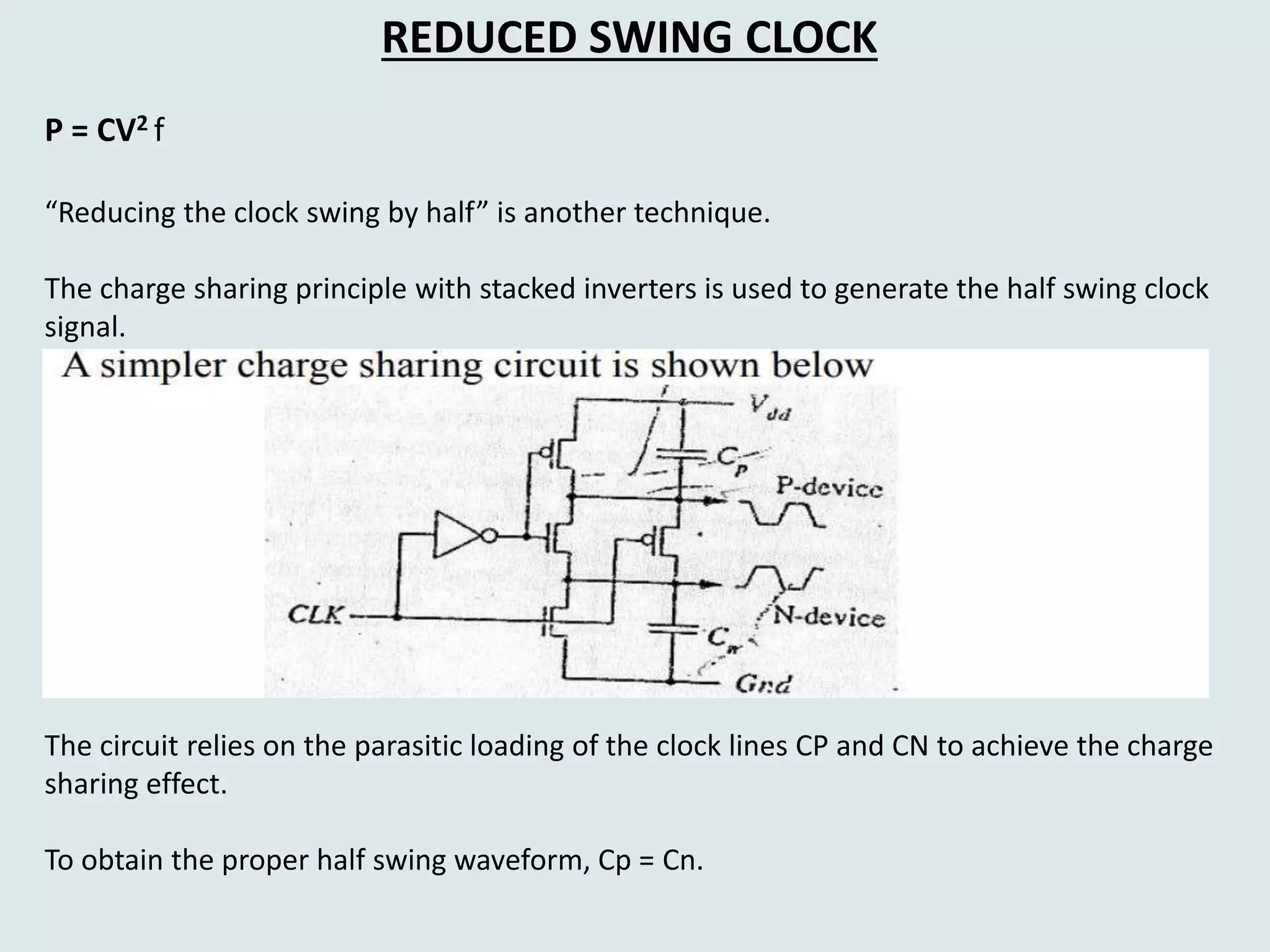
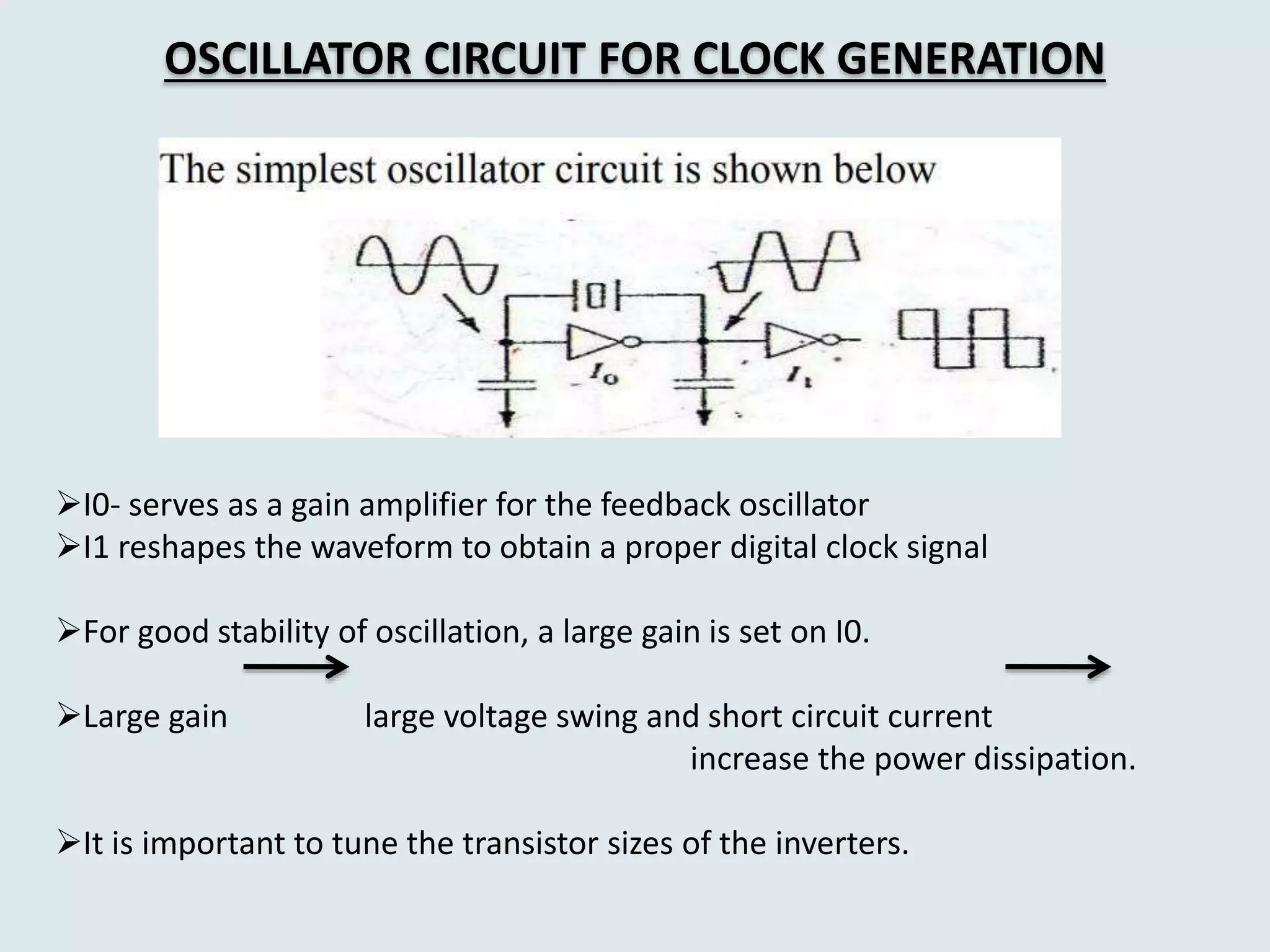
The document discusses techniques for reducing power dissipation in high performance microprocessors, emphasizing the significance of clock signals as major sources of power loss. It details methods such as clock gating, which minimizes unnecessary clock activities, and reduced swing clock techniques, which lower power consumption by manipulating clock signal swings. The text also highlights the importance of avoiding floating CMOS nodes to prevent circuit overheating and failures.