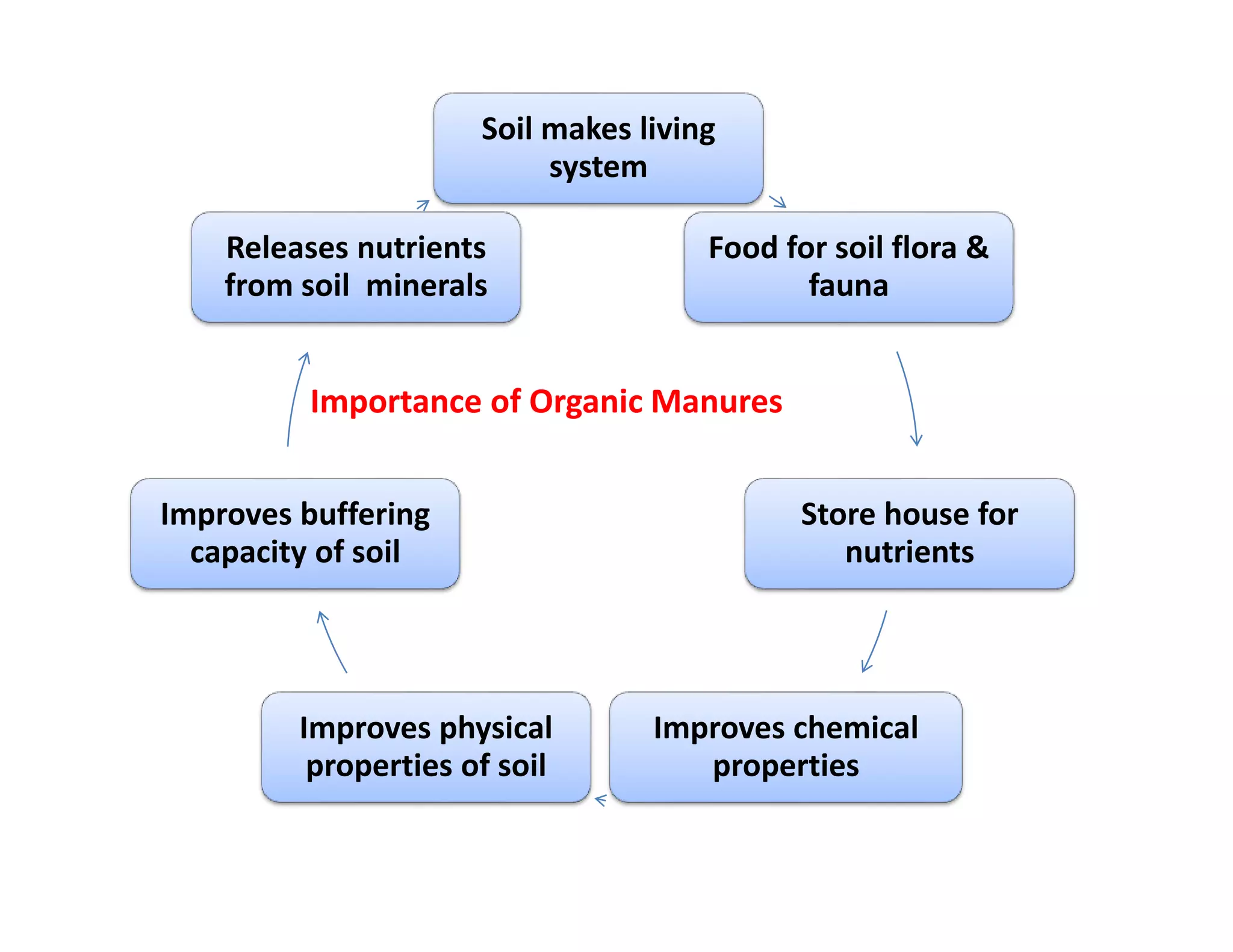
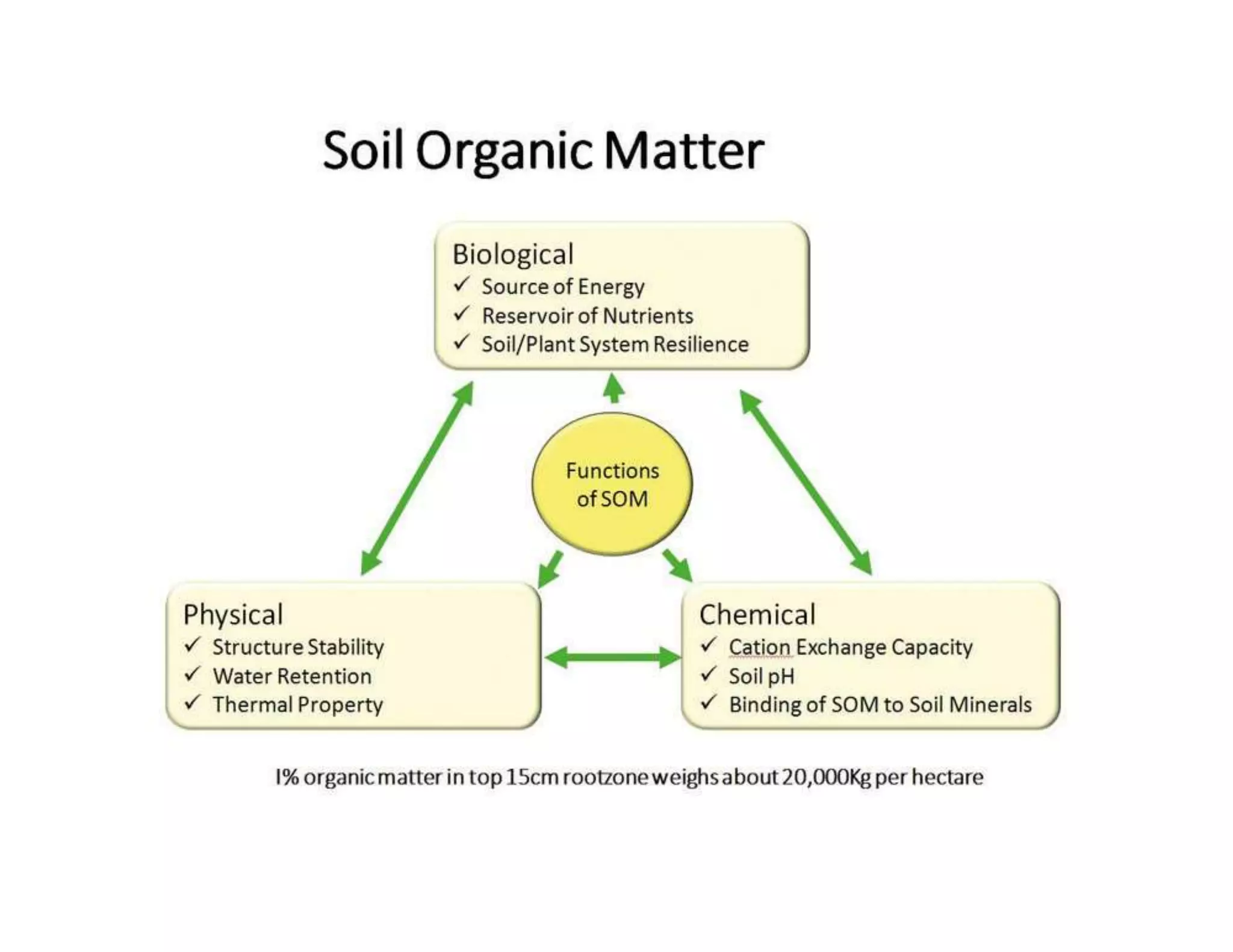
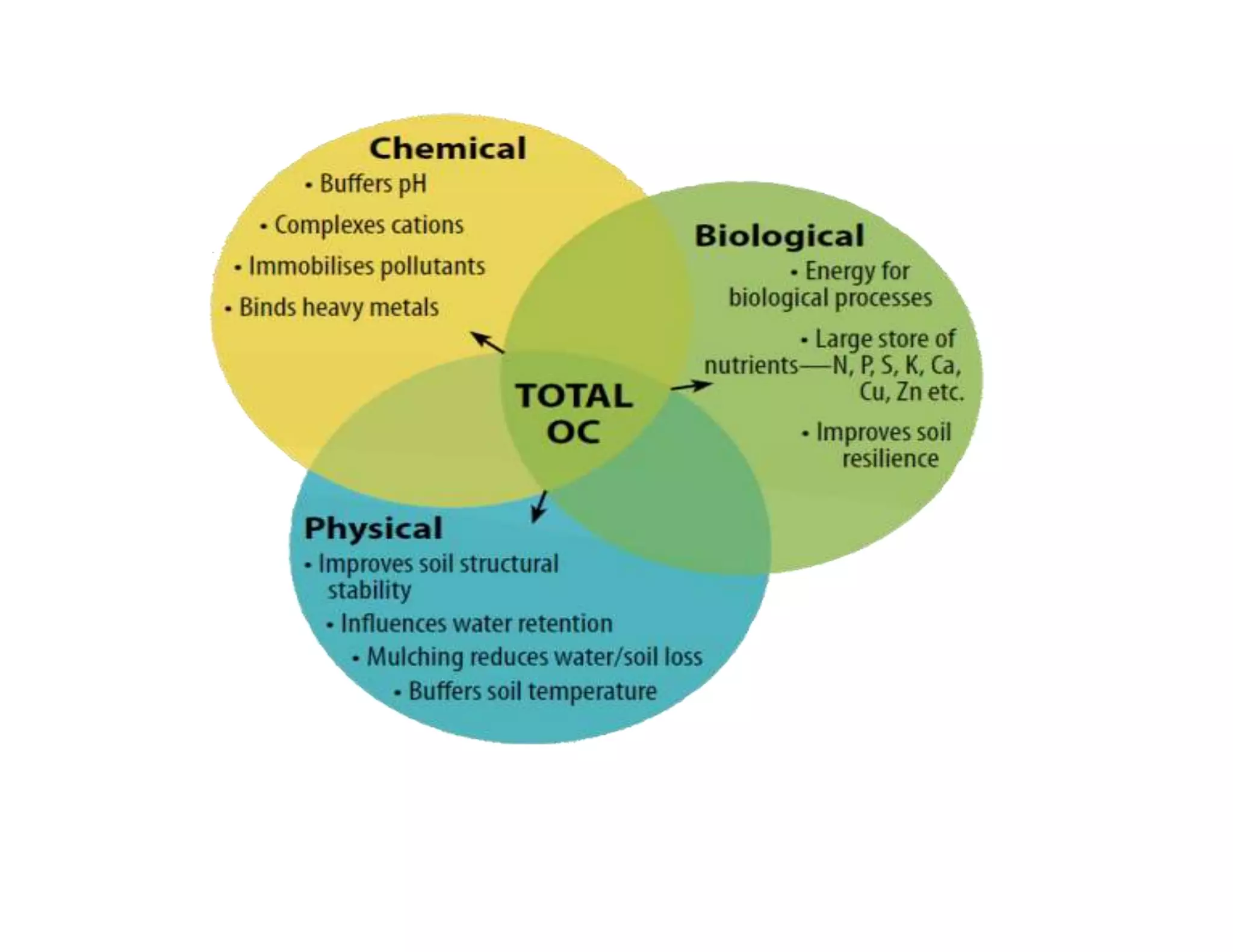
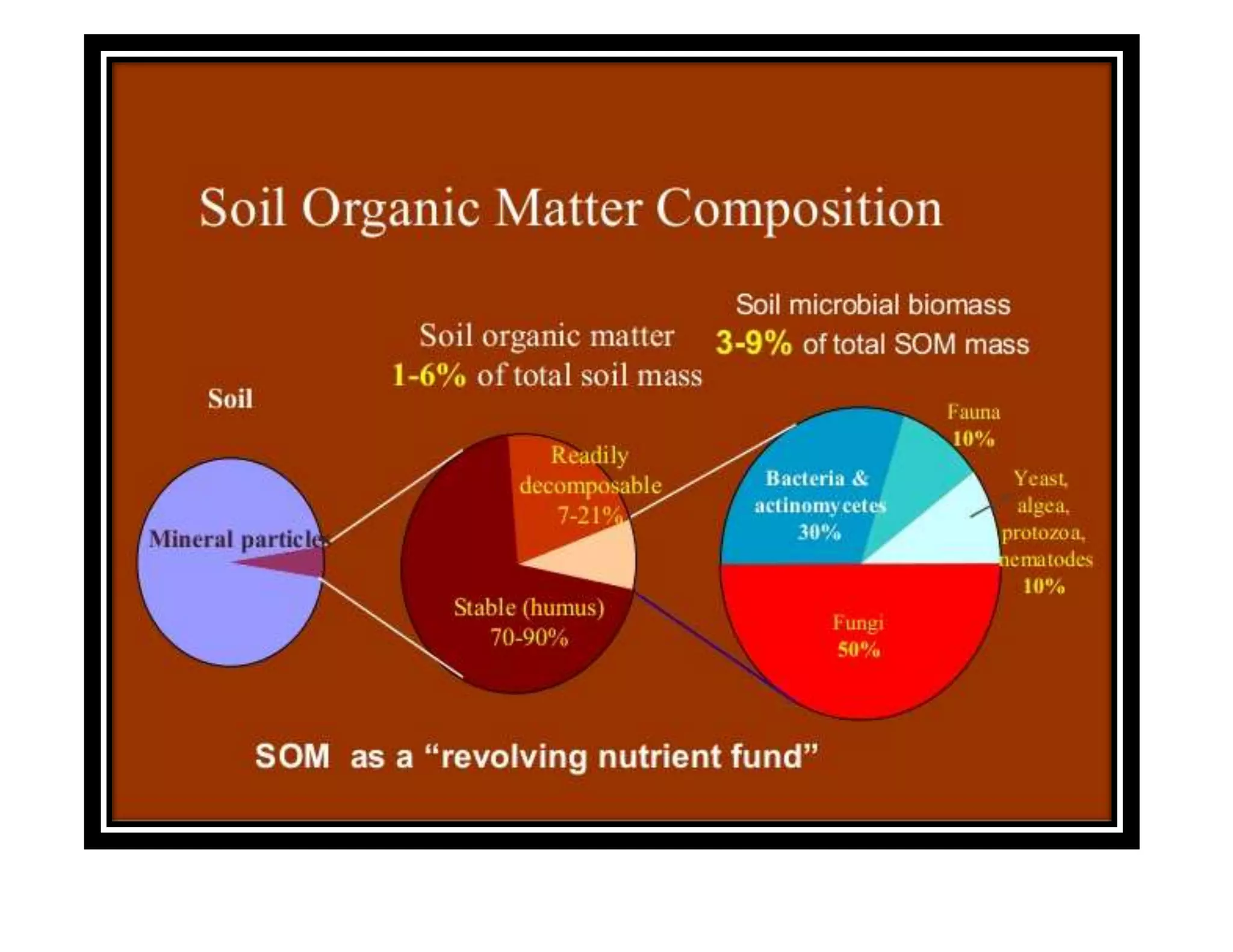
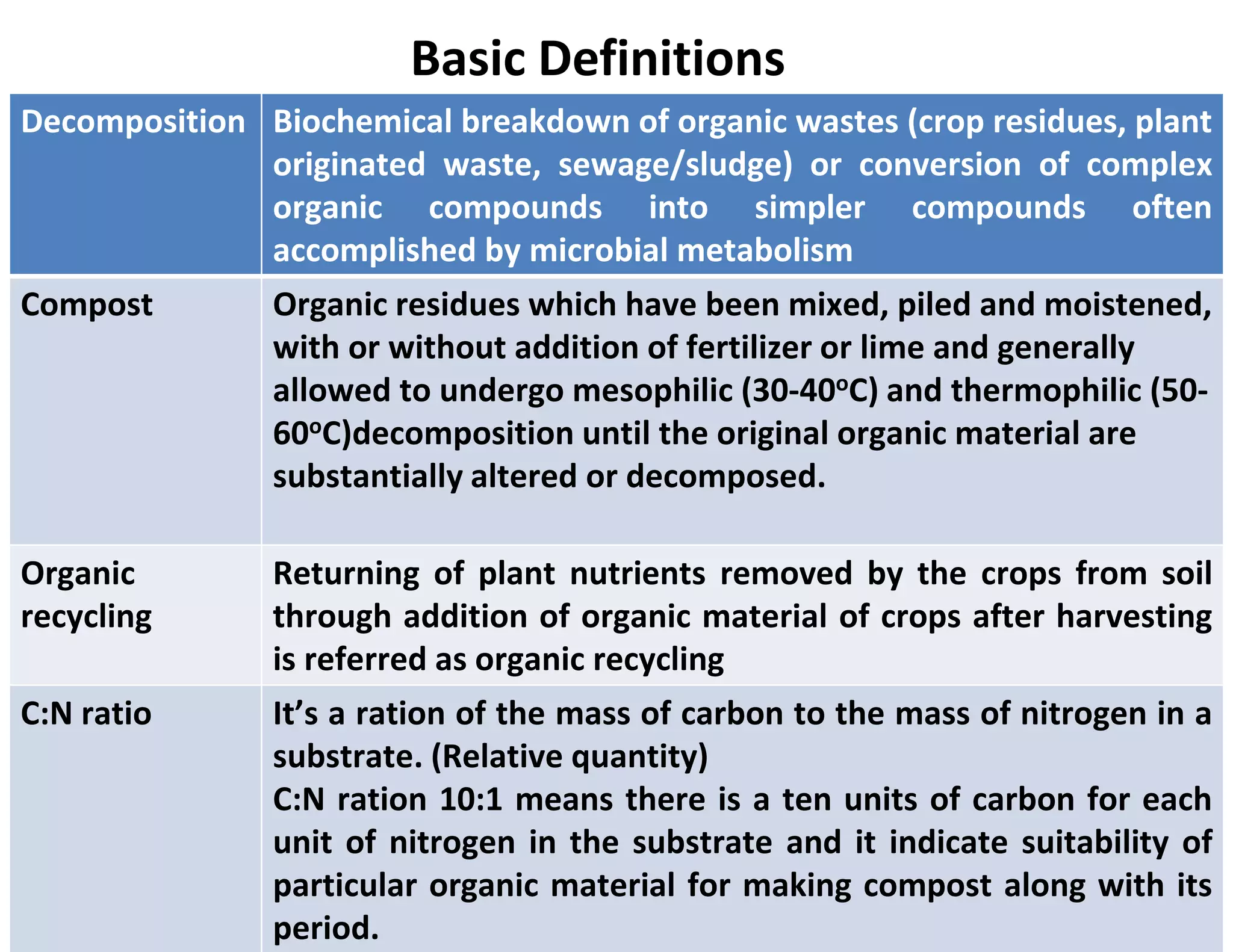
