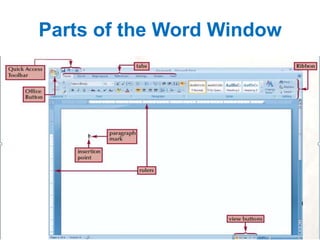
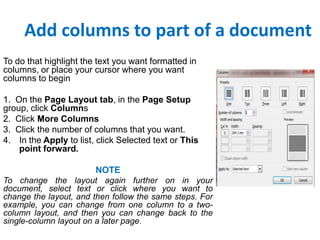
The document outlines a Microsoft Word seminar presented by Mamma Sawaneh, covering essential features for document creation, editing, and formatting. It details the use of tools such as the ribbon, quick access toolbar, and formatting options to enhance document efficiency and appearance, along with techniques for tables, headers, footers, and thesis formatting guidelines. The presentation aims to equip attendees with the skills needed to navigate and utilize Microsoft Word effectively for professional document creation.