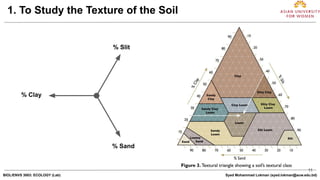
This document provides instructions for a soil analysis lab. Students will analyze various physical properties of soil, including texture, moisture content, pH, and water holding capacity. The lab covers the components and structure of soil profiles. Students will use a soil texture triangle to classify soil samples based on percentages of sand, silt and clay. They will also measure moisture content by weighing soil samples before and after drying, test pH using indicator paper or solutions, and determine water holding capacity by measuring water retained in a soil sample. The goal is for students to understand key physical properties and their importance for soil function.
























![26
26
BIOL/ENVS 3003: ECOLOGY (Lab) Syed Mohammad Lokman (syed.lokman@auw.edu.bd)
Calculation:
1. Record the level of water (W2) passed through the filter. Using the
below formula, calculate the water holding capacity of the soil:
4. Water Holding Capacity of Soil
Volume of water retained (Wr) = W1 - W2
Water Holding Capacity of Soil (WHCs) = [(Wr/Ws) ✕100] %](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab7soilanalysis-230110040256-9441ebff/85/Soil-Analysis-26-320.jpg)
