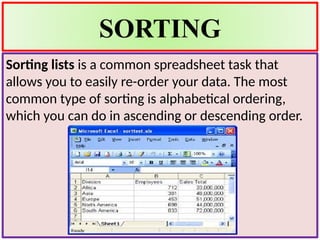
The document provides guidance on sorting and filtering data in Microsoft Excel, detailing steps for both alphabetical and numerical sorting as well as multi-level sorting. It explains how to filter data using Autofilter to display subsets of data based on specified criteria and offers options for filtering by lists, formats, or colors. Additionally, it covers the creation and modification of charts to represent numerical data visually, including different types of charts and formatting options.