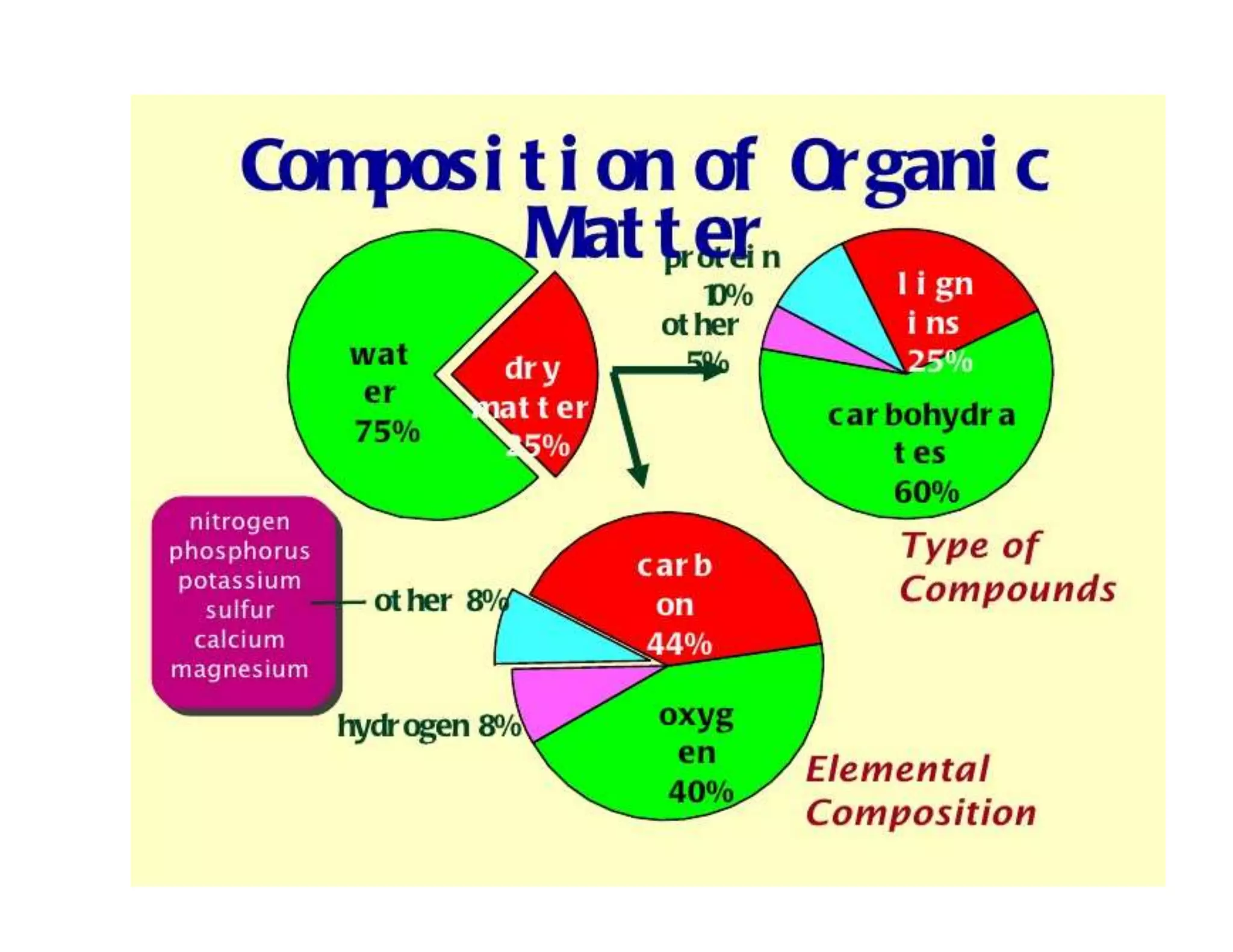
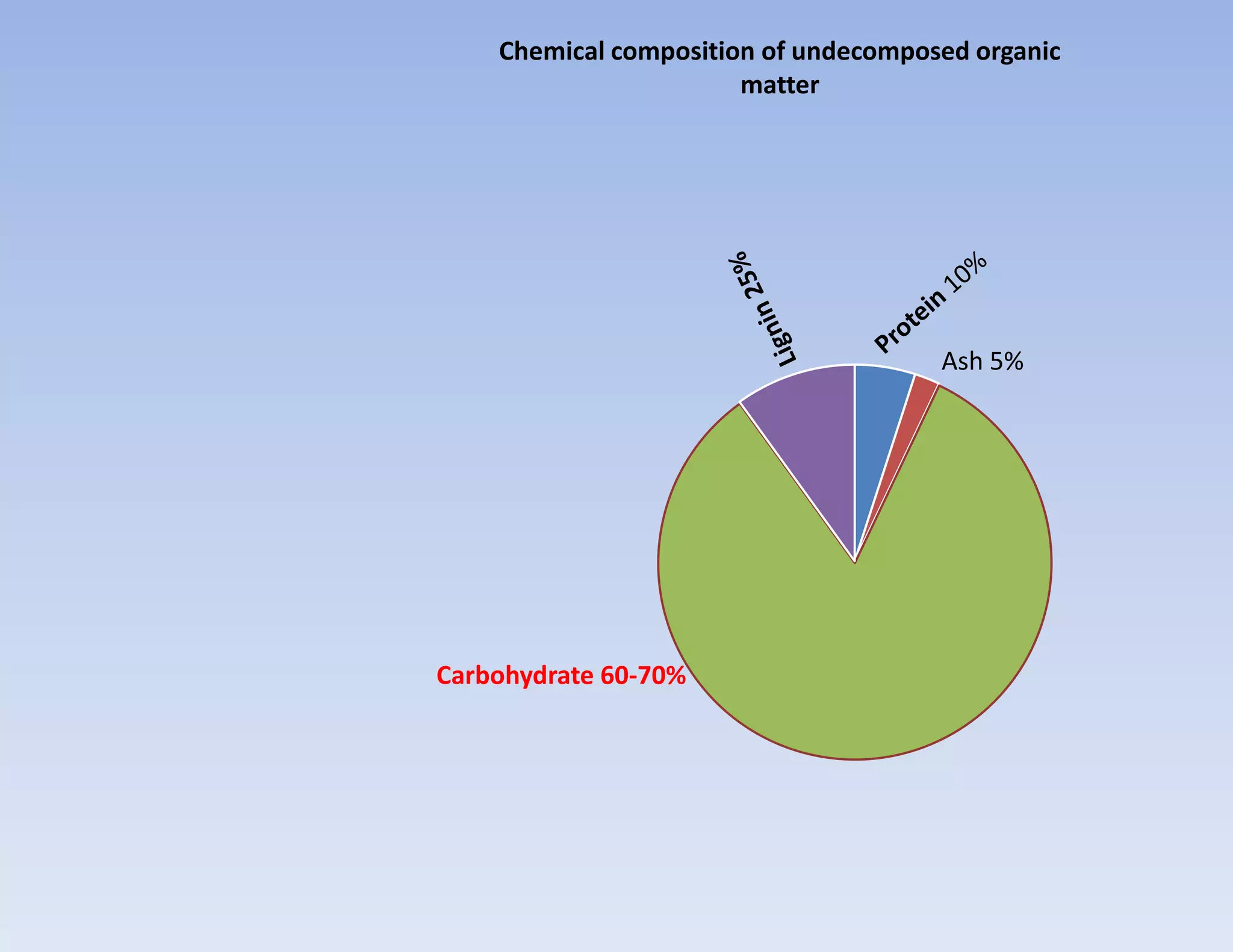
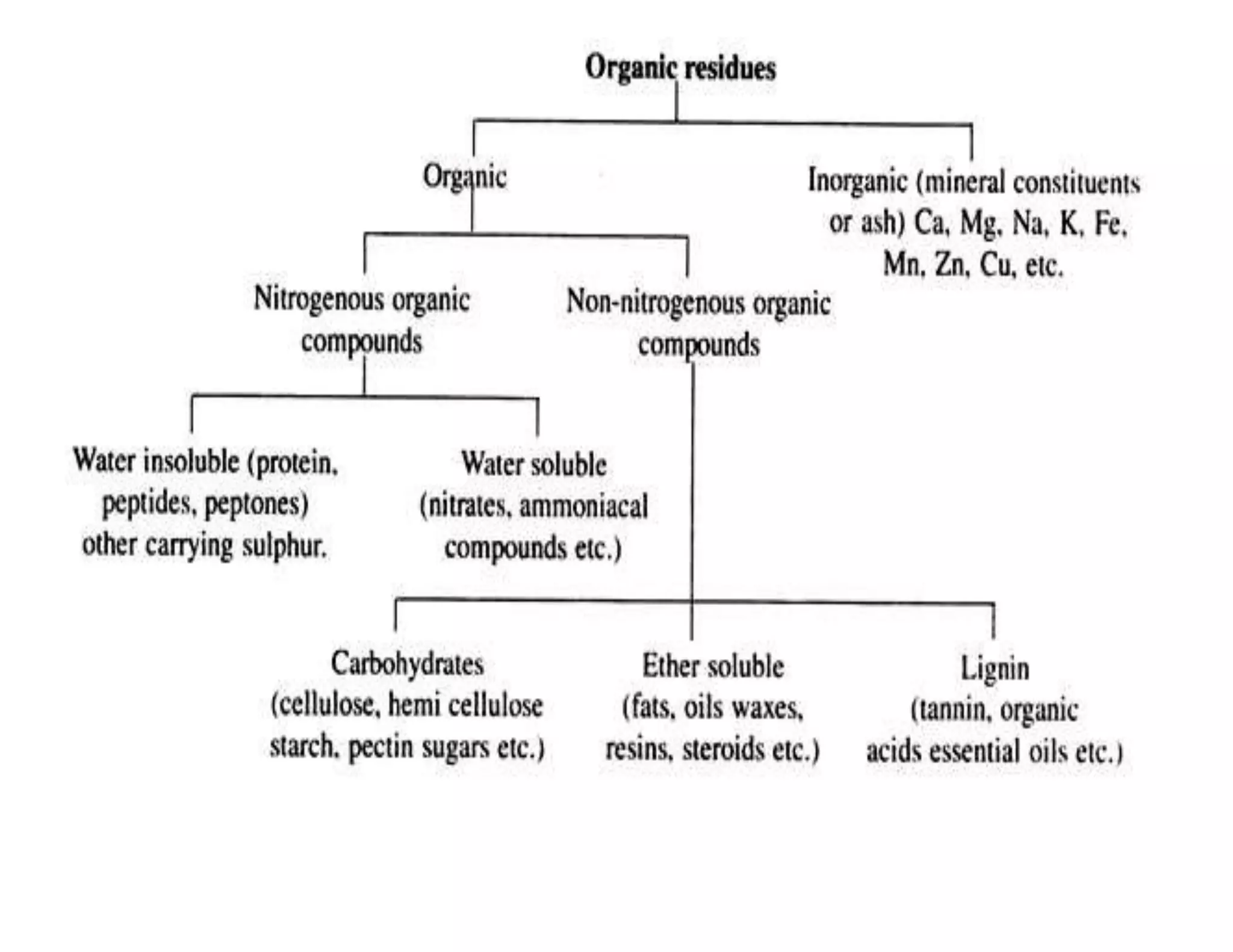
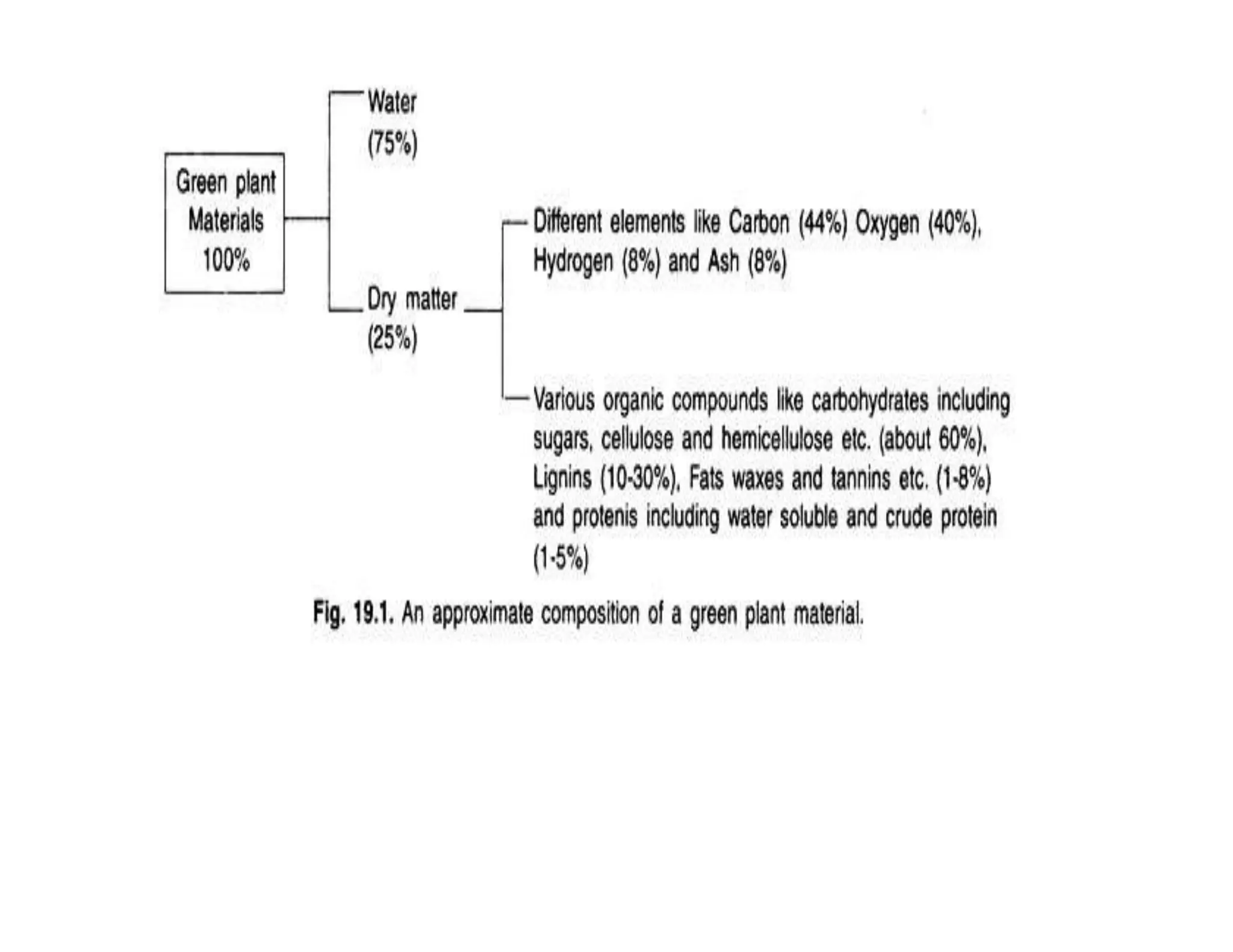
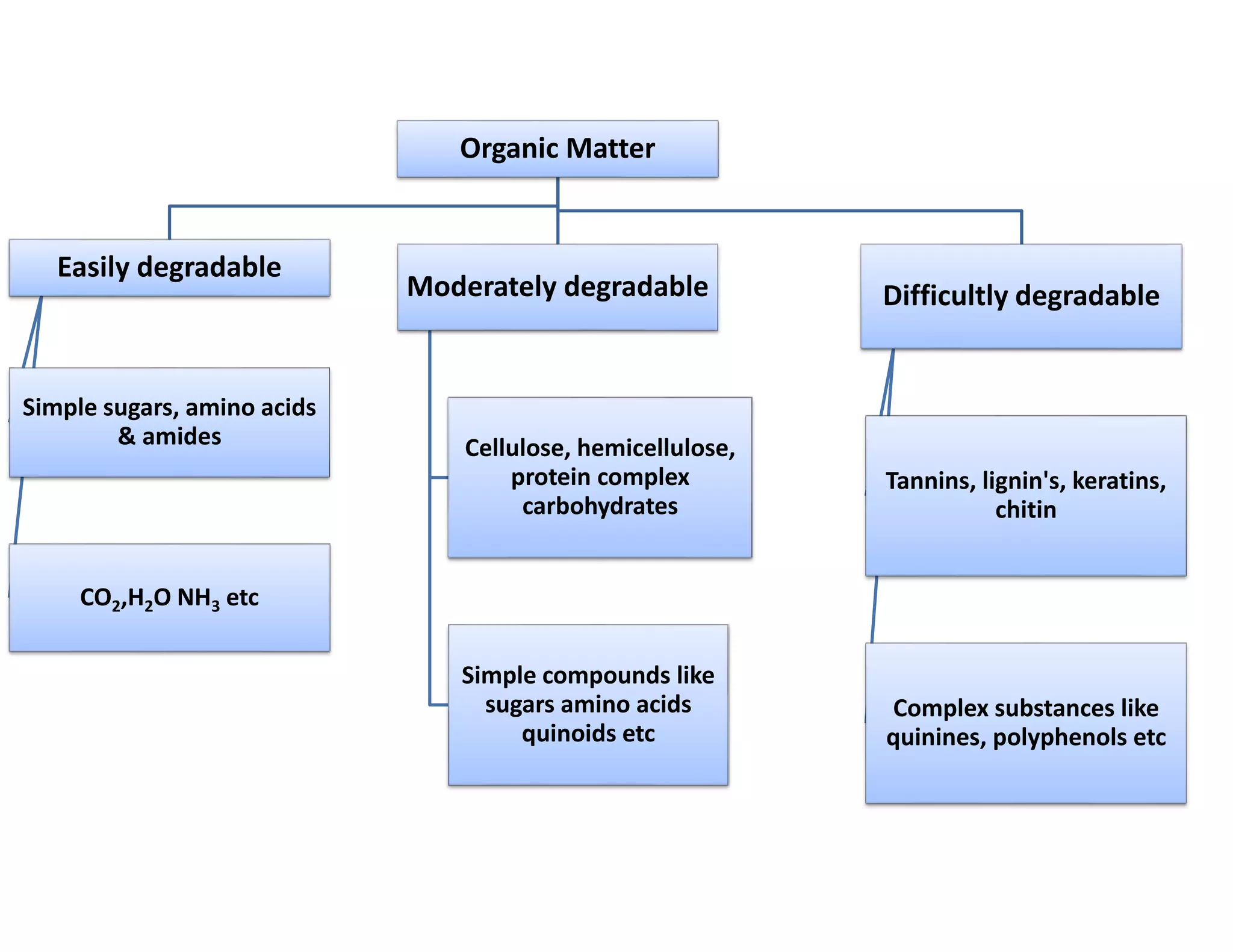
