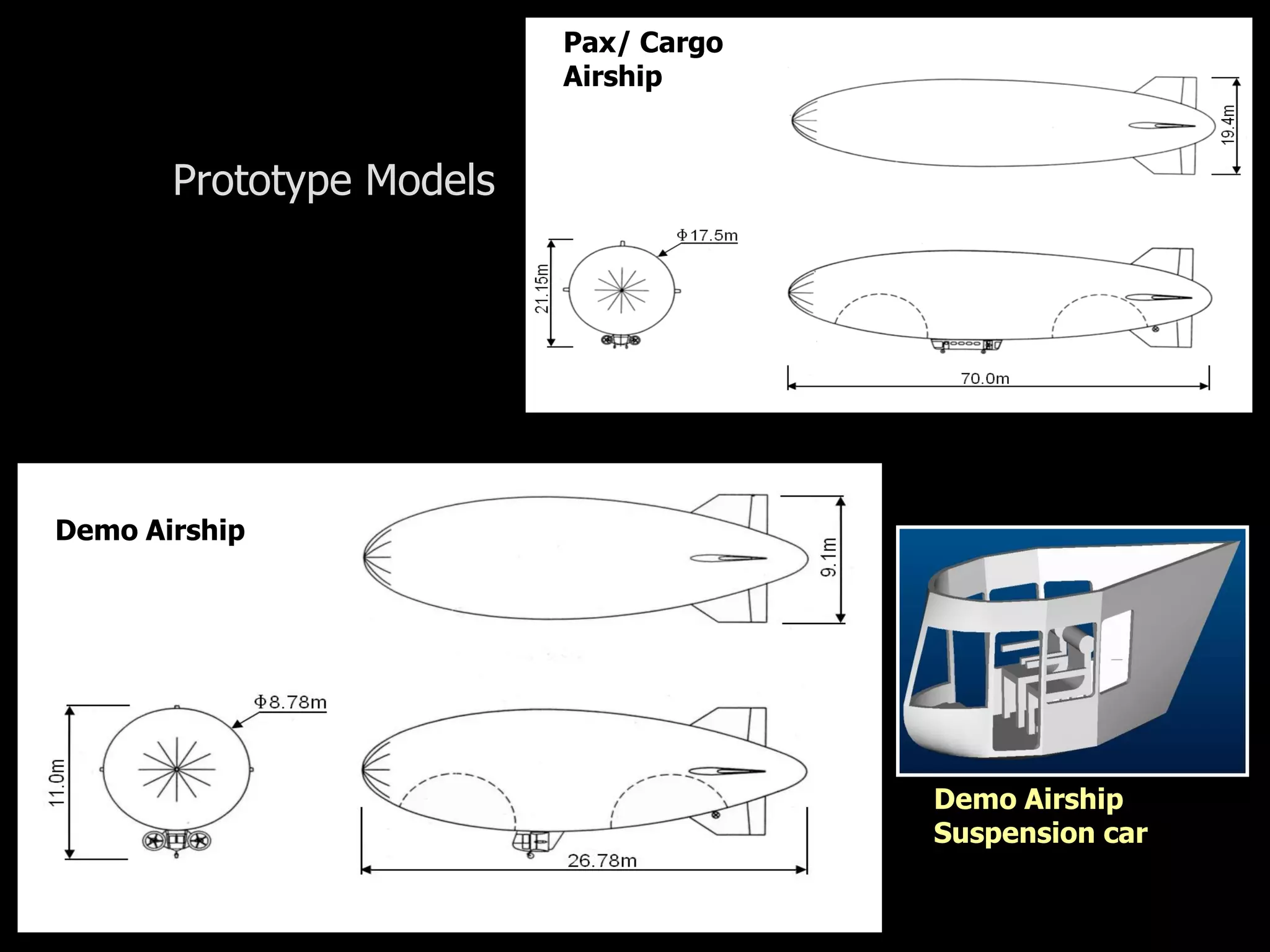
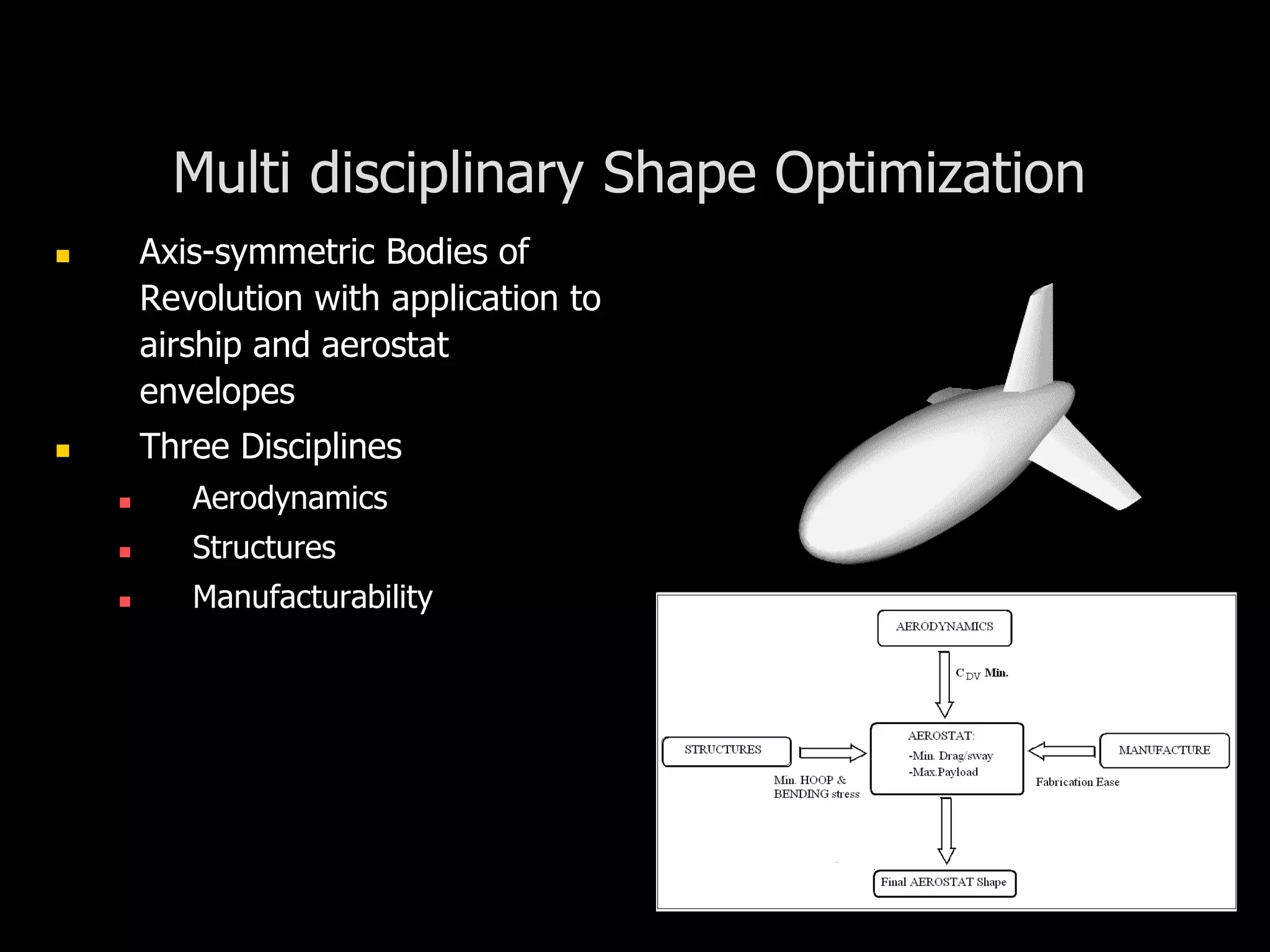
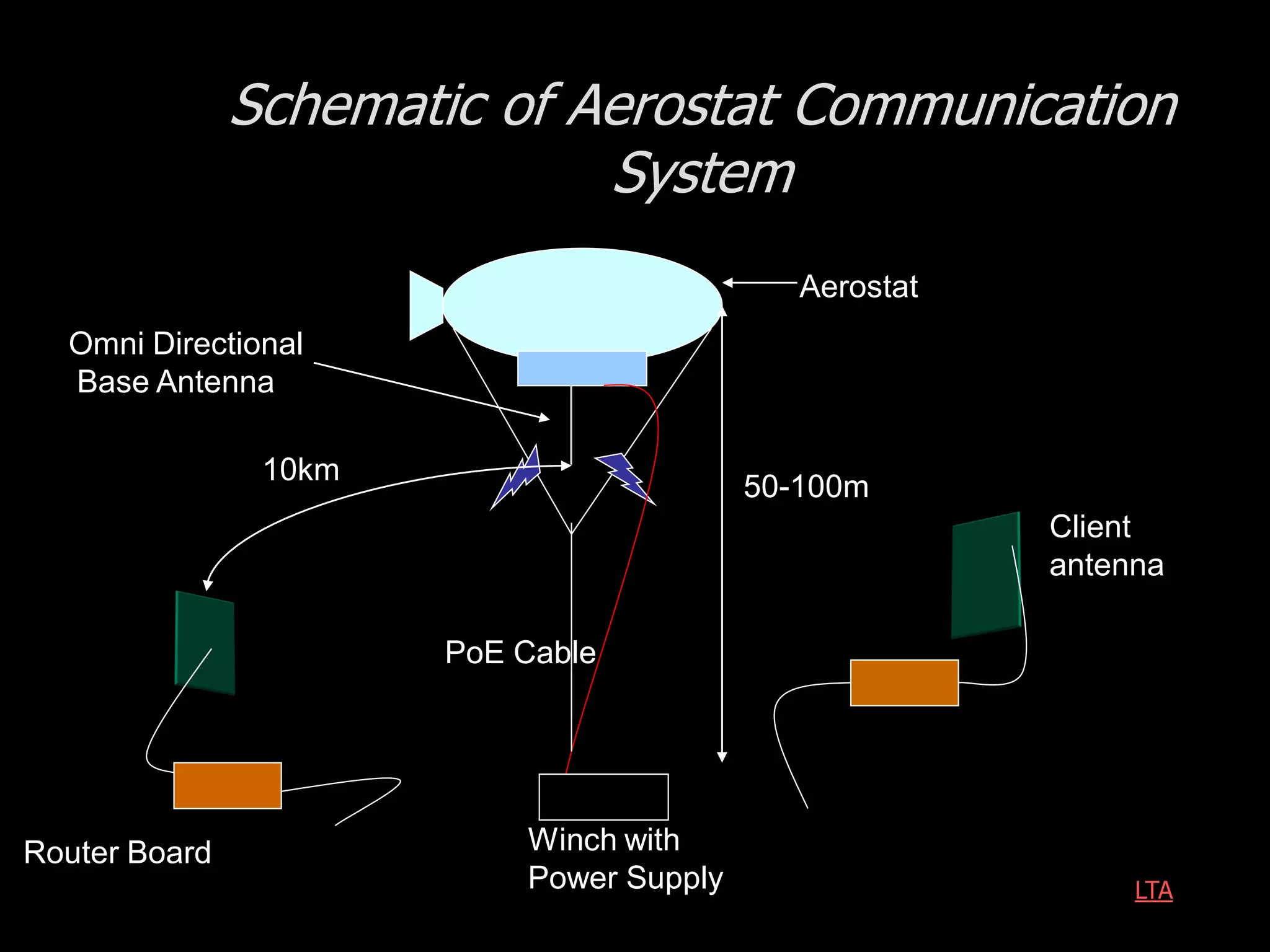
