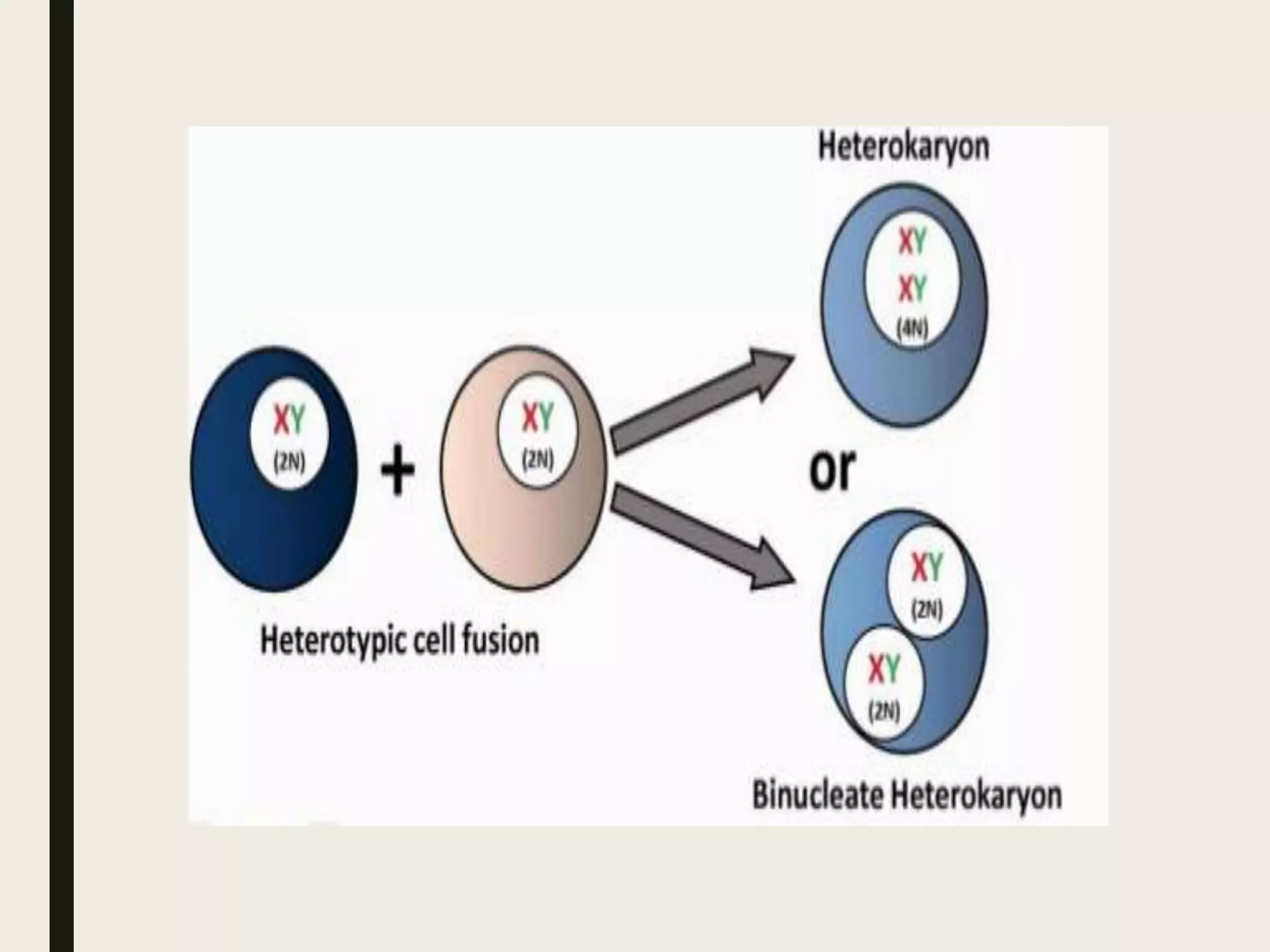
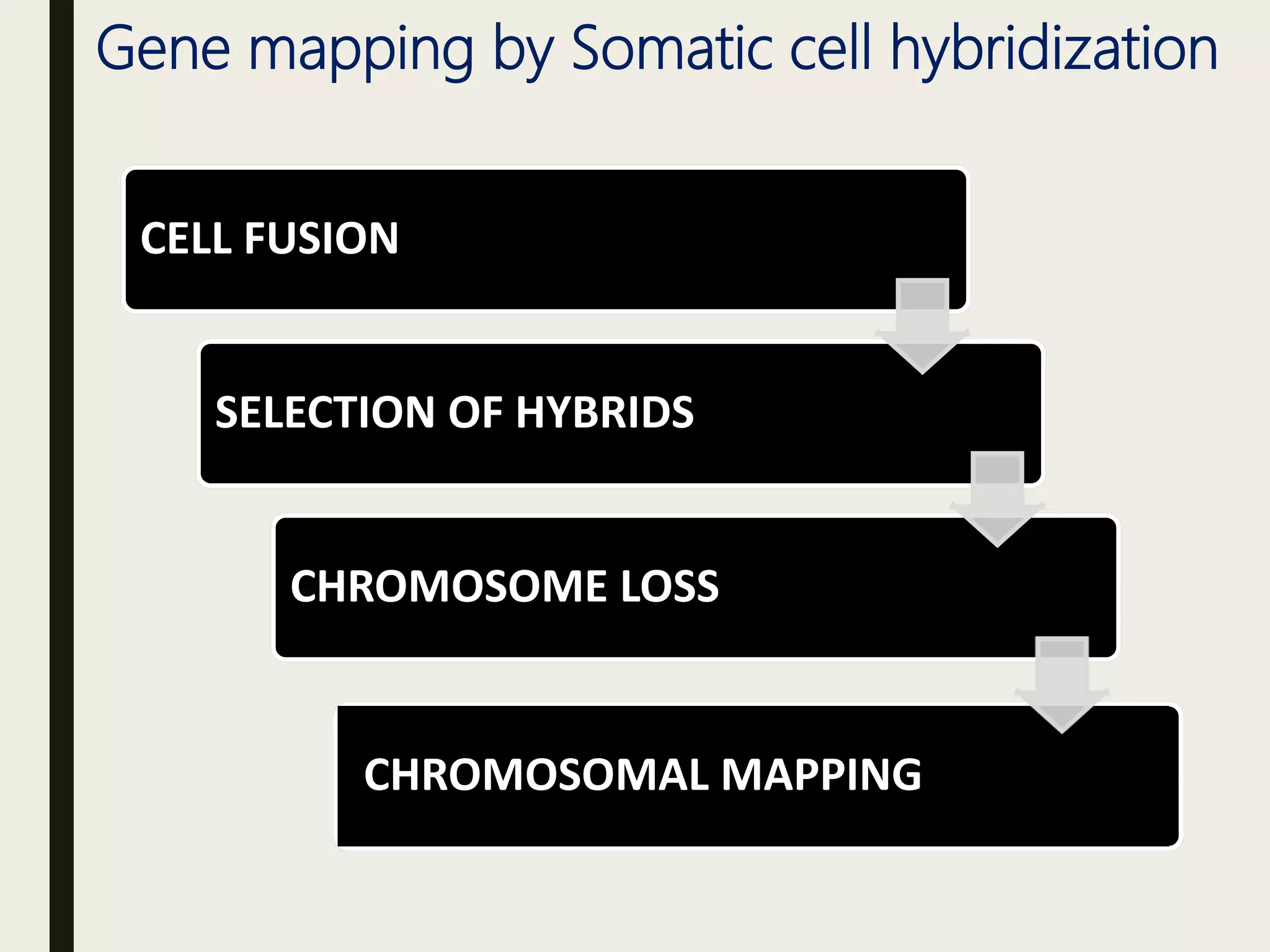
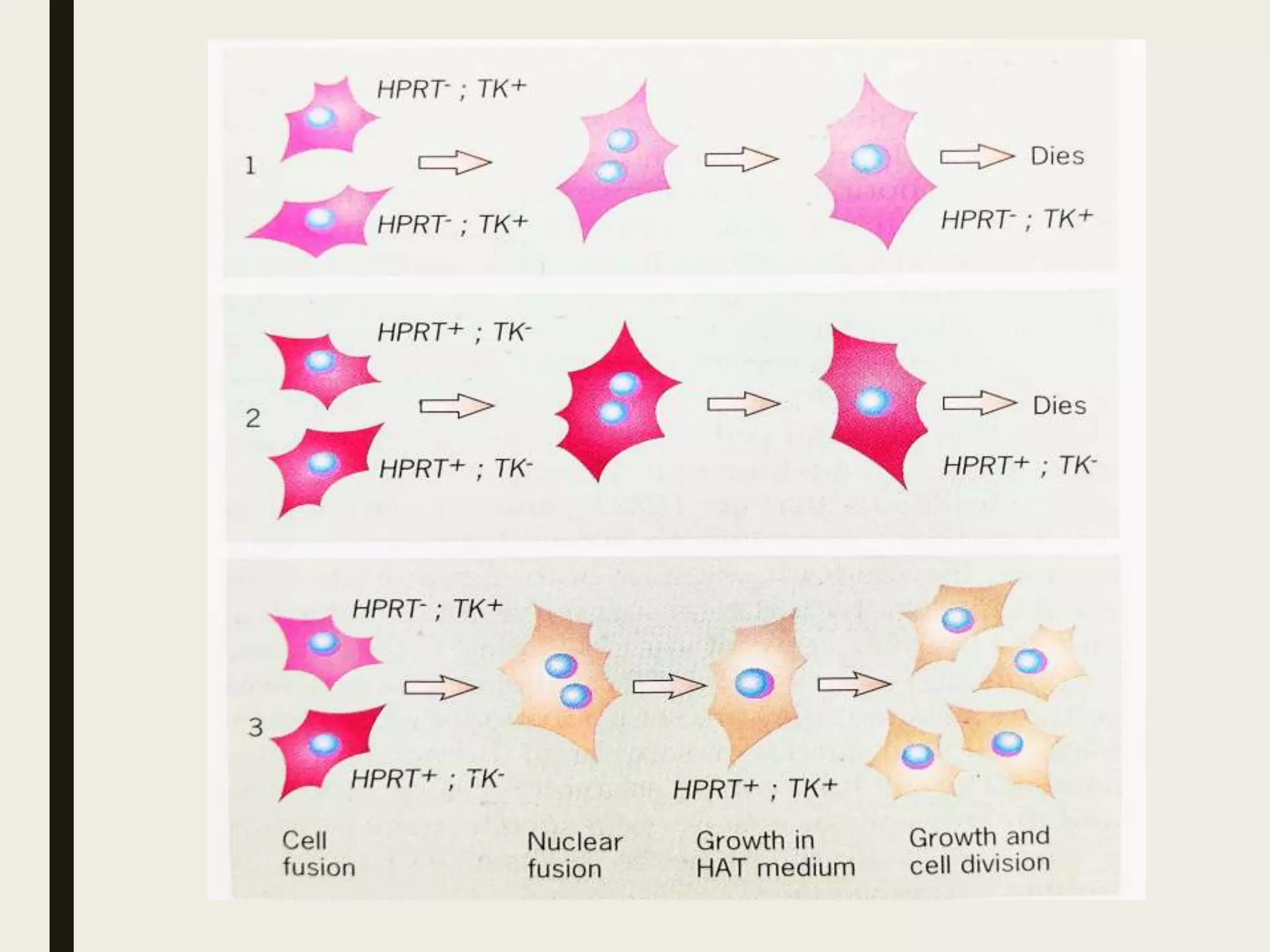
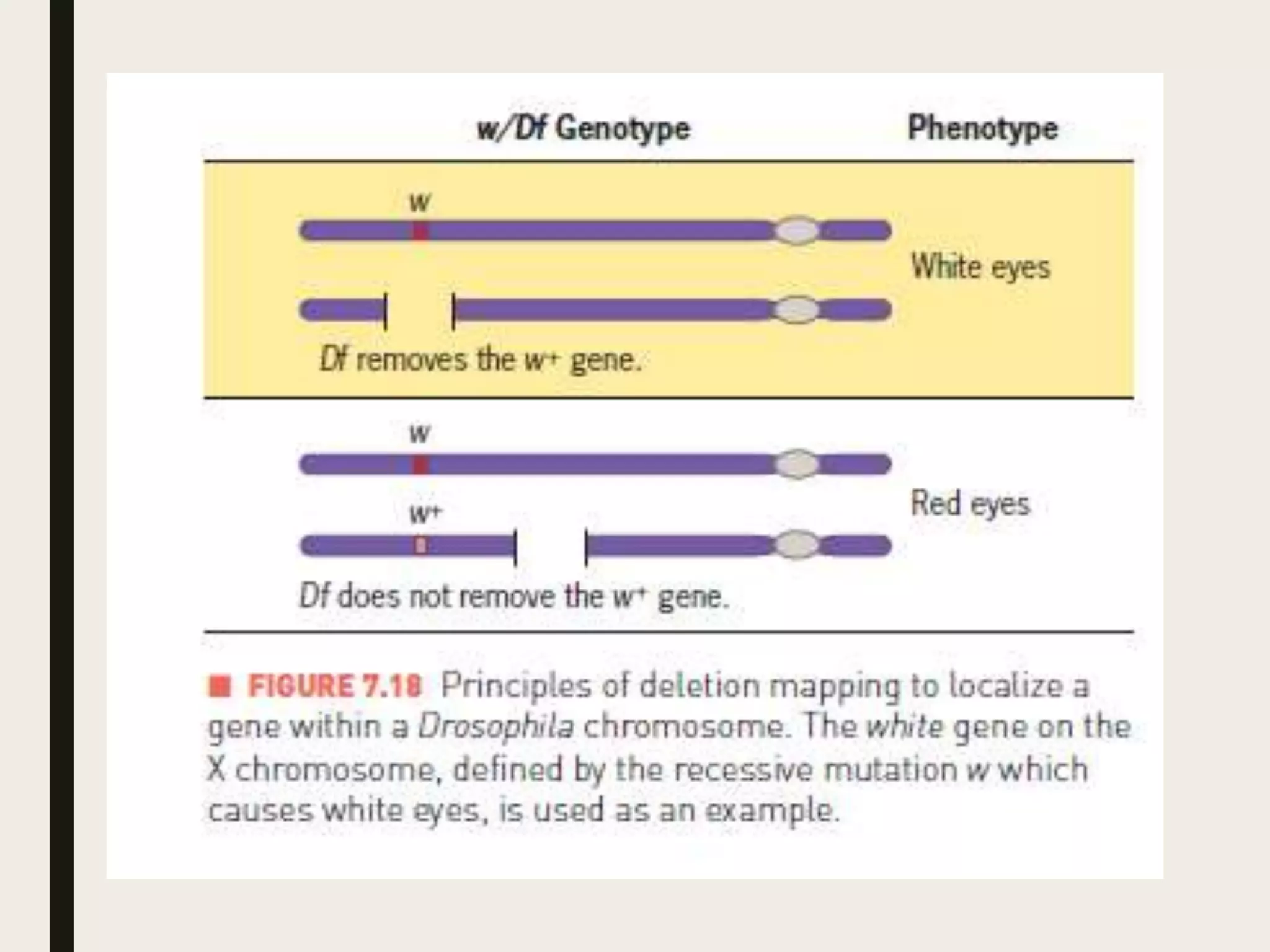
Somatic cell hybridization allows genetic analysis using cell culture rather than sexual reproduction. It involves fusing somatic cells from two different species or tissues to form hybrid cells. Gene mapping can be done by selecting hybrids that retain specific genes as parental chromosomes are lost. Chromosomal rearrangements like deletions, duplications, and translocations also help map genes to specific chromosome regions. A case study describes using somatic cell selection in potato cultures with a herbicide to recover resistant variants with mutations in the AHAS gene.