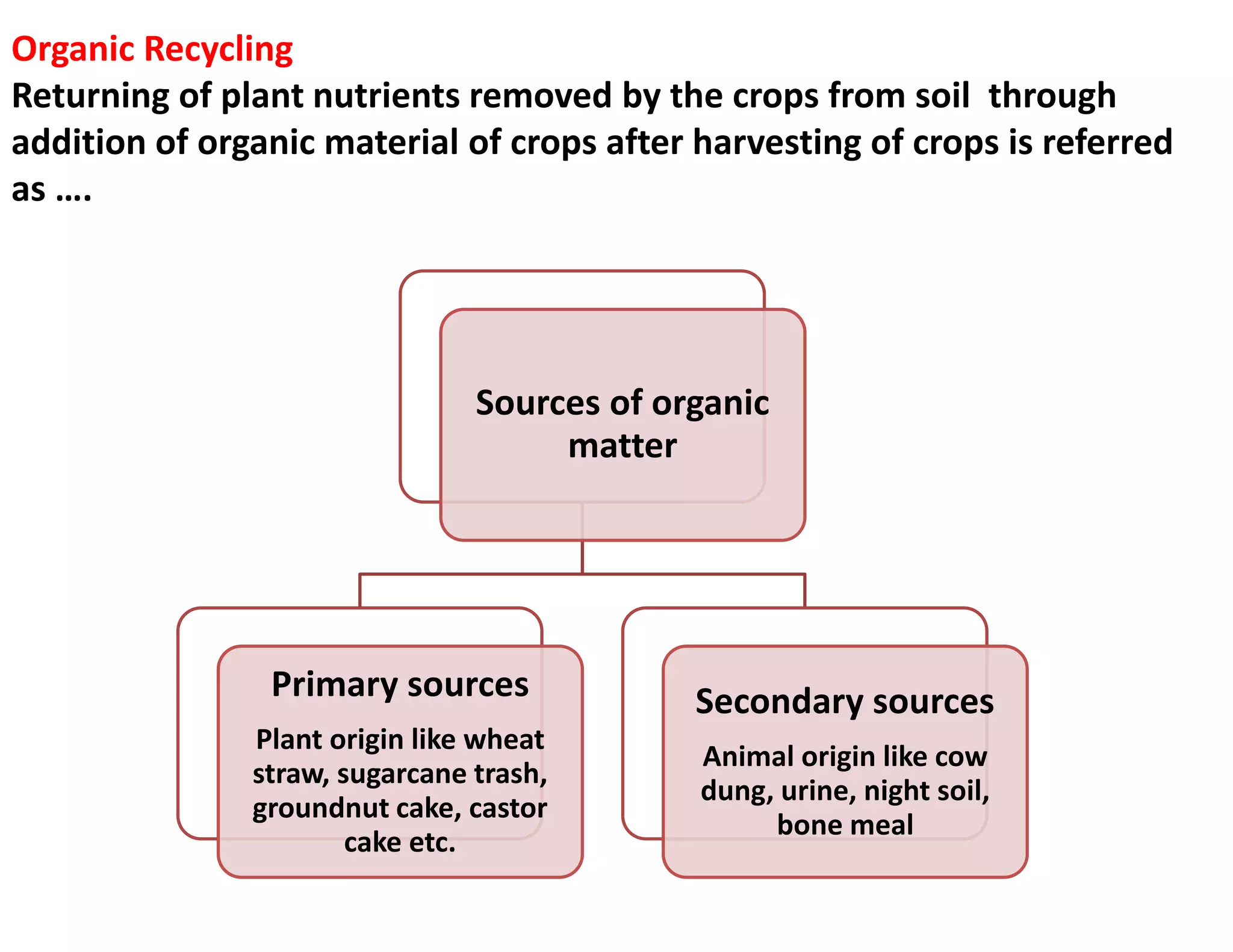
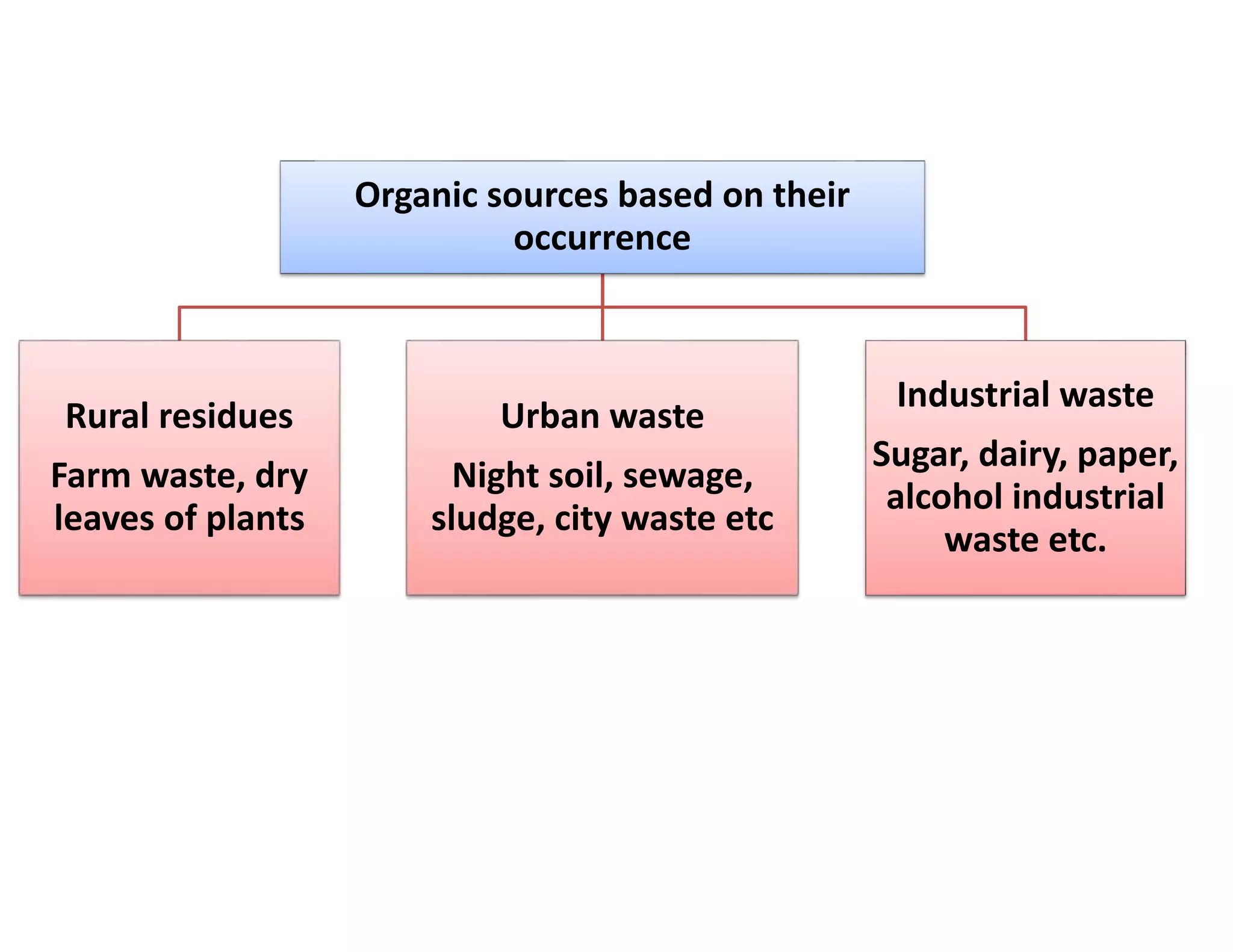
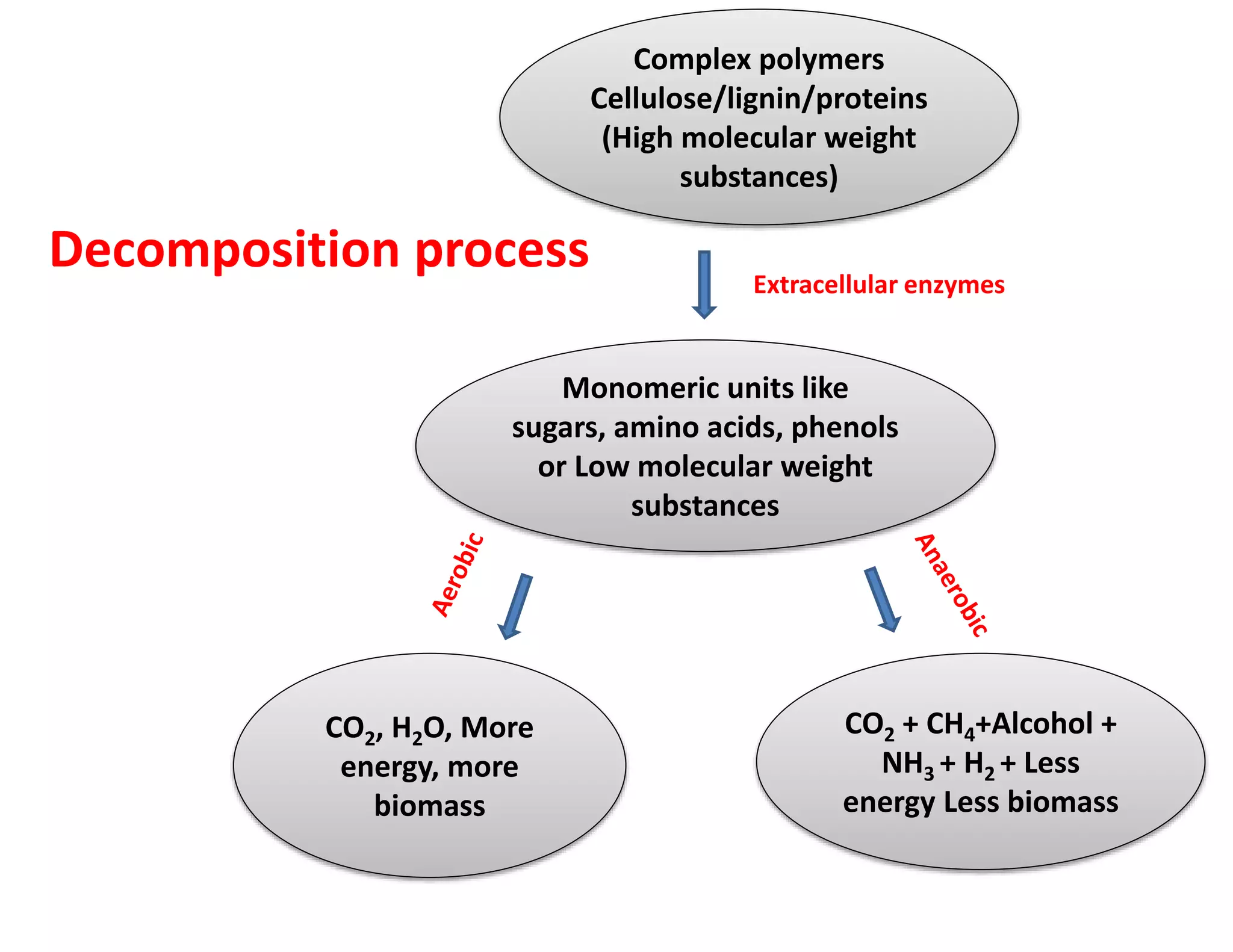
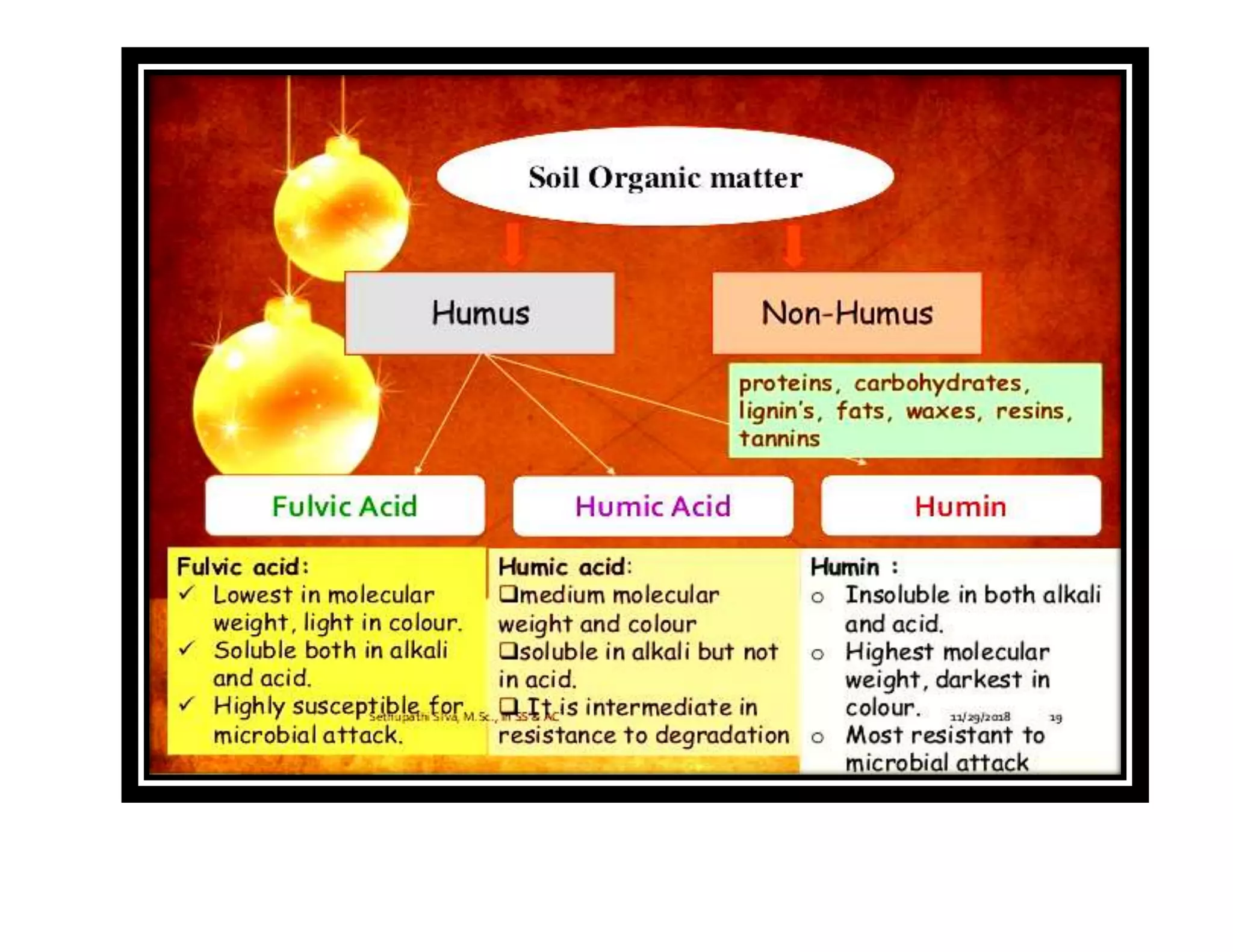
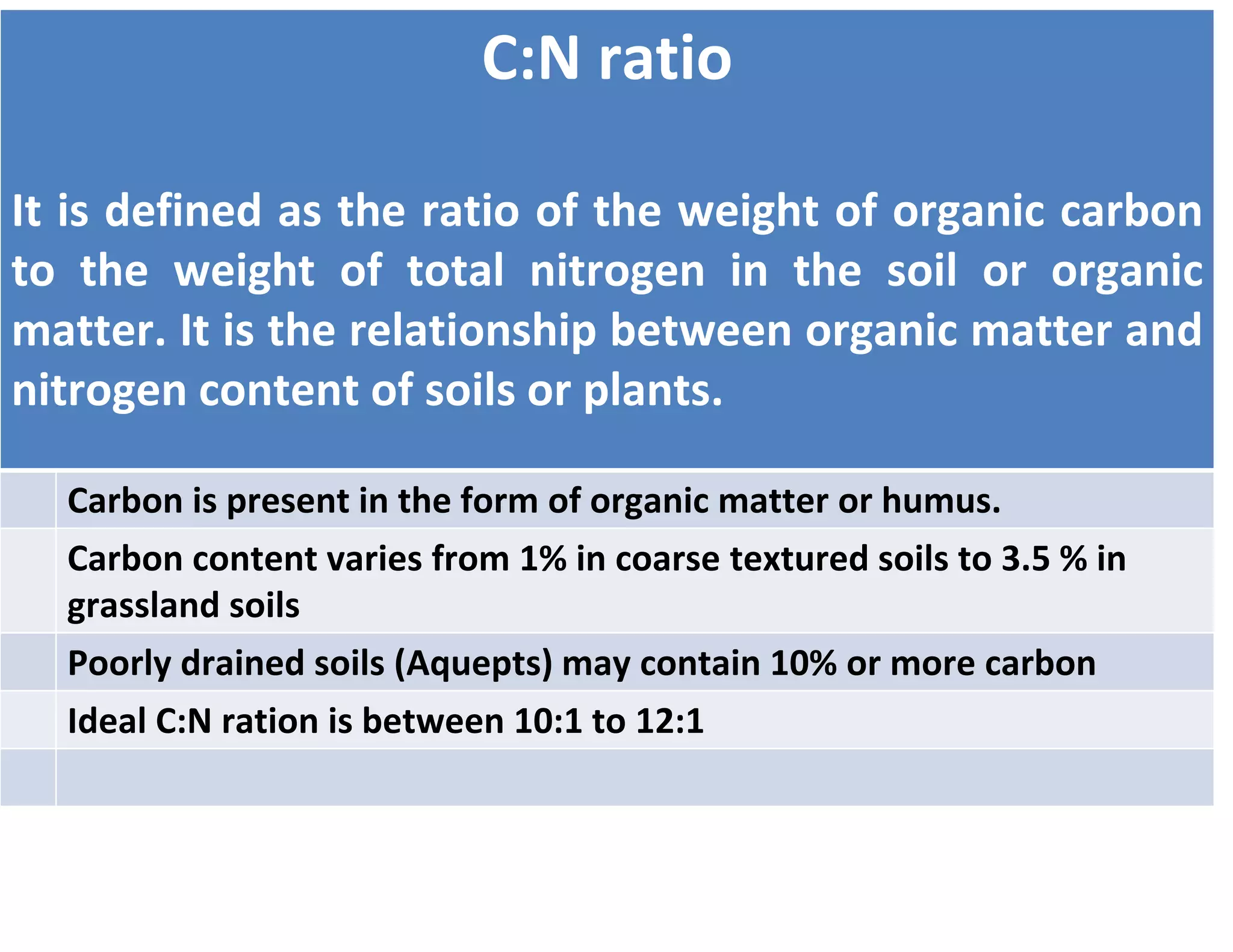
