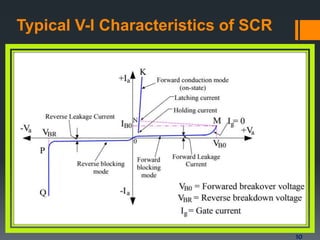
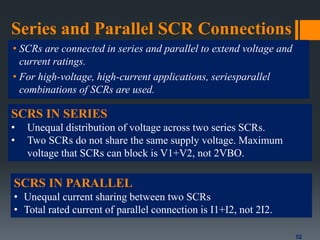
Thyristors are four-layer semiconductor devices that can efficiently control and convert large amounts of power in AC or DC systems. They have higher power handling capabilities than diodes and transistors. A thyristor is turned on by applying a voltage at its gate terminal and remains on until the current drops to zero. Thyristors are used in applications that require switching or controlling high currents like speed control, voltage regulation, and circuit protection. They can be connected in series and parallel configurations to achieve higher voltages and currents.