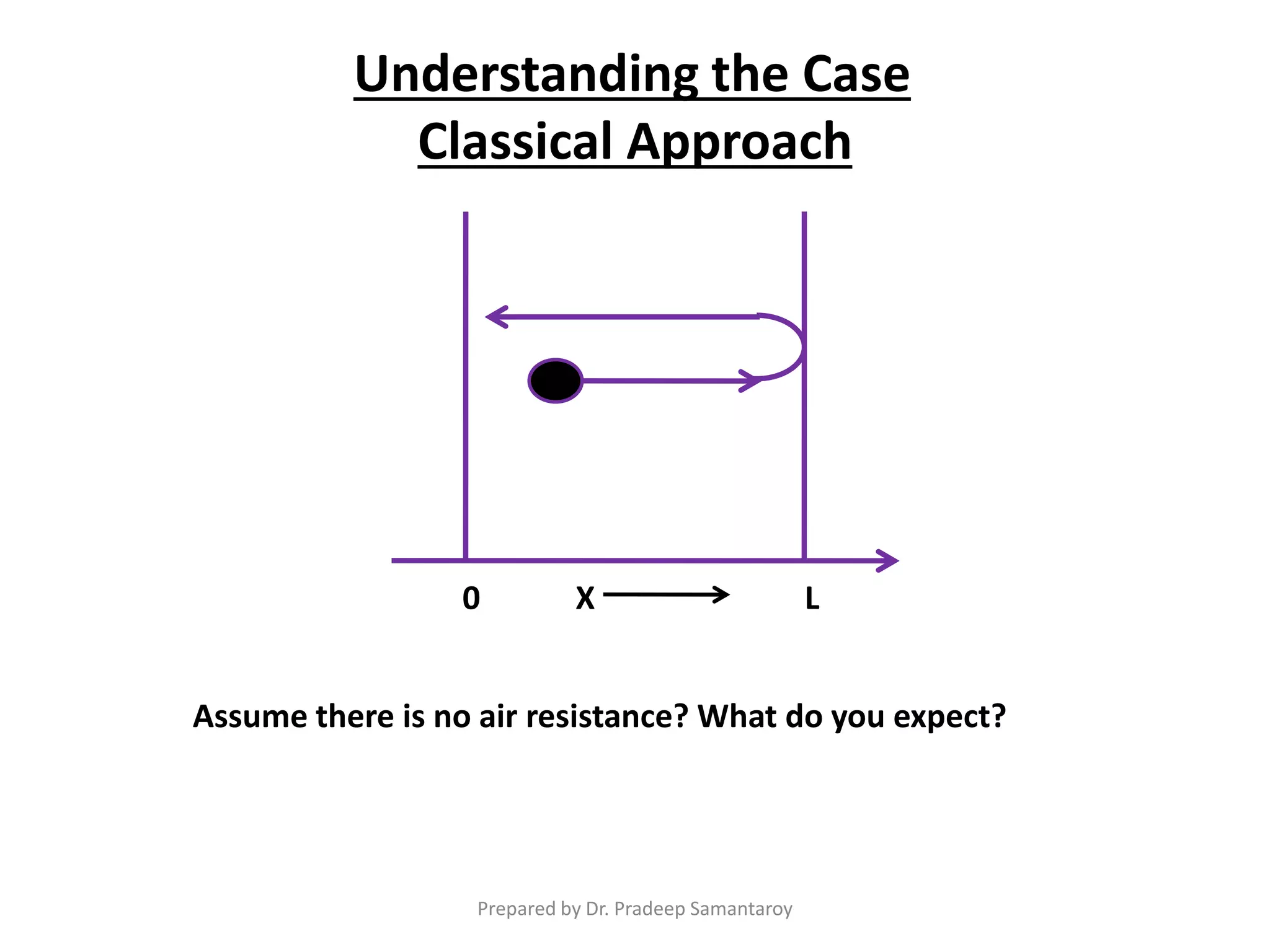
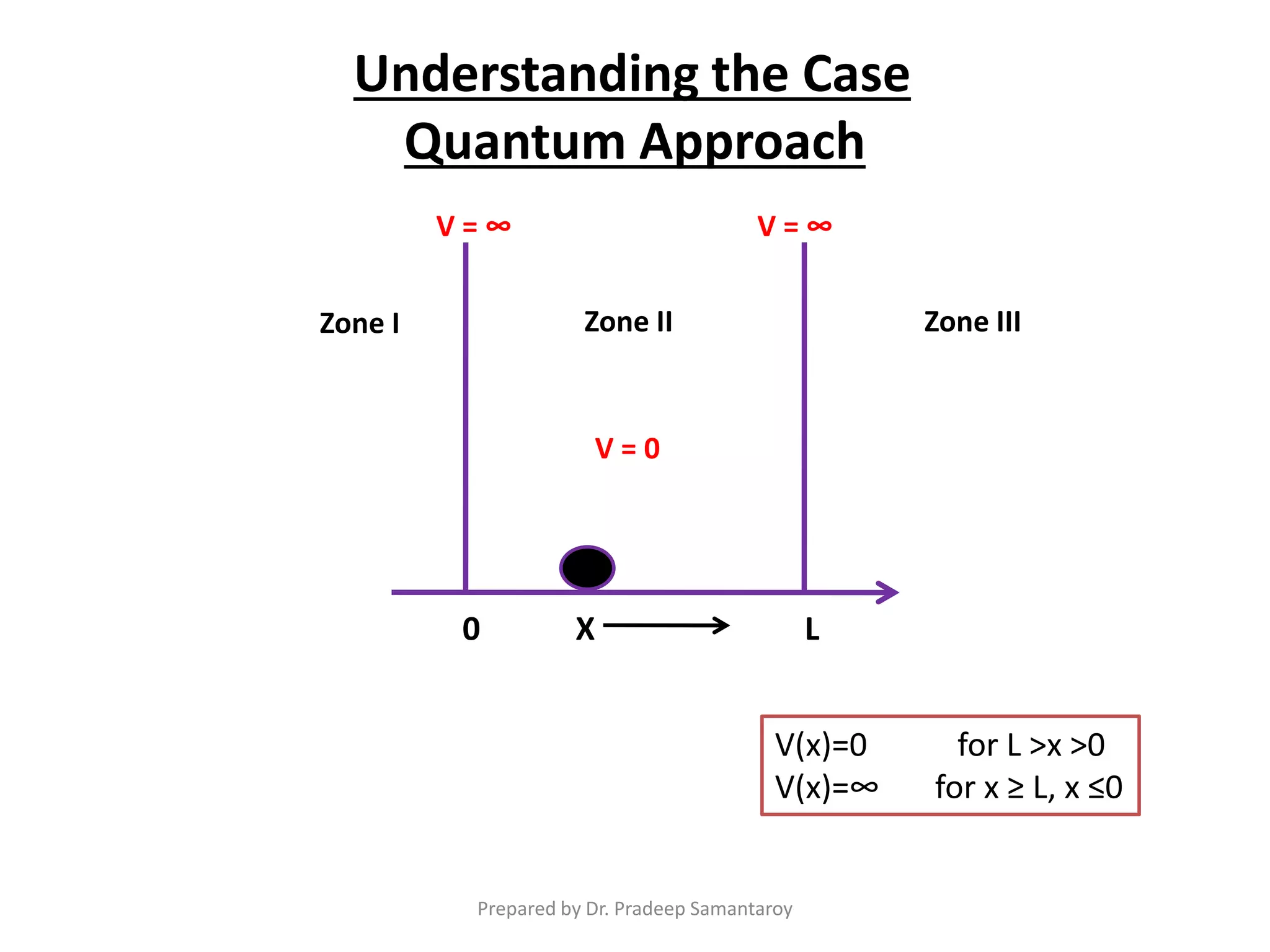