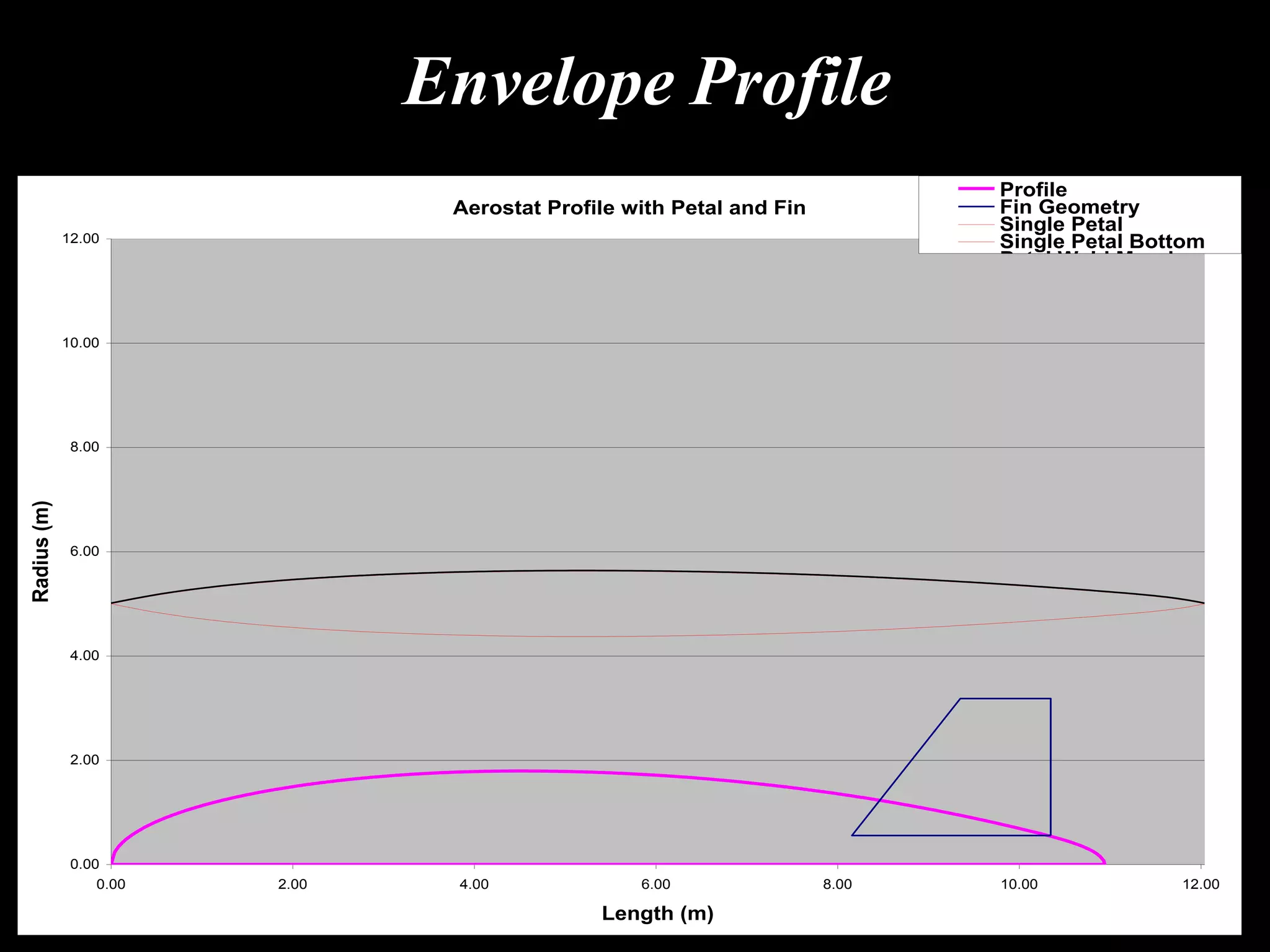
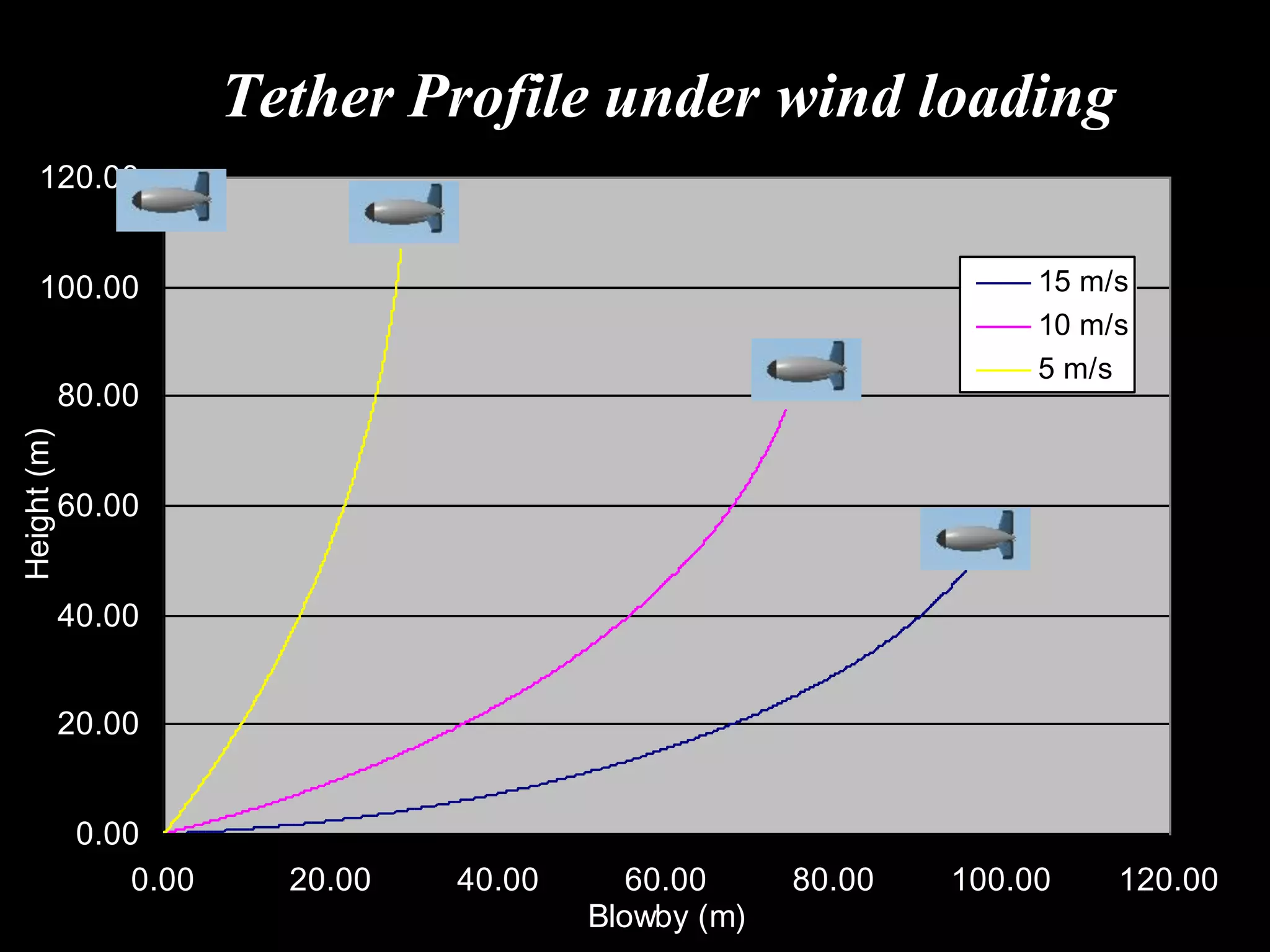
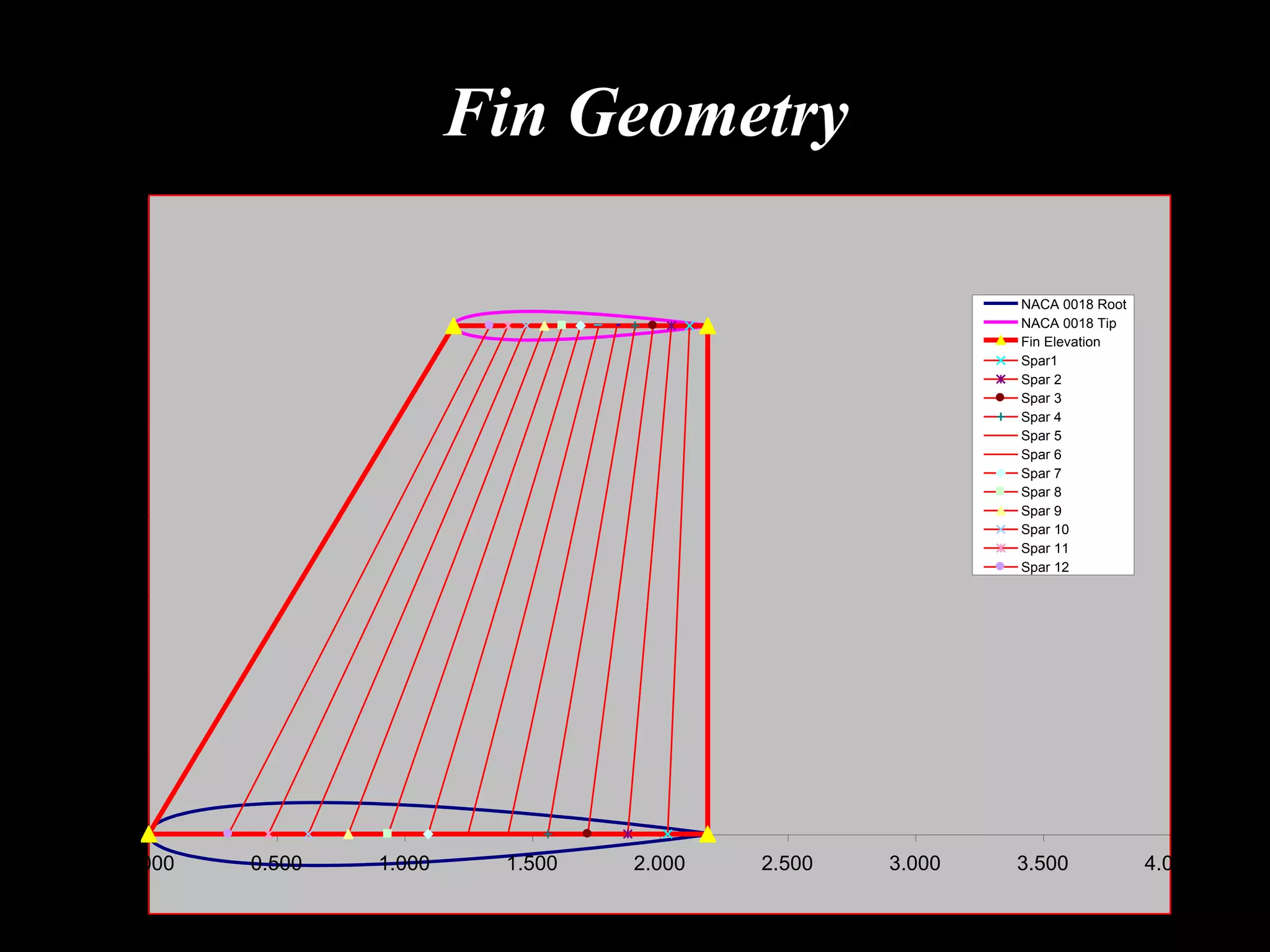
