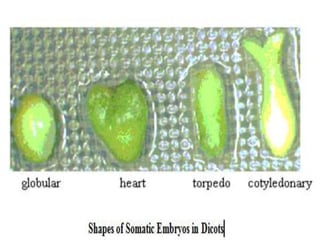
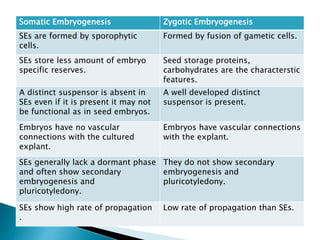
Somatic embryogenesis is a process where embryos are formed from somatic (non-sex) cells in vitro. These embryos, called embryoids, can be formed directly from explant tissue through direct somatic embryogenesis or indirectly through an intermediate callus phase in indirect somatic embryogenesis. Somatic embryos are different from zygotic embryos in that they form from sporophytic cells rather than gametes and may lack structures like a distinct suspensor. Somatic embryogenesis allows for high rates of plant propagation in vitro and has applications for germplasm conservation and eliminating diseases.