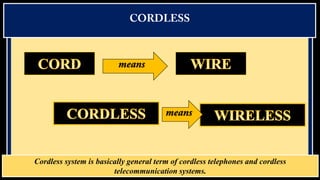
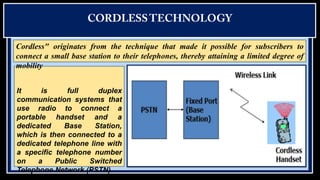
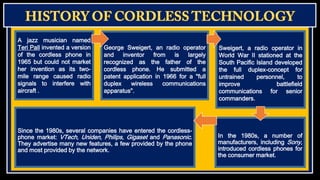
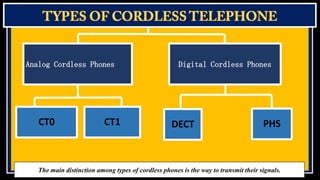
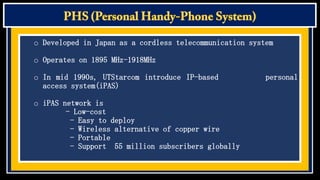
Cordless phones allow wireless communication between a portable handset and a base station connected to a telephone line. There are different generations of cordless phone technology, from early analog systems to newer digital standards like DECT and PHS. DECT is widely used in Europe and other parts of the world for home and office cordless phone systems, offering better voice quality and security than analog predecessors. Digital systems also provide features like extended battery life and range compared to early cordless phones.