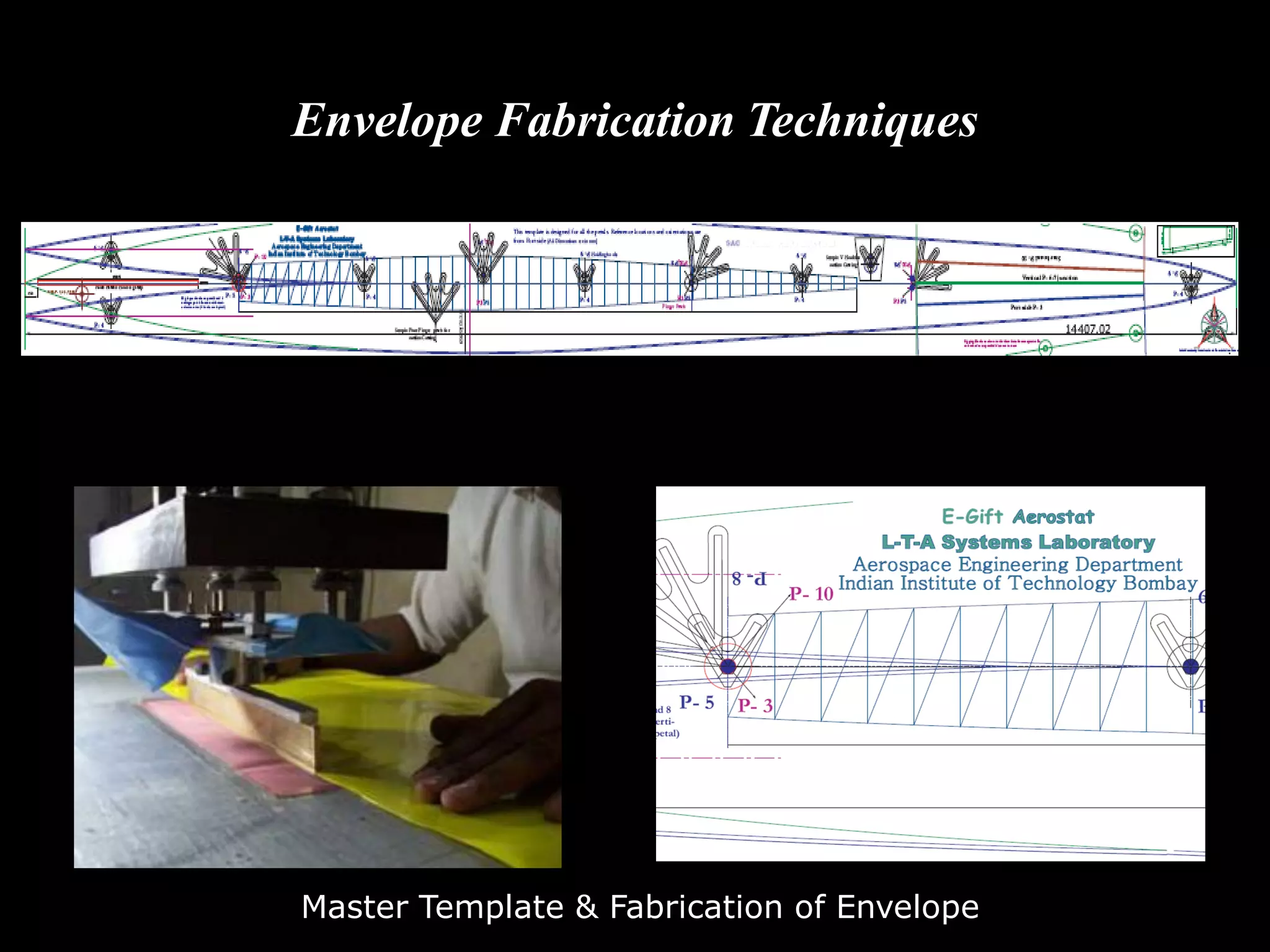
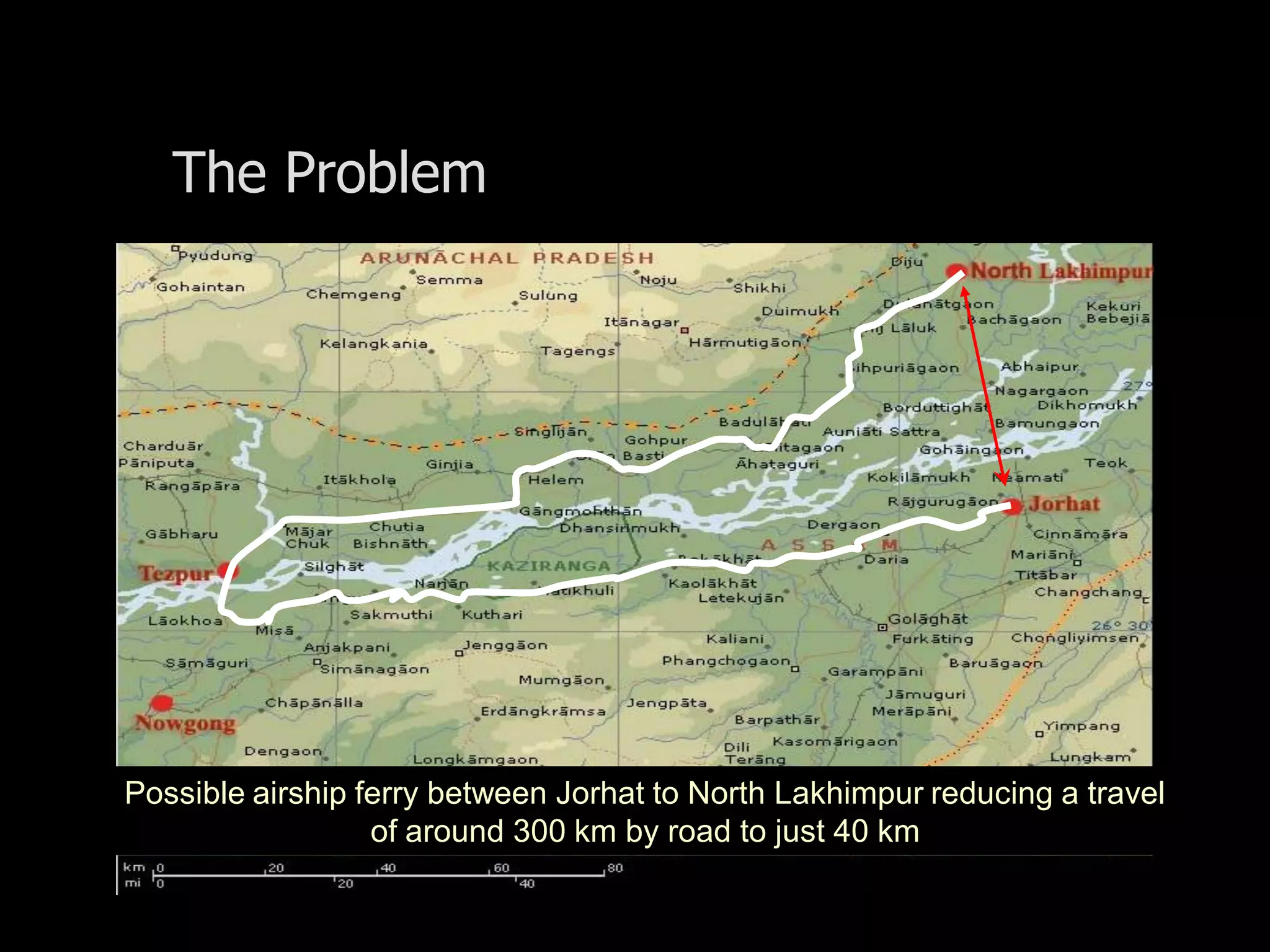
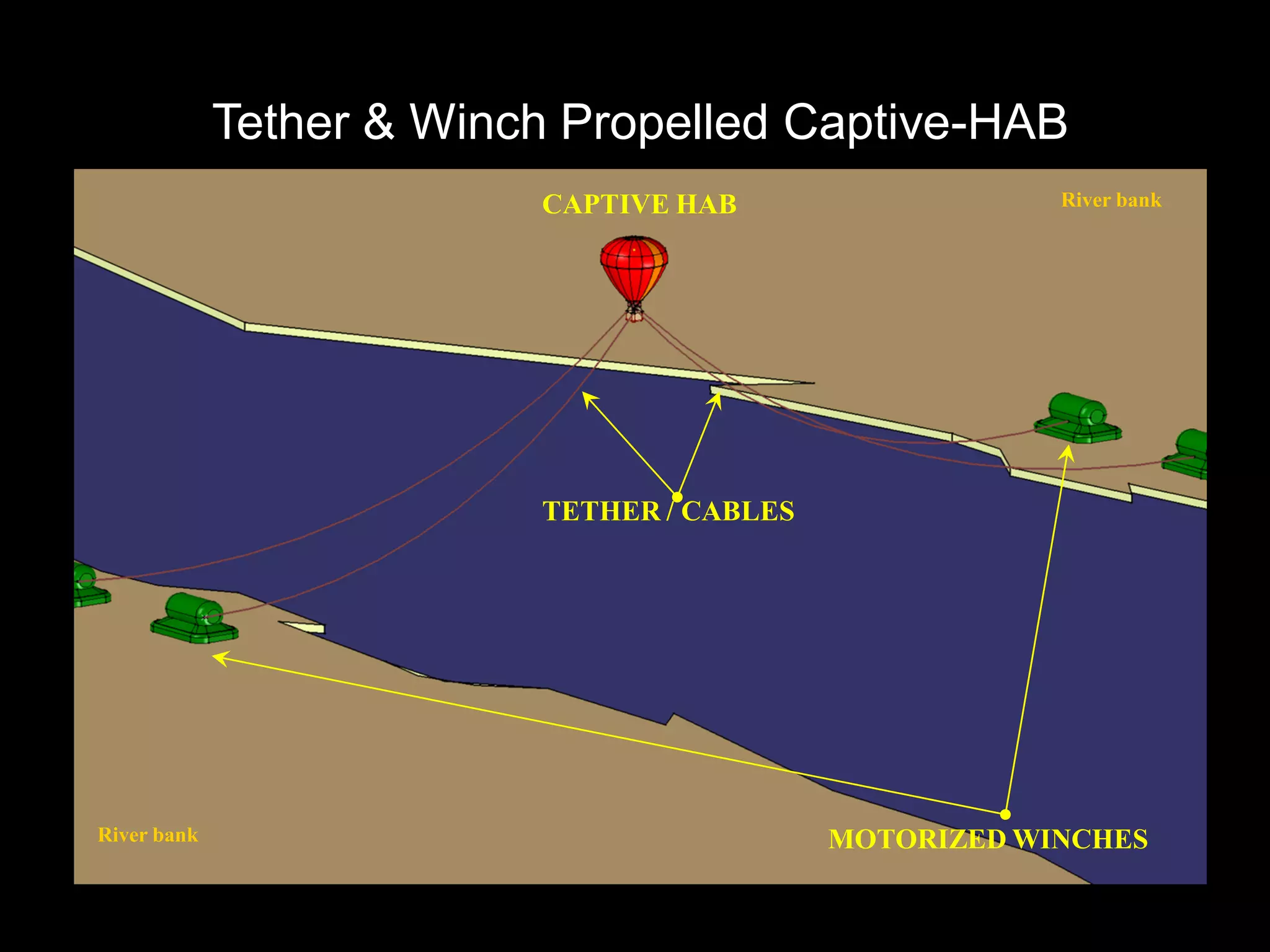
