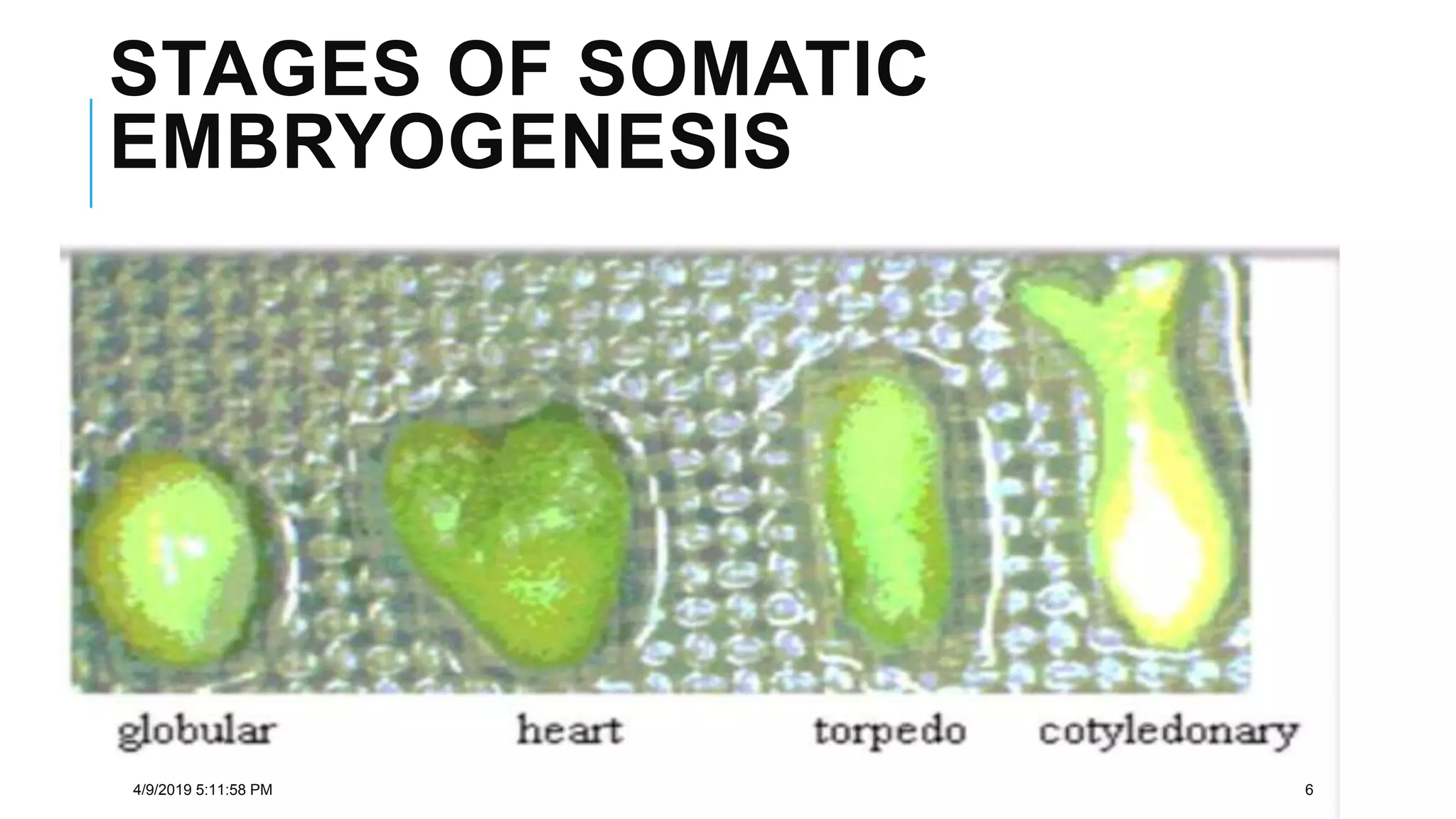
Embryogenesis is the process by which a plant embryo develops from a fertilized ovule. It involves asymmetric cell division and differentiation of unspecialized cells into tissues and organs. There are two types of embryos: zygotic embryos formed from the zygote, and non-zygotic embryos like somatic and parthenogenic embryos formed from non-zygote cells. Somatic embryogenesis is the process where somatic cells develop into embryos and can regenerate whole plants. It occurs through direct or indirect routes. Key stages of somatic embryogenesis include globular, heart, torpedo and mature stages. Growth regulators like auxins and cytokinins play an important role in somatic embryogenesis.