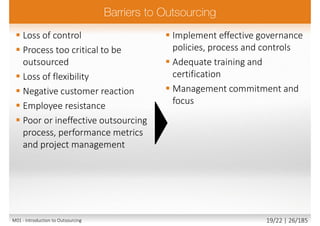
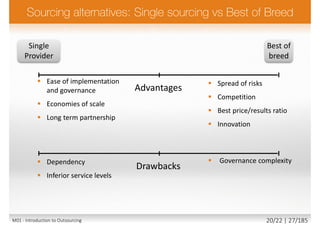
The document outlines a comprehensive course on outsourcing and its strategies, focusing on understanding demand-supply governance frameworks, and preparing for a sourcing governance foundation exam. It includes various topics such as supplier selection, financial cases, contract negotiations, and risks associated with outsourcing. In addition, it discusses the roles of trainers and coaches, and highlights the benefits and complexities involved in outsourcing processes.