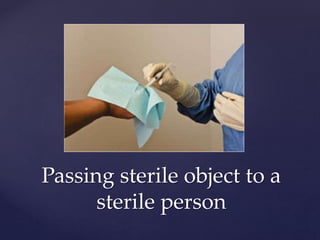
This document discusses the importance of asepsis and surgical asepsis. It defines asepsis as the state of being free from microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Surgical asepsis involves proper preparation of facilities, equipment, surgical site, and surgical team to prevent infection. This includes practices like hand washing, skin preparation, sterilizing instruments, and wearing proper attire. It emphasizes maintaining a sterile field during procedures and limiting movement and conversation to minimize contamination. Strict aseptic techniques help reduce the need for antibiotics after surgery.