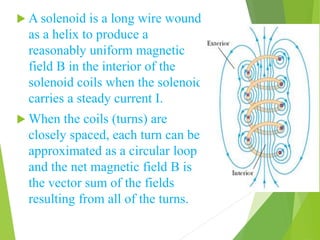
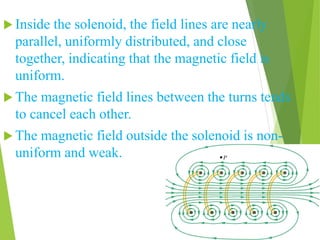
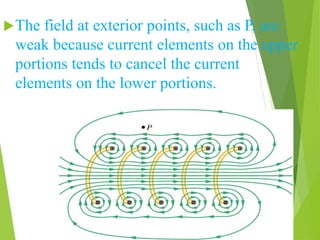
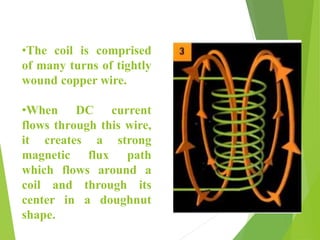
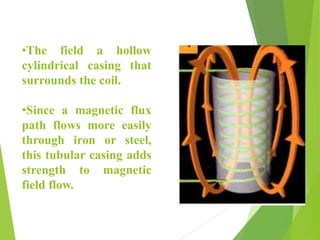
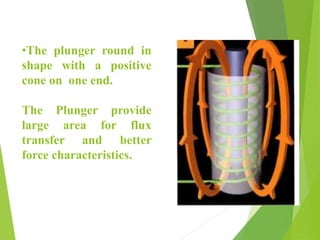
A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when electric current passes through it. Inside the solenoid, the magnetic field lines are parallel and uniform. Outside the solenoid, the magnetic field is non-uniform and weak due to cancellation of opposing field lines between coil turns. Solenoids can operate using direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). DC solenoids consist of a coil, field/helix, and plunger that moves in one direction when energized. Solenoids have many applications including locking mechanisms, automotive systems, medical devices, railways, and industrial machinery.