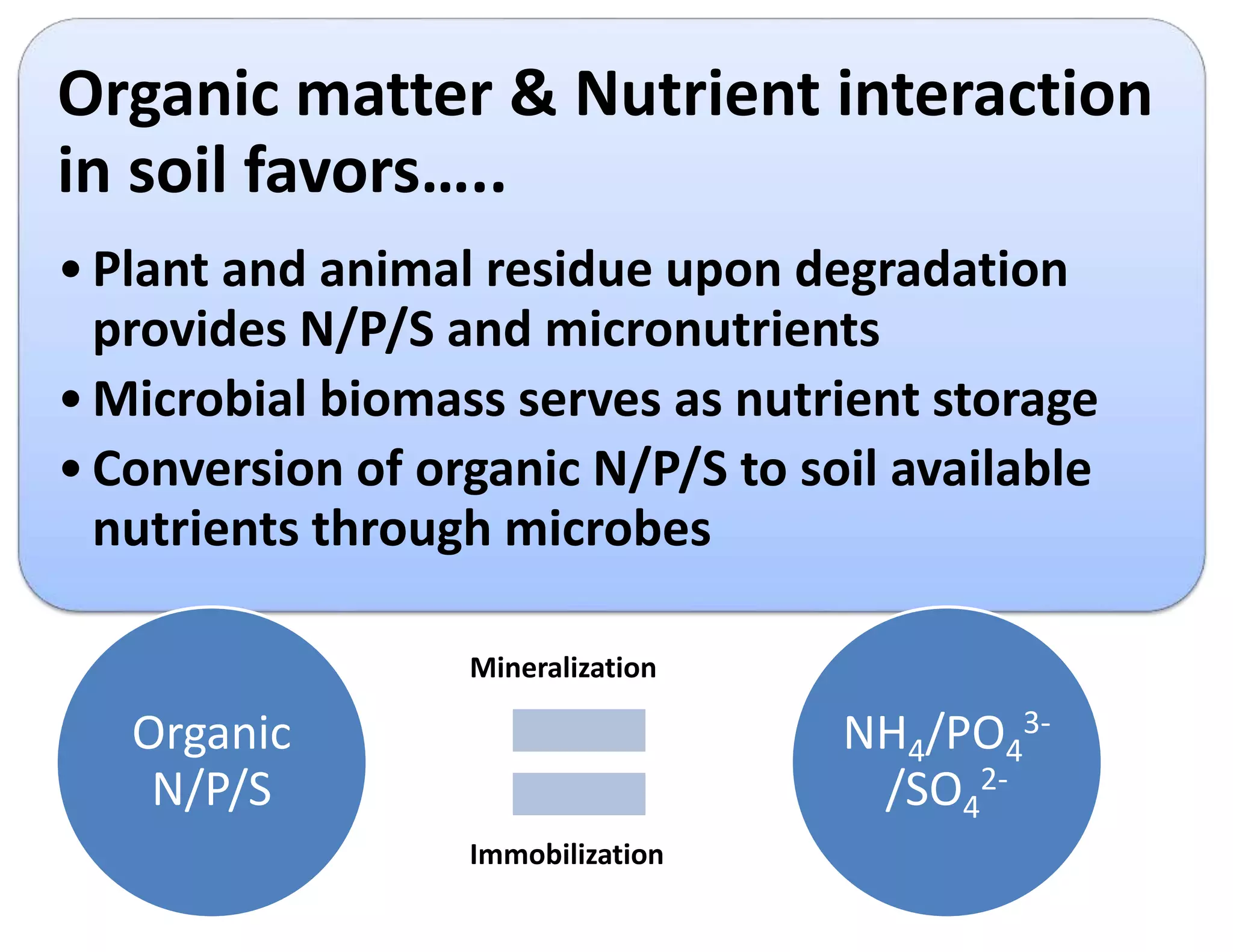
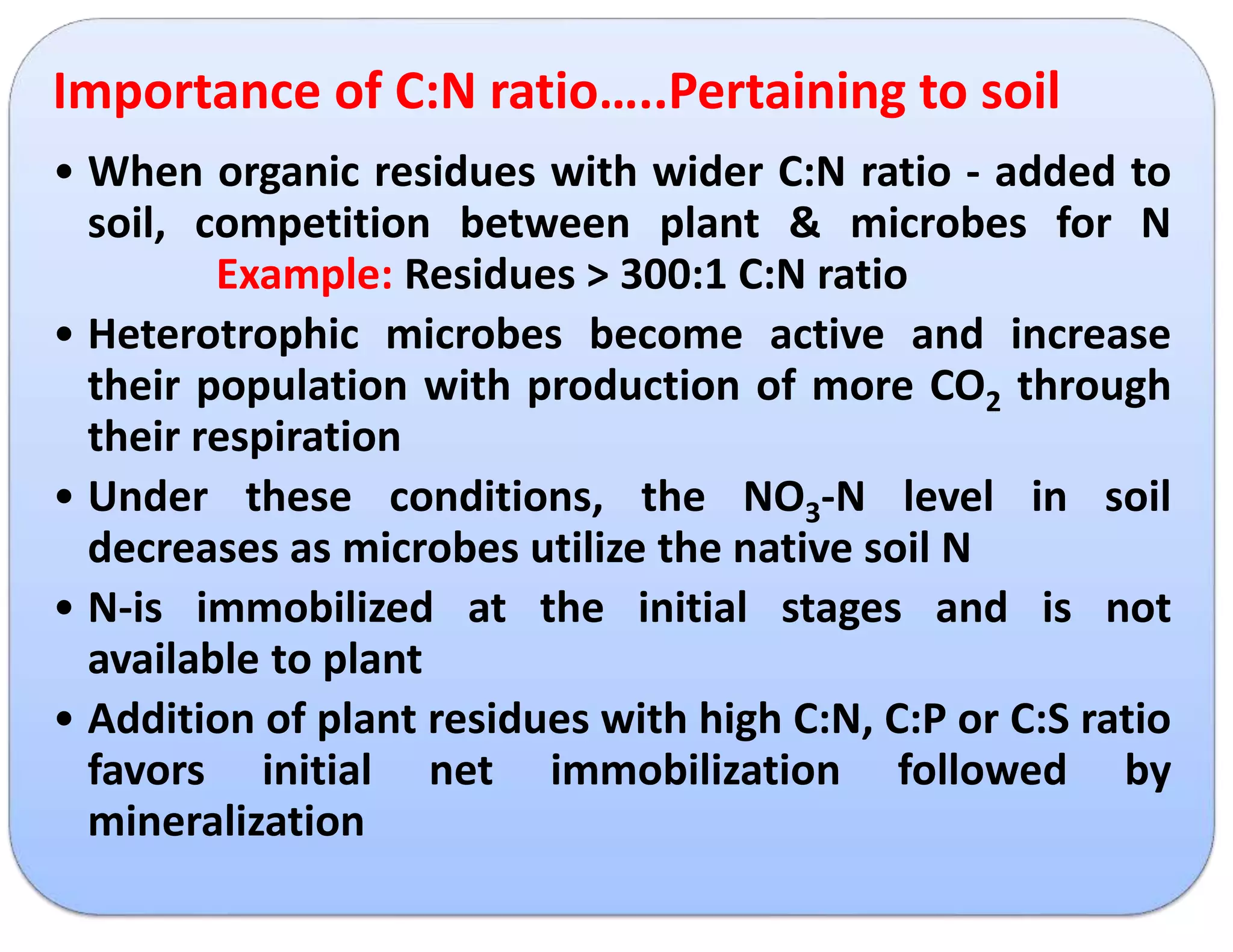
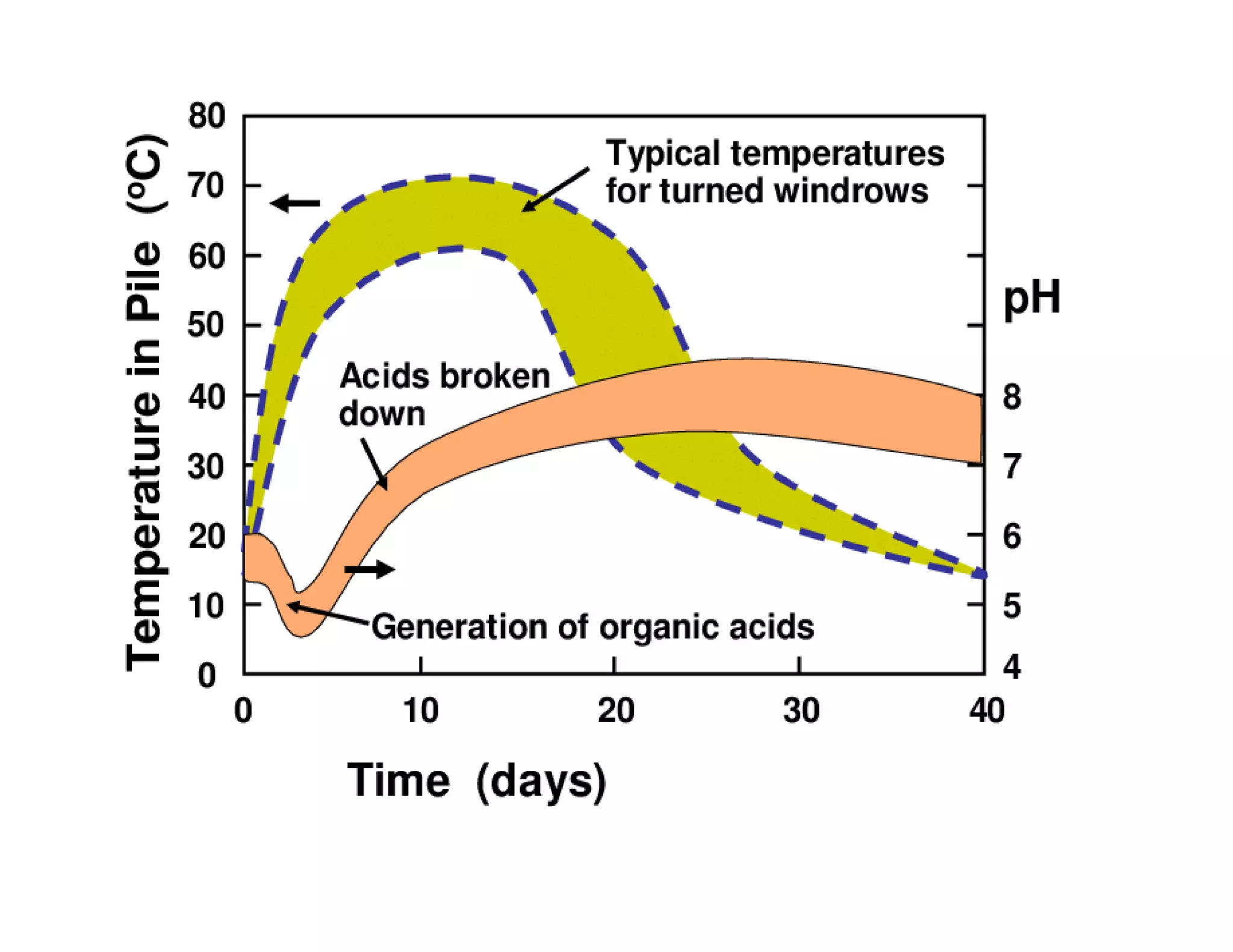
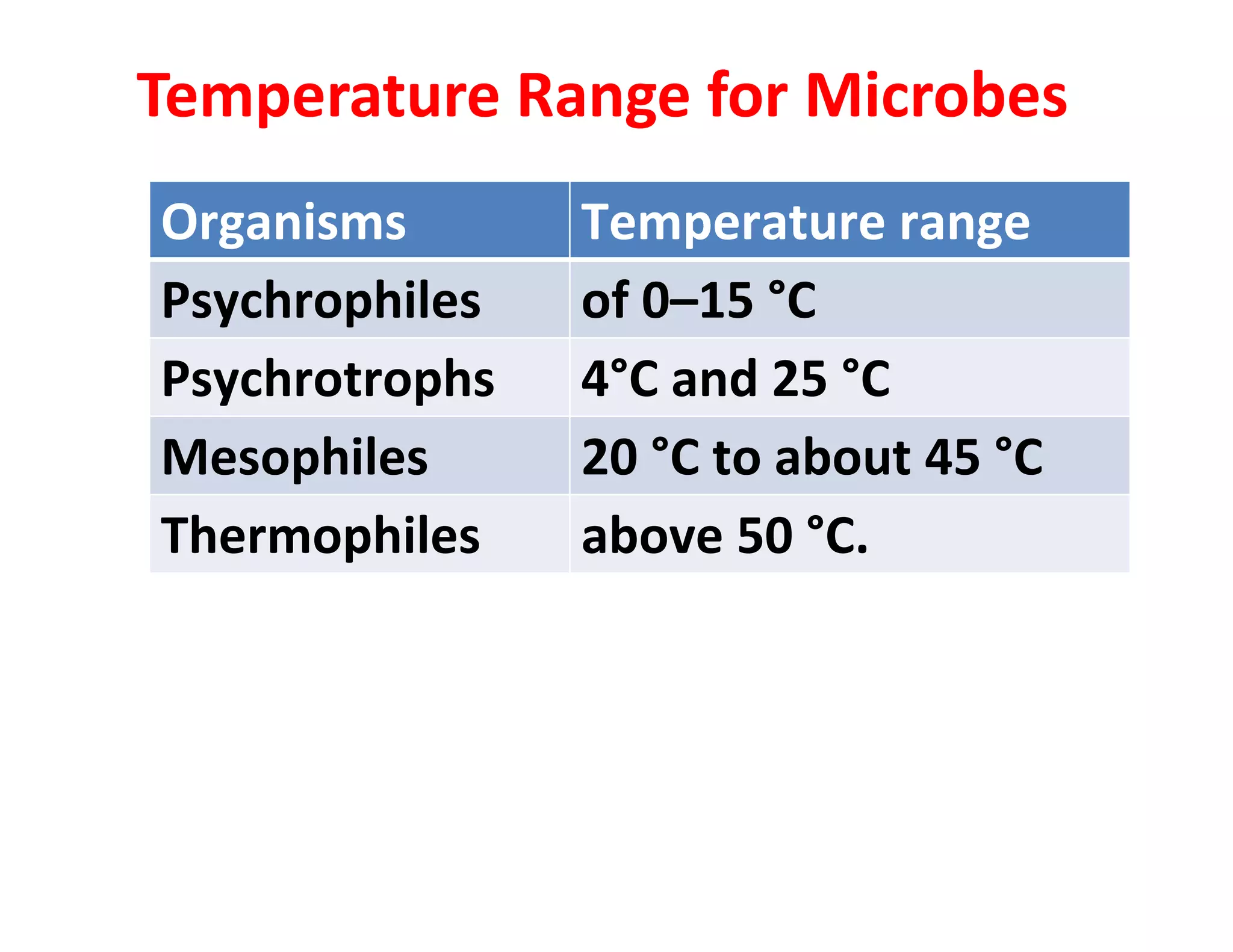
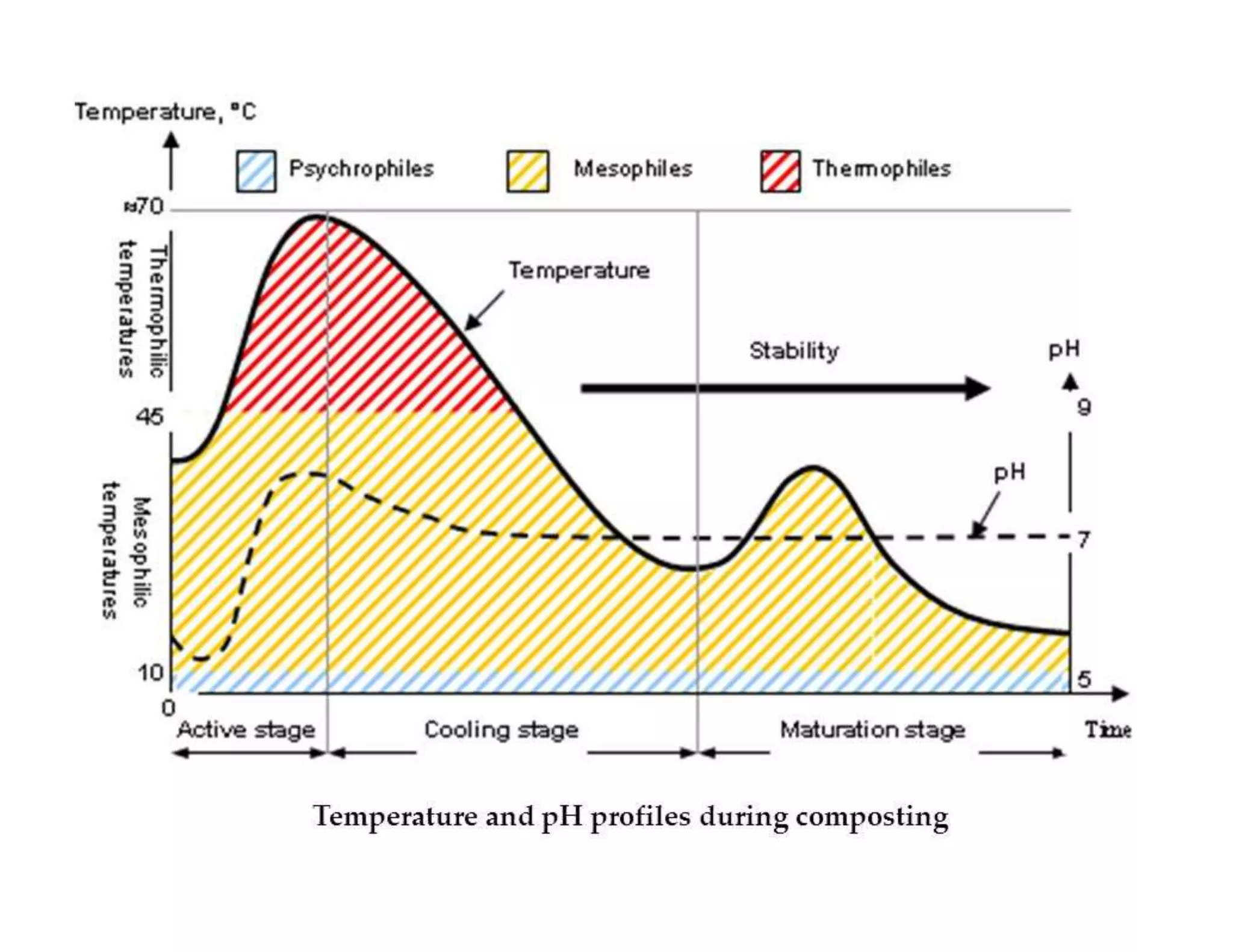
