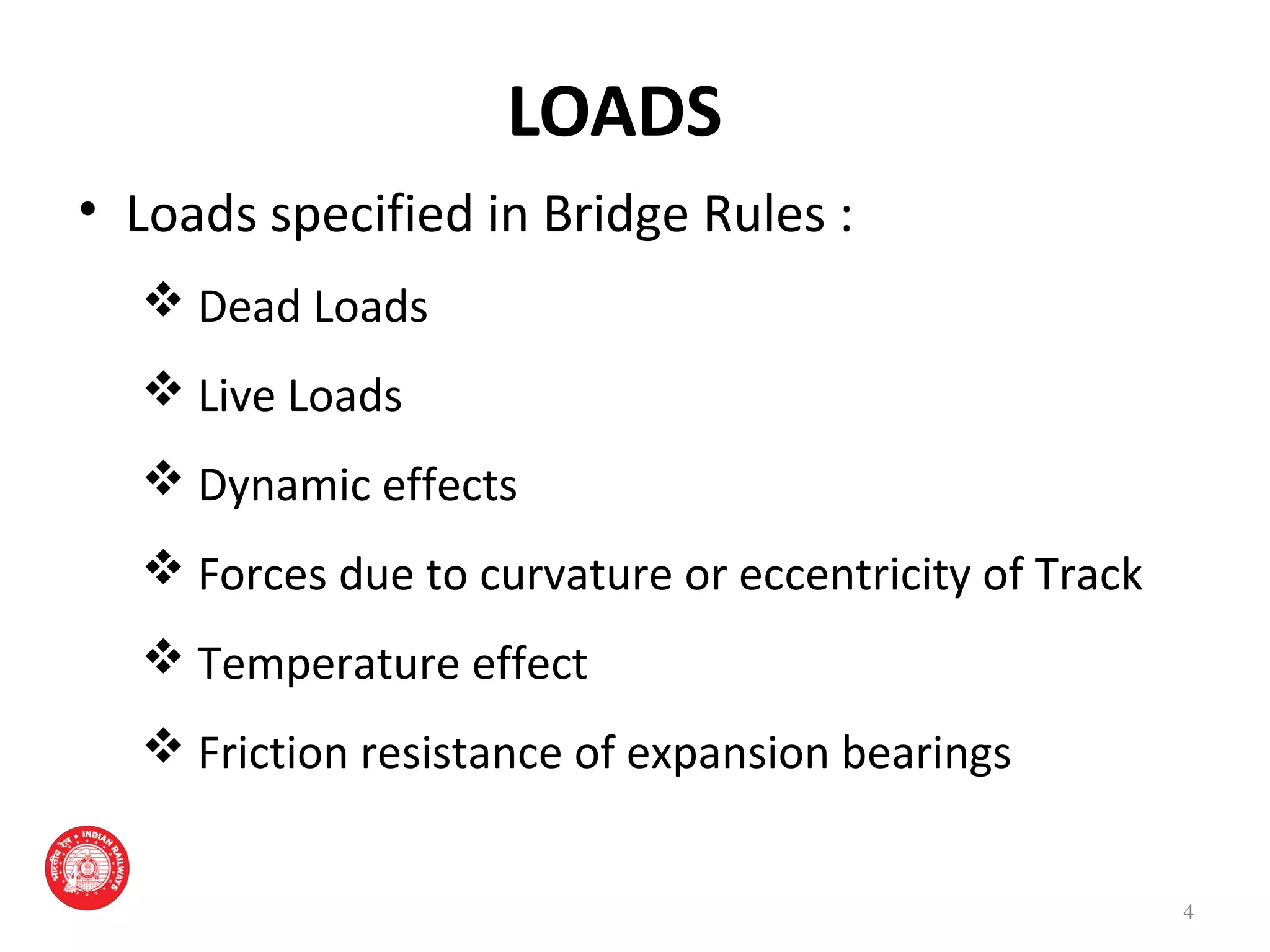
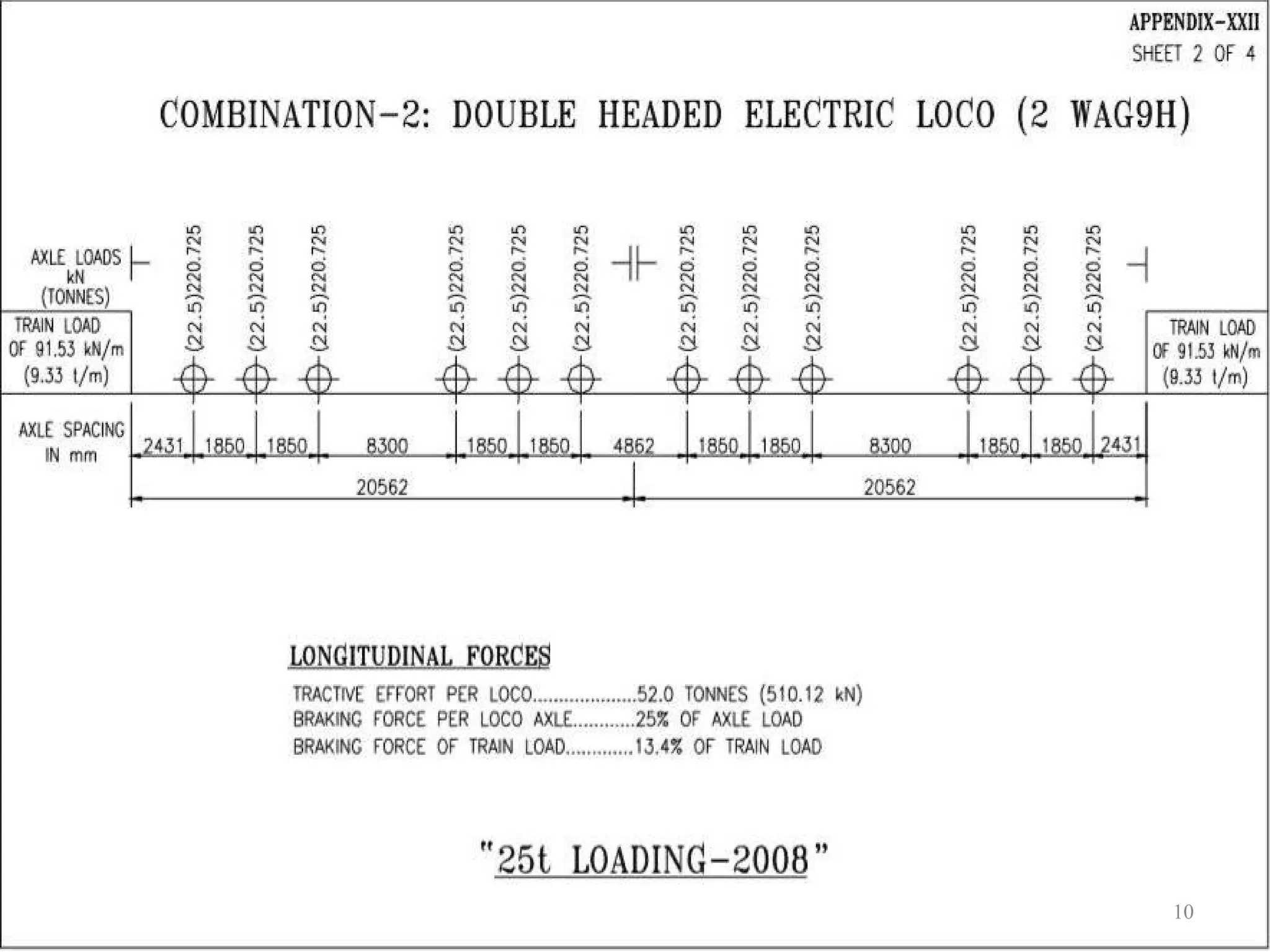
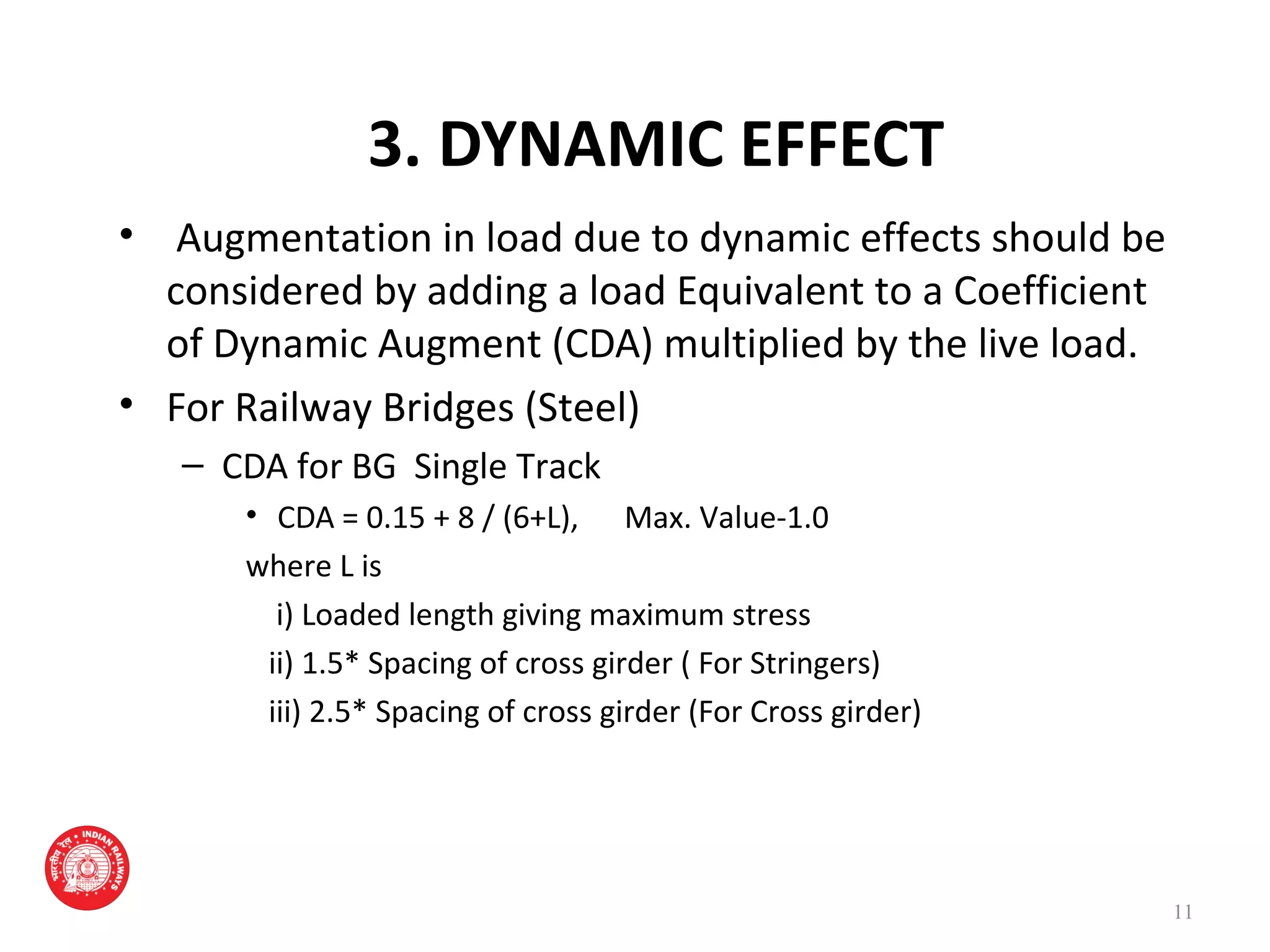
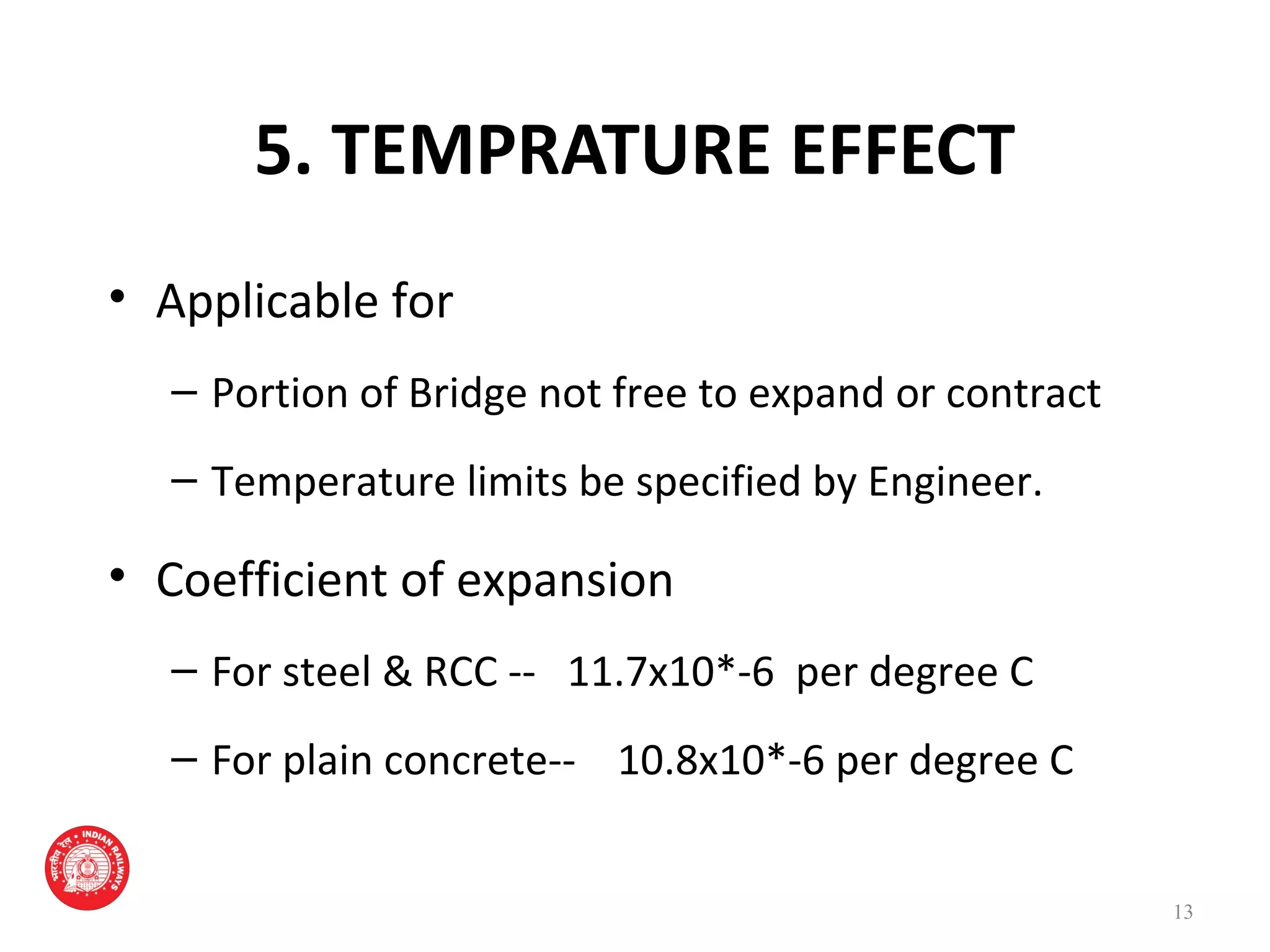
The document outlines the rules for loads that must be considered in designing and assessing the strength of railway bridges in India. It specifies loads like dead loads, live loads, dynamic effects, wind pressure, seismic forces, temperature effects, and derailment loads. Live loads have increased over time from 18 tonnes per axle in 1903 to 32.5 tonnes per axle currently for the highest class. Dynamic load effects are quantified using a coefficient between 0.15 and 1.0 depending on bridge properties. Seismic forces also depend on the zone the bridge is located in, with zones II-V having increasing seismic specifications.