The document provides information about the structure and function of the liver:
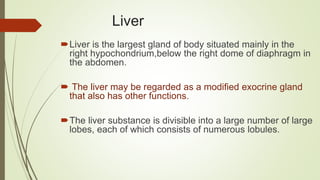
- The liver is covered by Glisson's capsule and is divided into lobules that contain hepatocytes arranged in plates separated by sinusoids. Bile canaliculi between hepatocytes drain into ductules.
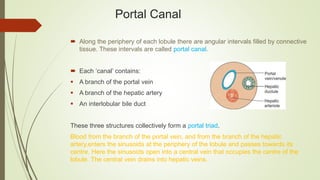
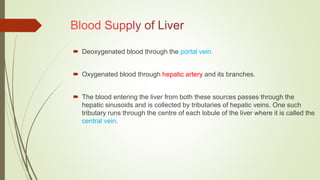
- Blood enters the liver through the hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery and flows through sinusoids before draining into the hepatic veins.
- The liver performs many metabolic functions like detoxification, protein synthesis, and glucose regulation. It also stores vitamins, glycogen, and lipids. Bile produced by hepatocytes is secreted into small bile ducts and stored in the gallbladder.