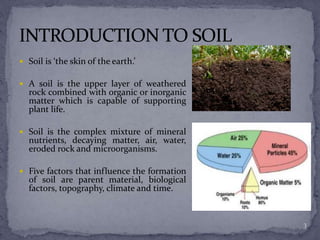
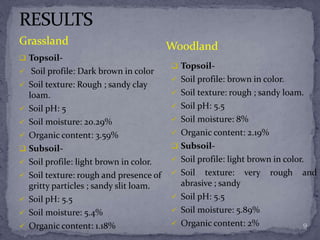
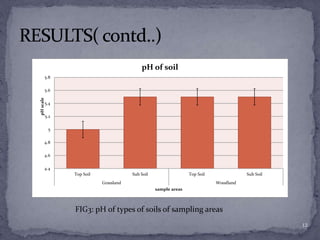
The document presented findings from a study on soil types and properties. It began with an introduction to soil and discussed major soil types based on texture. It described the methodology used, which involved examining soil profiles, measuring pH, moisture content, and organic matter. The results showed that in the grassland sample area, the topsoil had higher moisture content and organic matter than the subsoil. Meanwhile, the woodland sample area had lower levels of moisture and organic matter overall. The conclusion was that various soil properties, like pH, were similar between areas, but factors like location affected moisture content and organic matter levels.