Embed presentation





















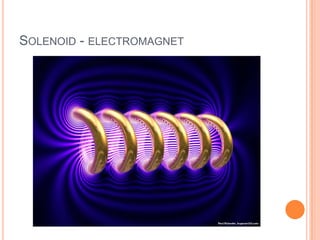





This document discusses magnetism and electromagnetism. It explains that ferromagnetic objects like iron, nickel, and cobalt can be attracted to magnets. It describes magnetic fields and field lines, and how they behave and can be visualized. It also discusses how electric currents can induce magnetic fields based on the right hand rule, including around wires and in solenoids. The strength of electromagnetic fields depends on factors like the number of turns in a solenoid and the current.

