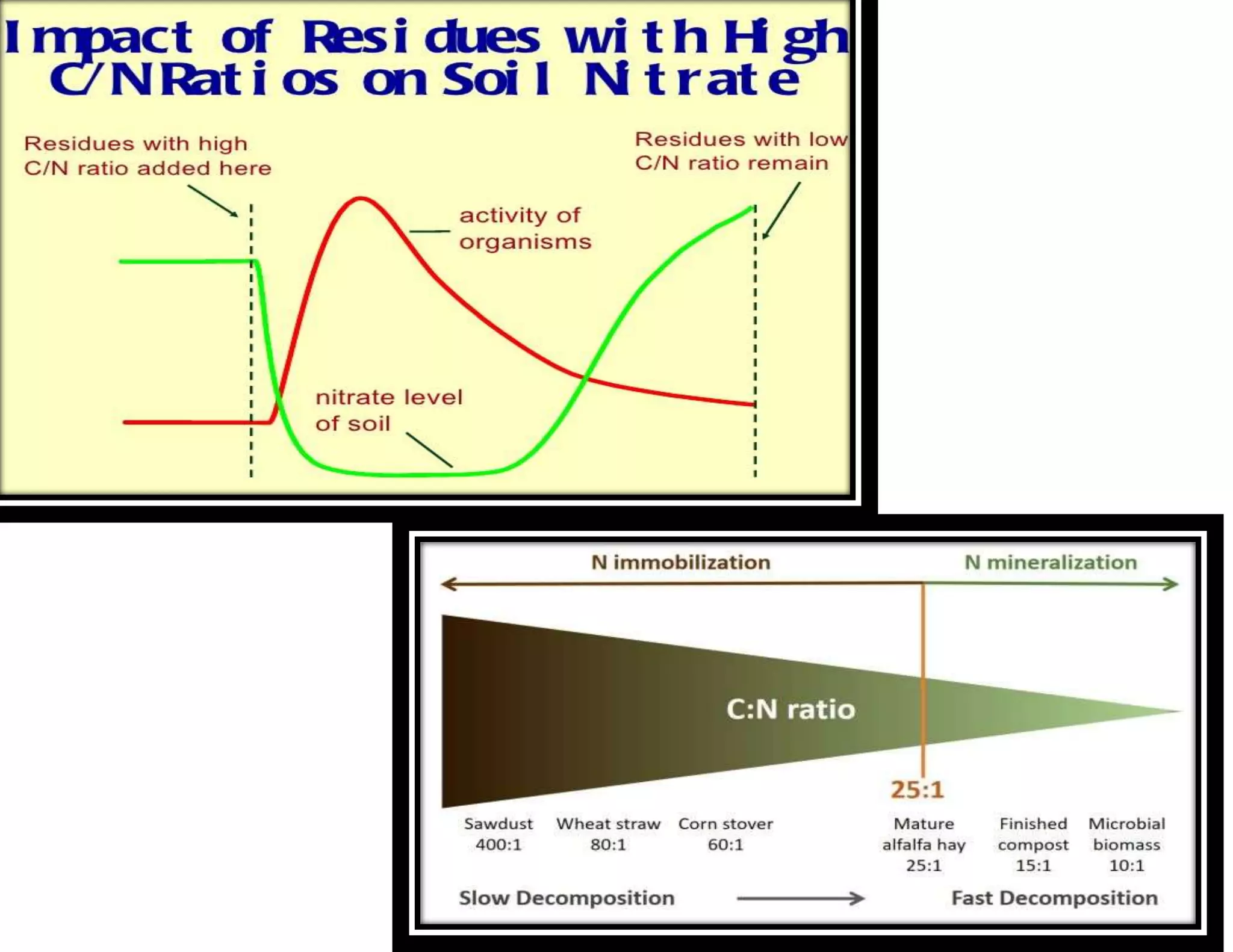
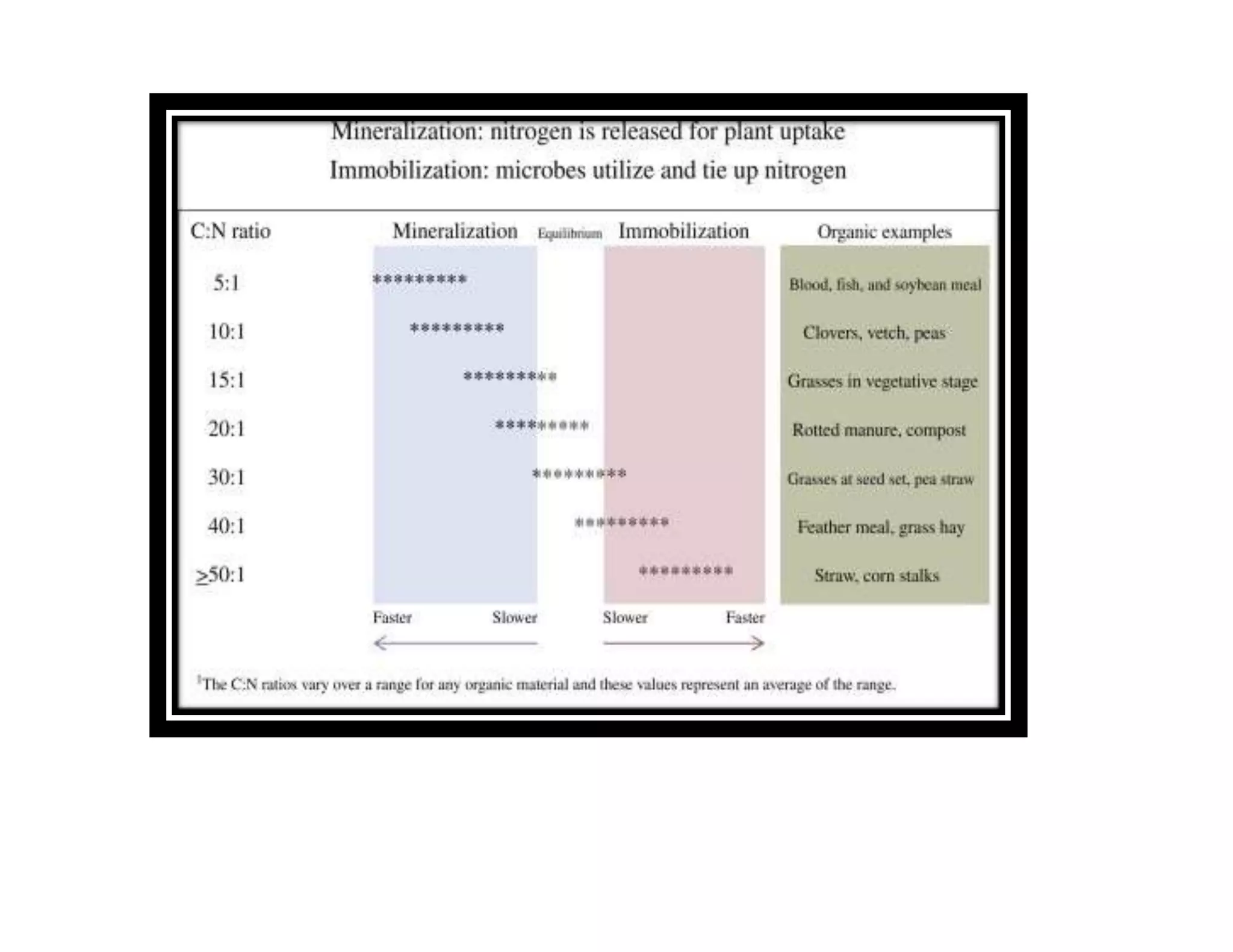
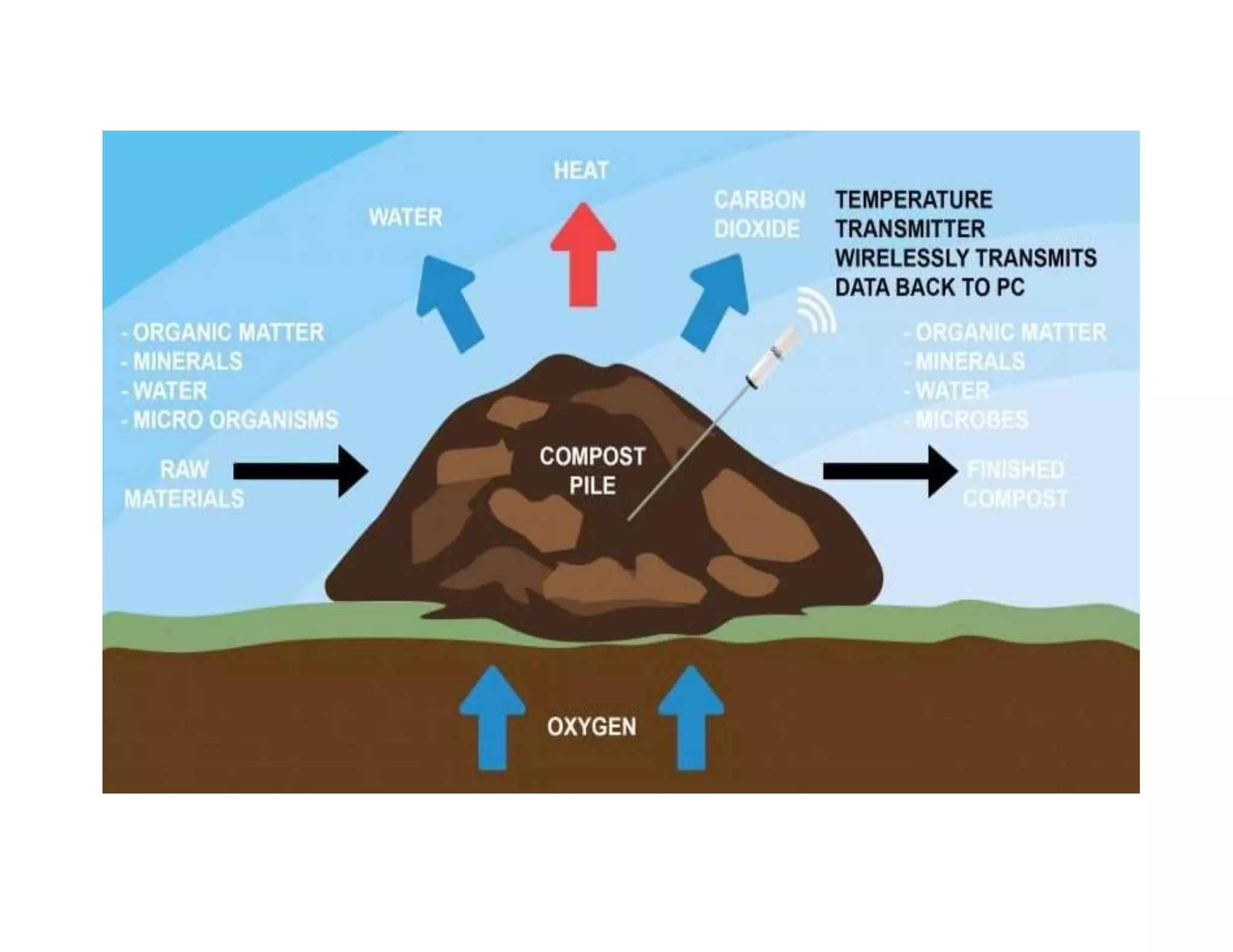
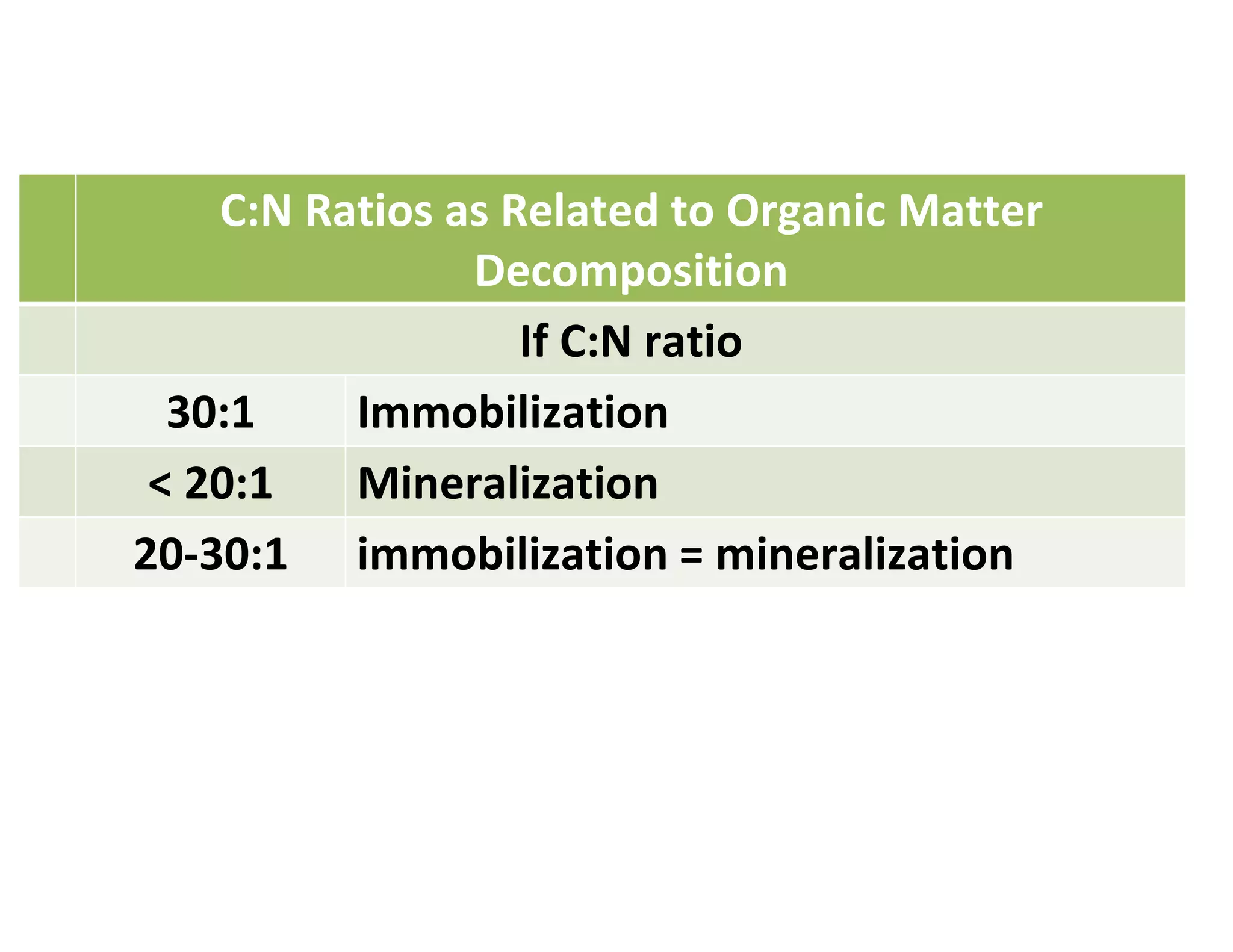
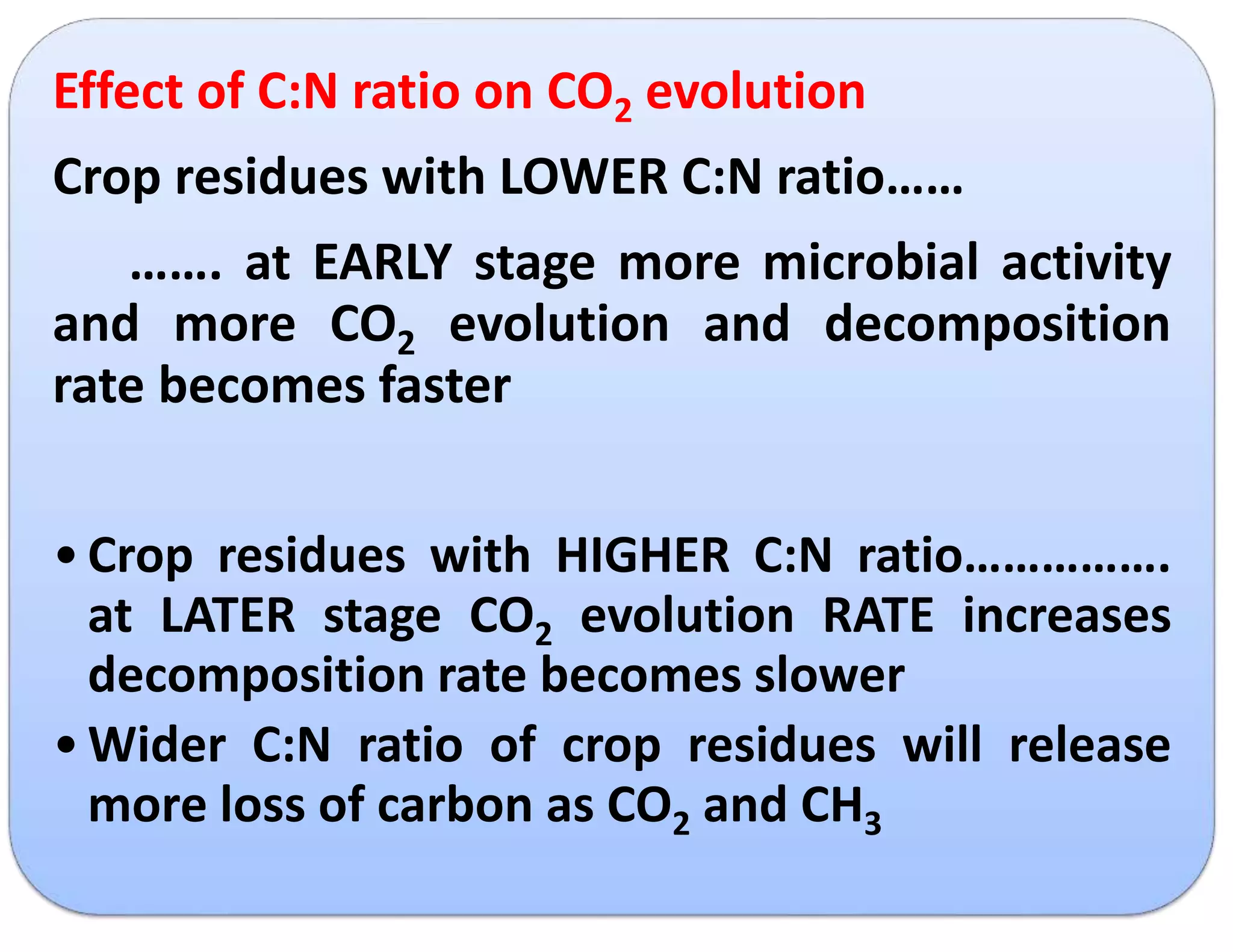
