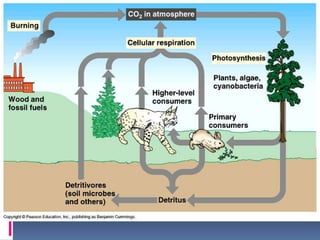
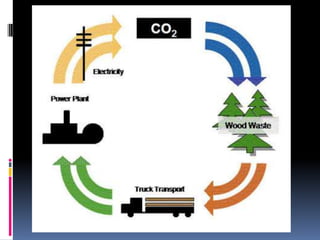
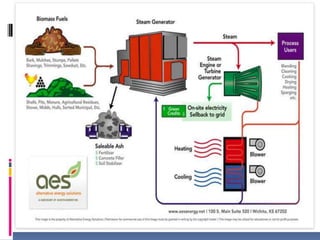
This document discusses biomass energy, identifying fuels like trees, grasses, crops and residues that can be used, and describing how biomass produces electricity by heating water into steam to turn a turbine. It lists current uses of biomass as ethanol, space heating and cooking, and notes pros as biomass being available worldwide and potentially sustainable, while cons include needing fossil fuels for harvesting and transport and high production costs.