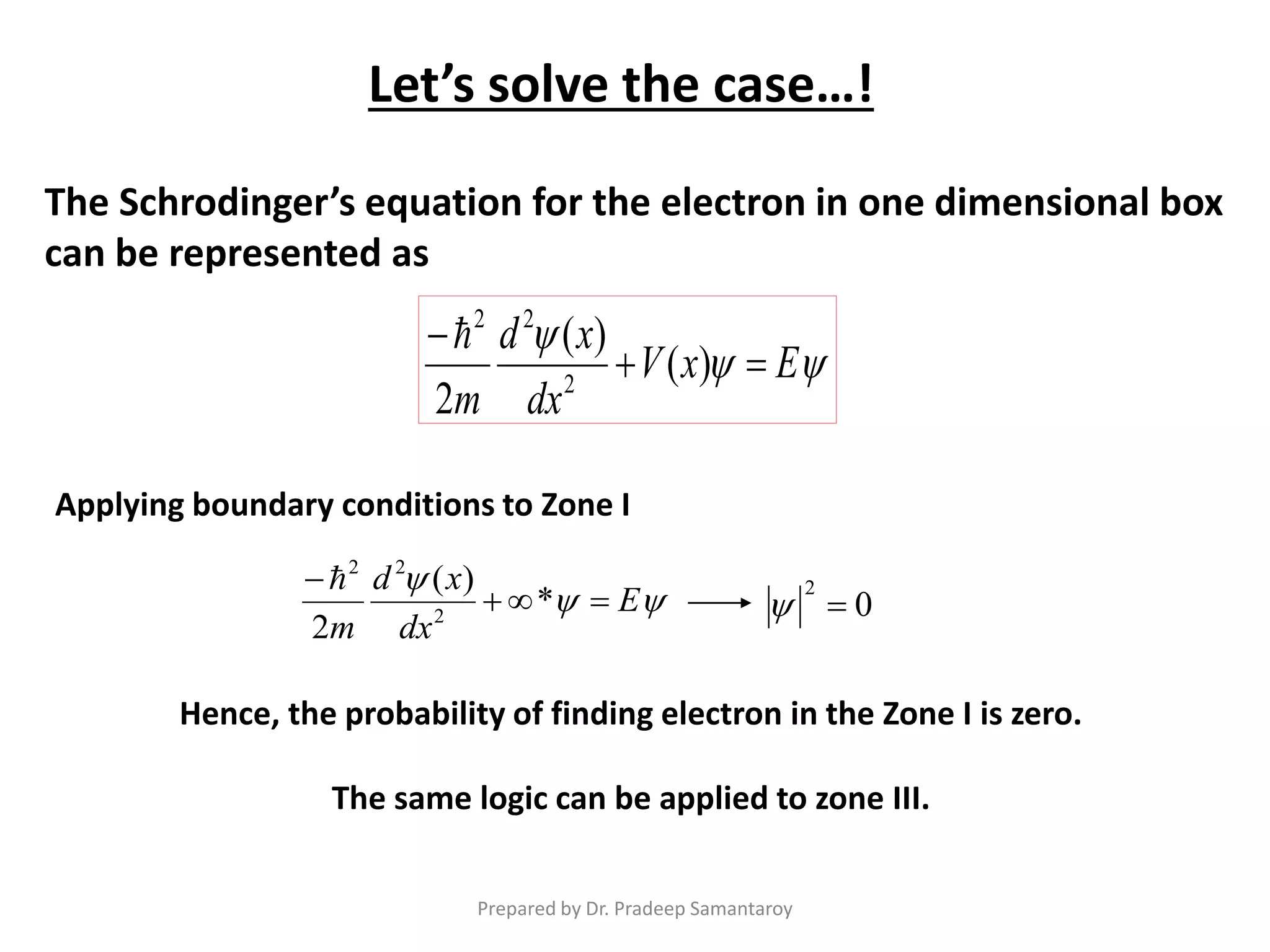
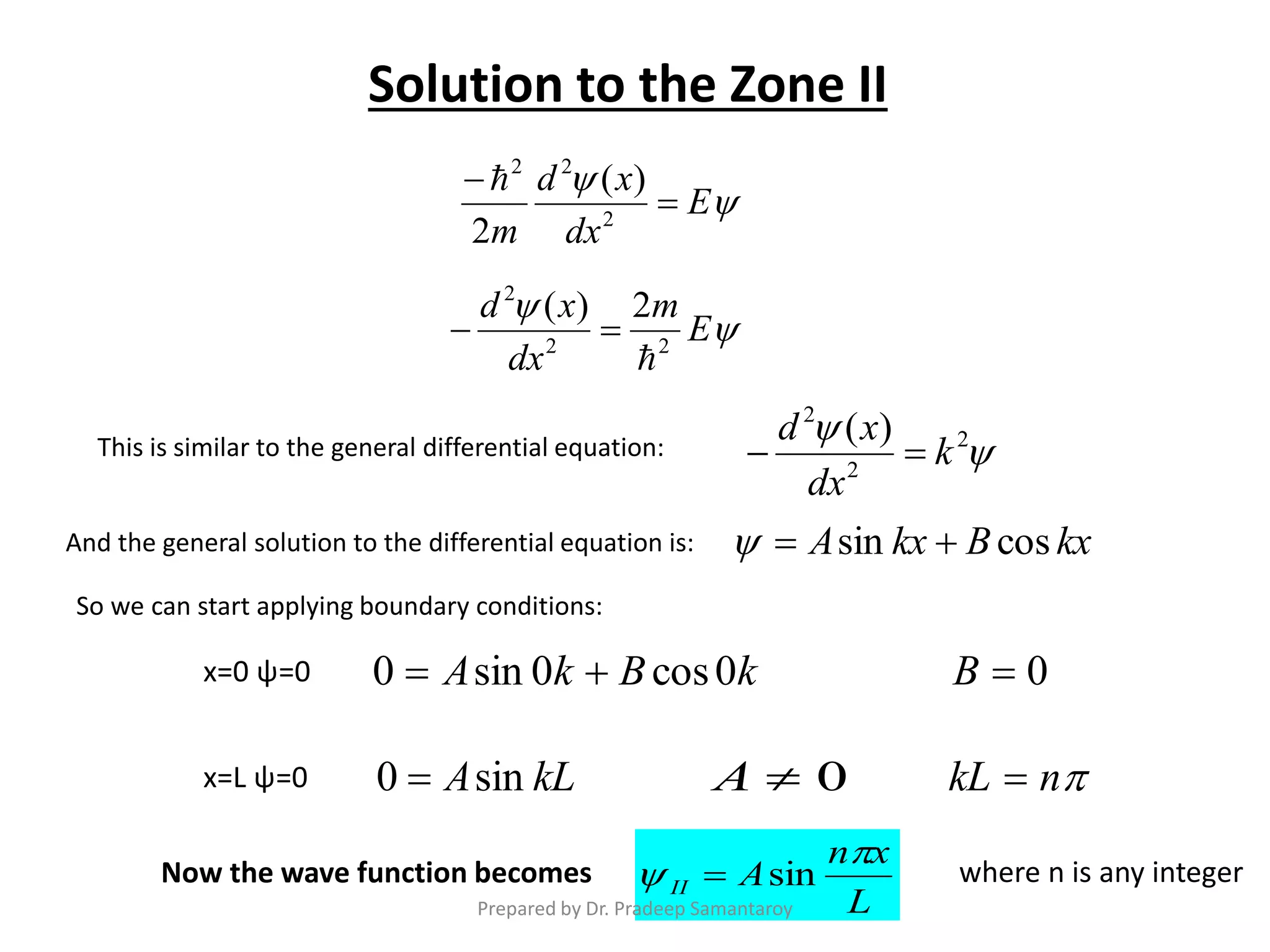
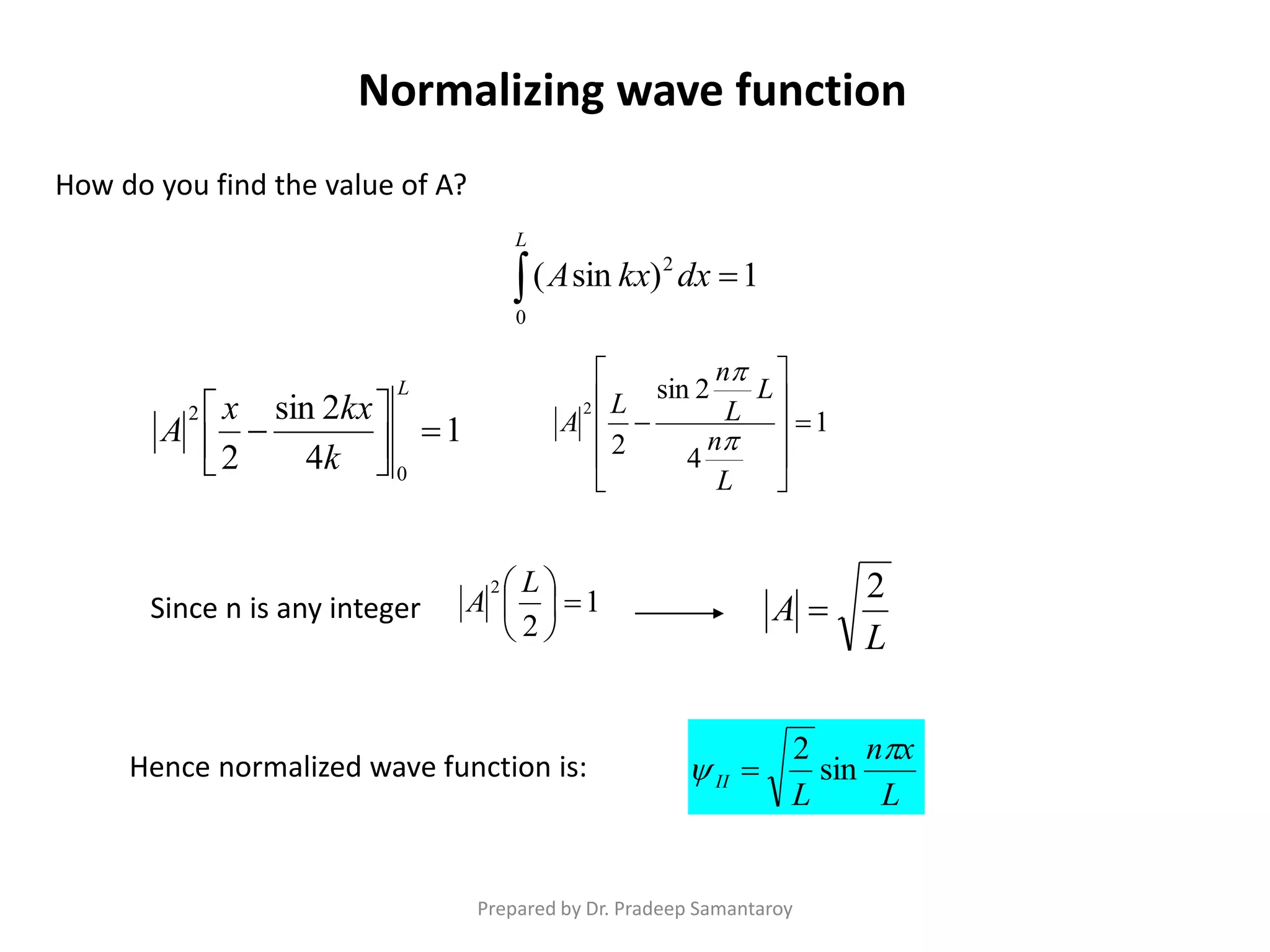
