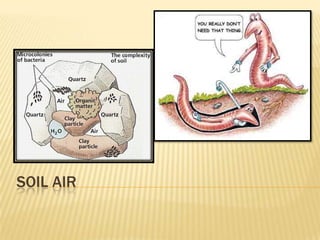
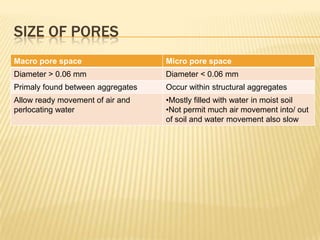
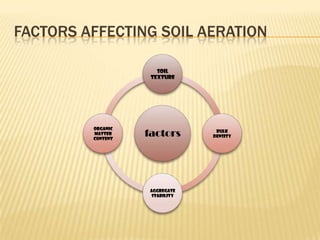
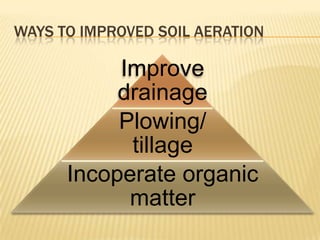
This document discusses soil air and aeration. It notes that soil air is important for root respiration and decomposition by microorganisms. Well-aerated soil allows for rapid oxygen exchange between the soil and atmosphere. Factors like pore space, temperature, depth, and wetting/drying influence gas exchange rates. Pore space occupies the volume not taken up by solids and is made up of spaces between aggregates and those created by roots, microbes, and expanding gases. Pore size and soil texture impact aeration. Aeration is the replacement of soil air by atmospheric air through diffusion and mass flow. Poor aeration can result from excess moisture or slow gas exchange. Improving drainage, tillage, and adding