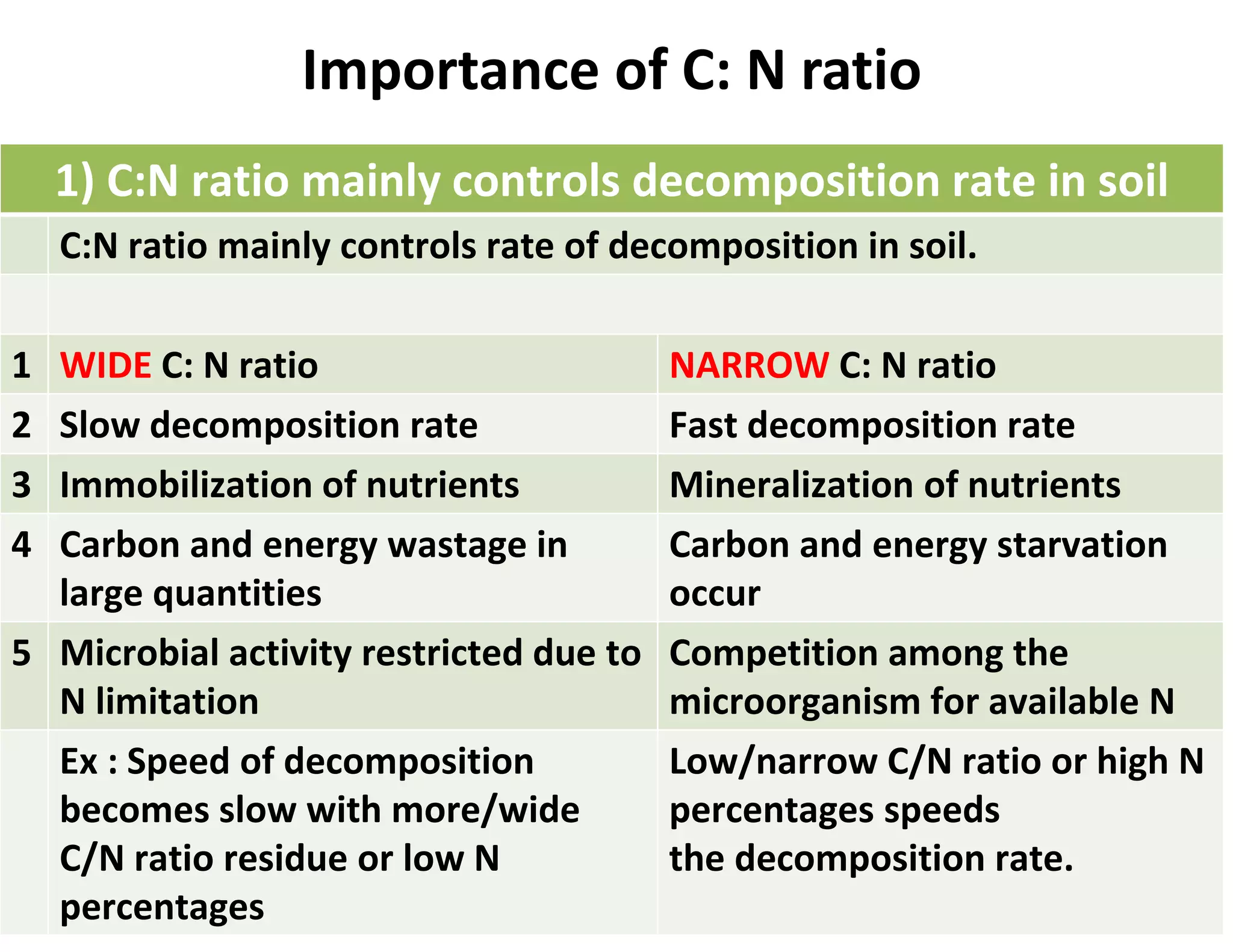
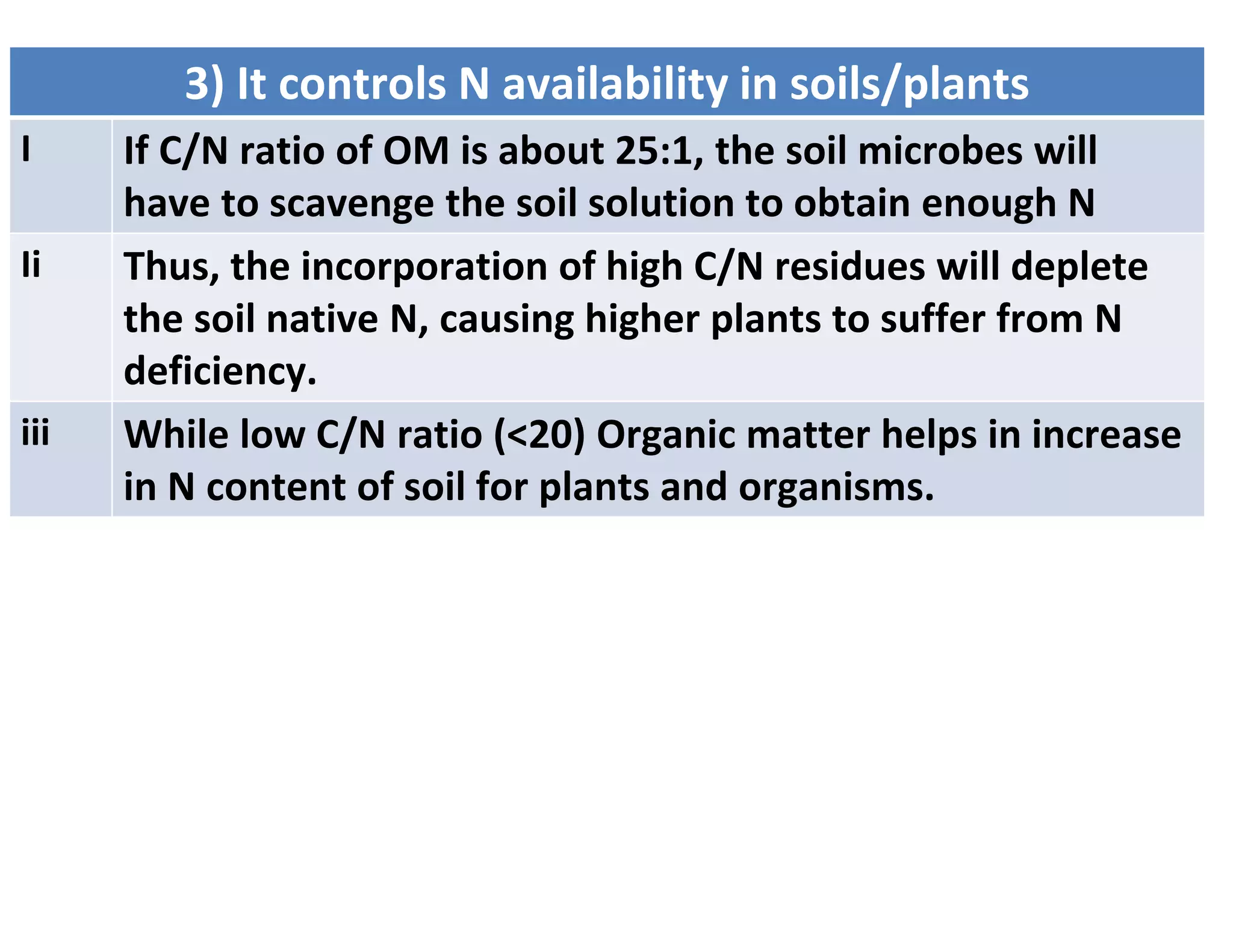
The document discusses the significance of organic manures, their decomposition, and the importance of the carbon-to-nitrogen (C:N) ratio in soil health. It explains how organic matter influences nutrient availability, soil properties, and microbial activity, emphasizing that the C:N ratio affects the rate of decomposition and nutrient release. Additionally, it categorizes organic material sources and outlines the roles of various microbes and environmental conditions in composting and nutrient cycling.