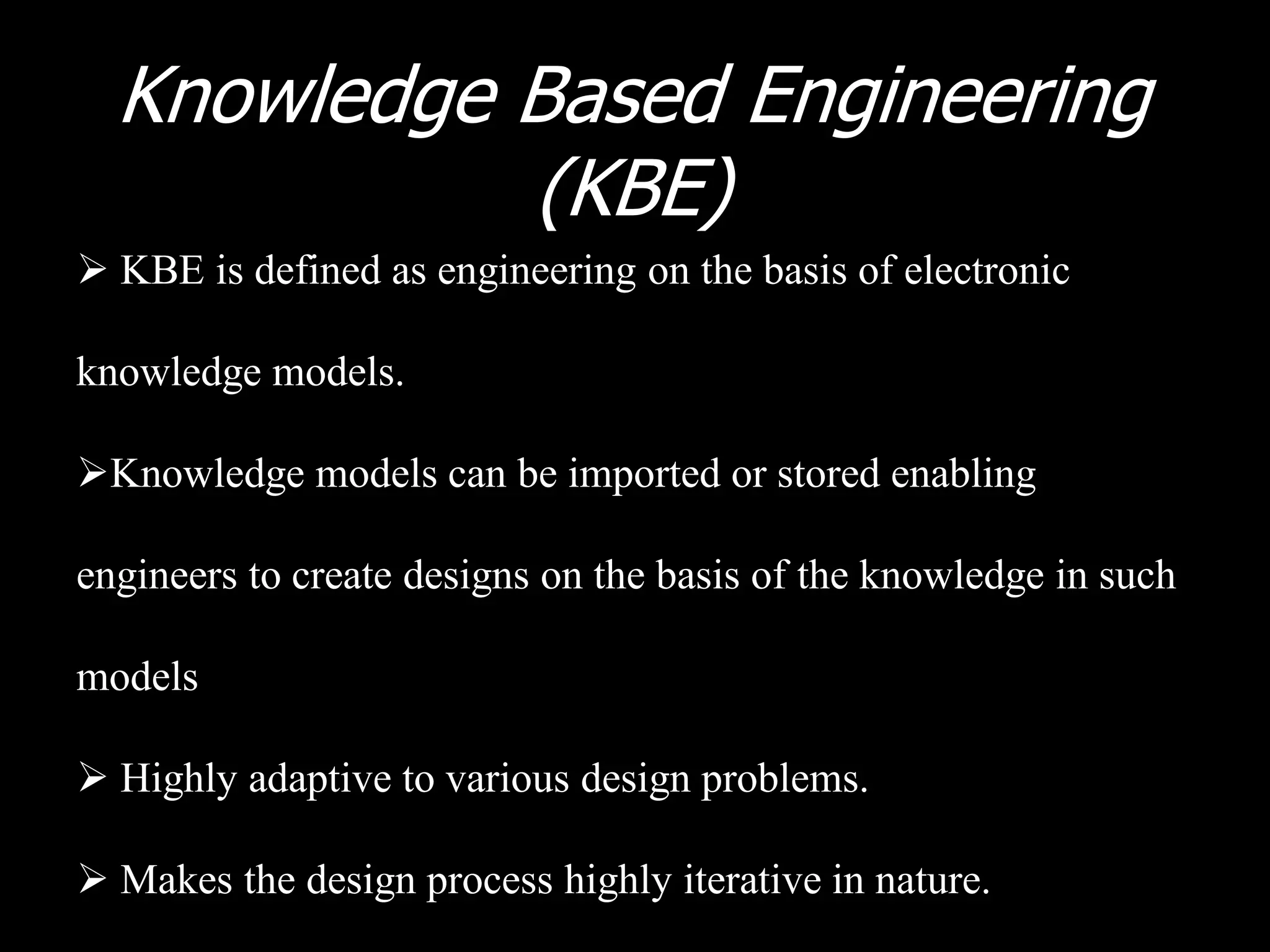
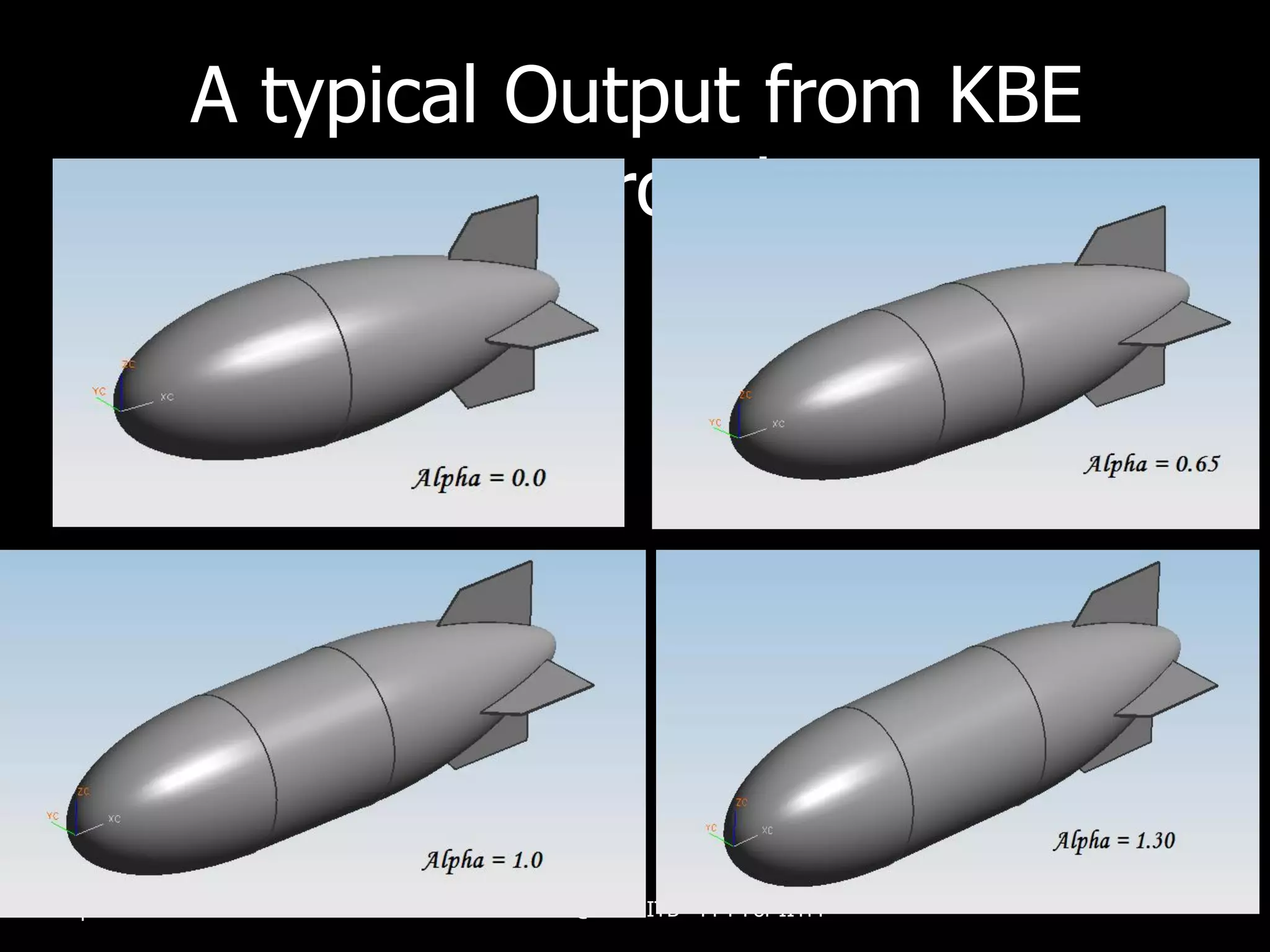
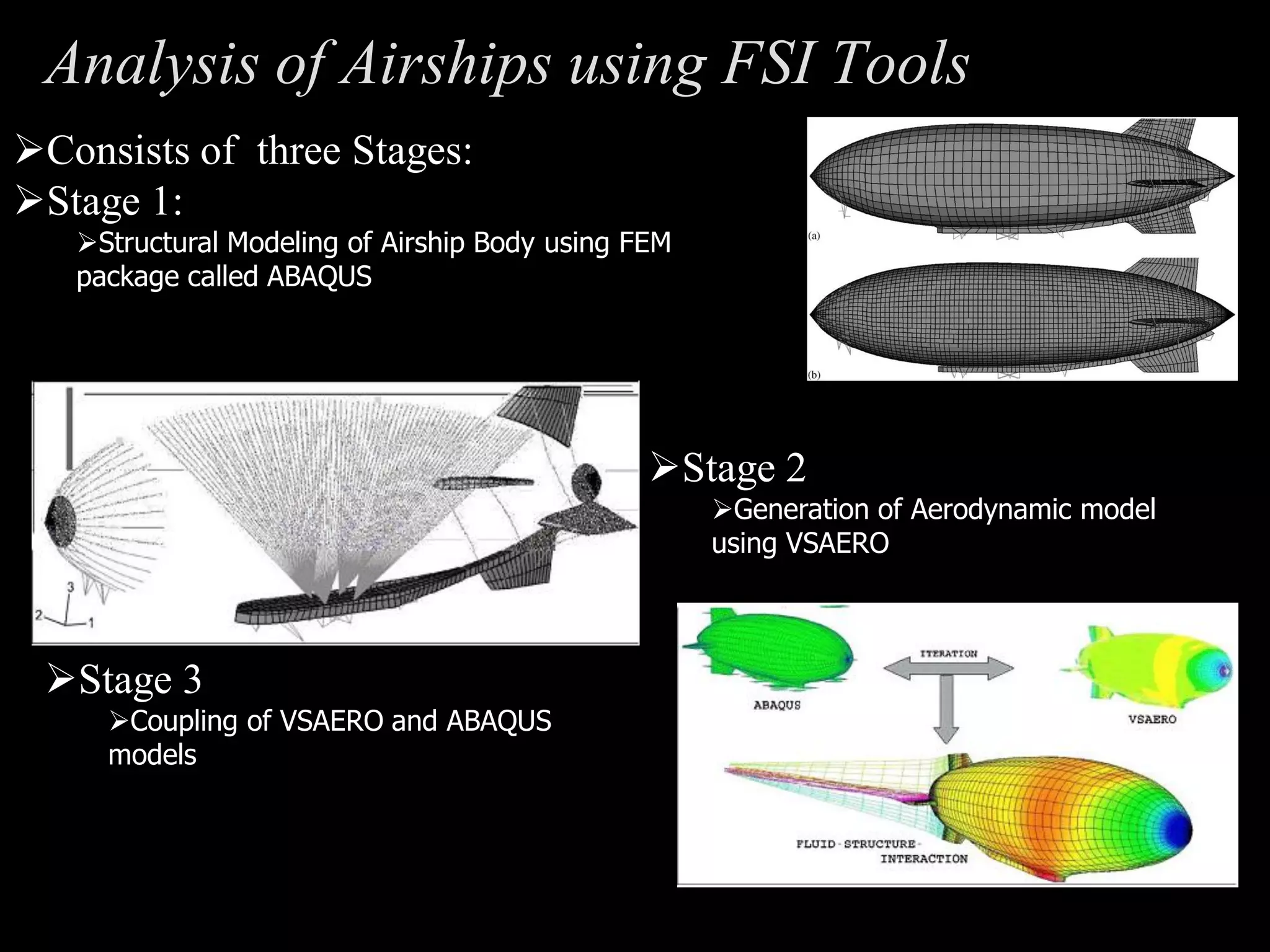
The document outlines research and development efforts on lighter-than-air systems, specifically focusing on airship design and optimization at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay. It details completed tasks such as prototype development, feasibility studies for airships in India, and knowledge-based engineering approaches for airship design. Additionally, it covers various projects, including aerial ferry designs and aerostat systems, showcasing methodologies for structural and aerodynamic analysis.