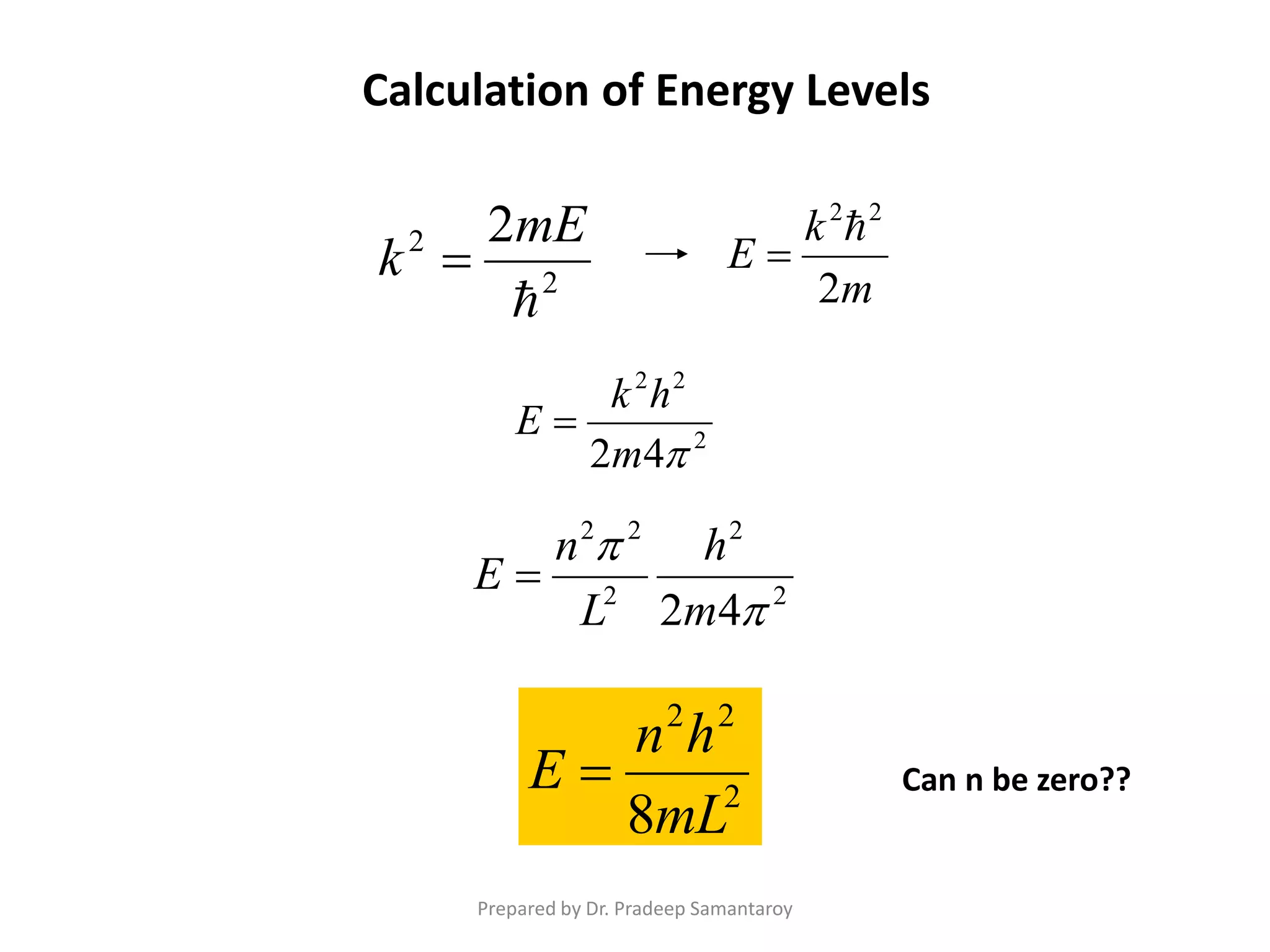
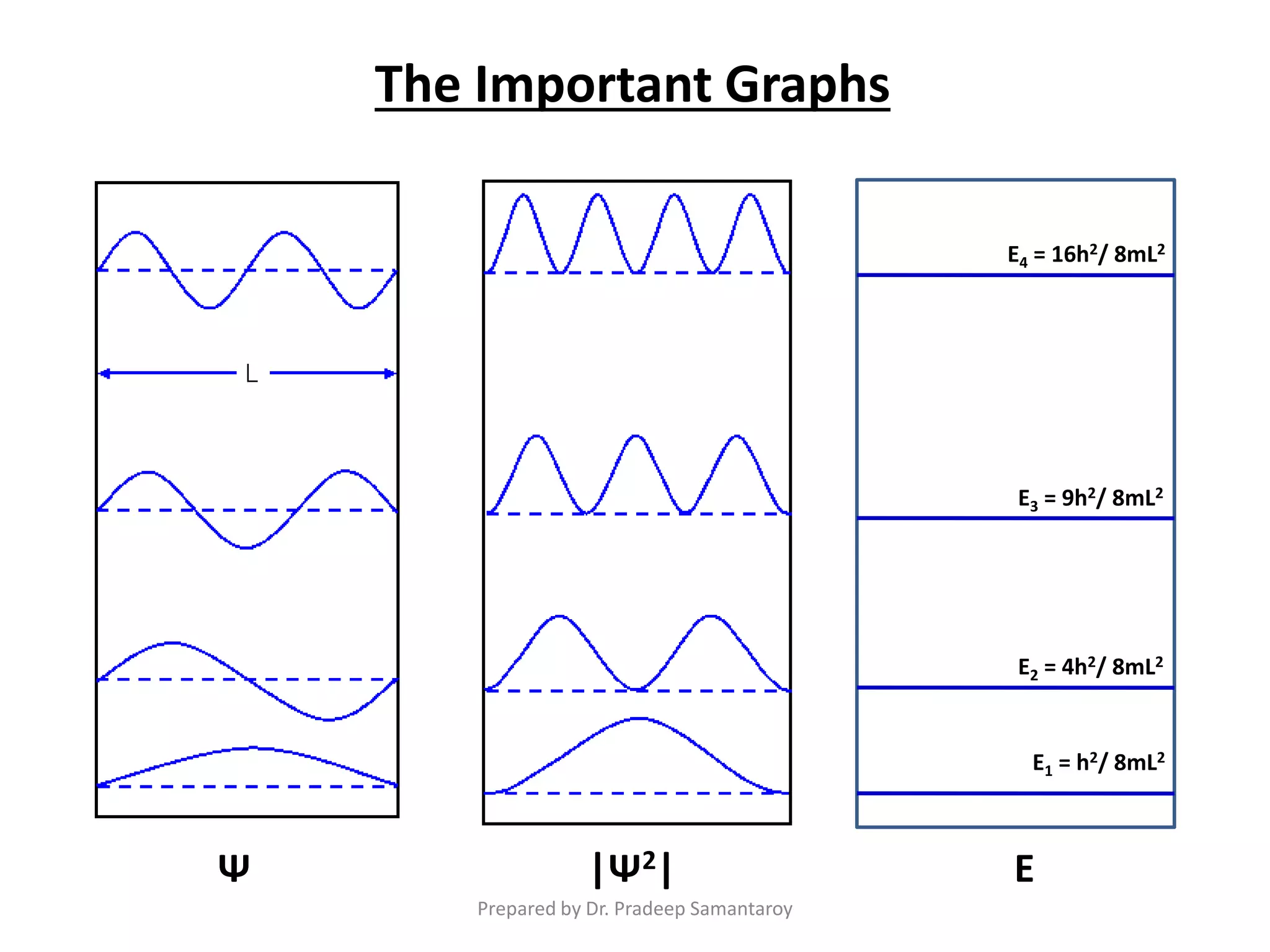
Dr. Pradeep Samantaroy discusses the classical and quantum approaches to understanding electron behavior in a one-dimensional box using Schrödinger's equation. He details wave function normalization, energy level calculations, and the implications of quantization. Numerical examples are provided to illustrate ground state energy and average energy values of confined particles.