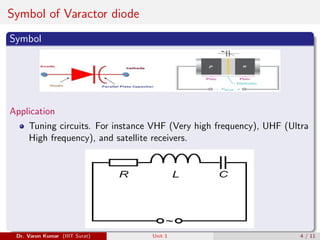
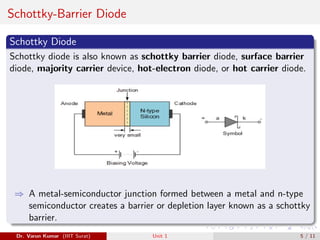
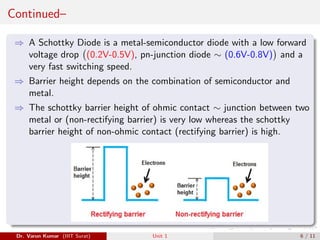
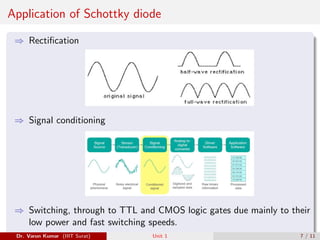
This document discusses several types of special diodes: varactor diodes, which have a variable capacitance controlled by the applied reverse voltage; Schottky barrier diodes, which have a low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed due to a metal-semiconductor junction; photodiodes, including PIN and avalanche photodiodes, which convert light to electrical signals; and light-emitting diodes, which emit light when current passes through. Each diode type has distinct properties and applications in electronic circuits.