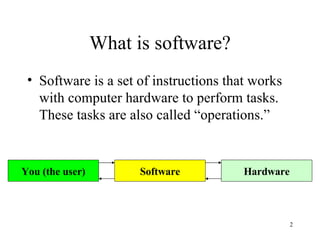
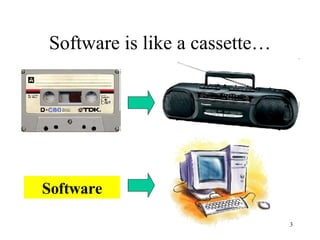
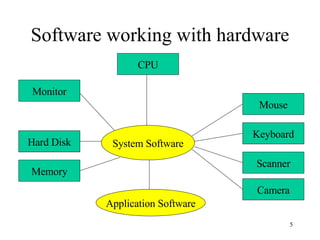
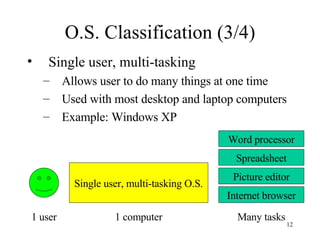
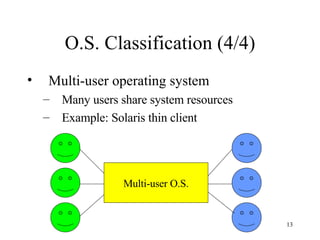
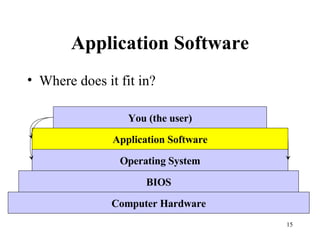
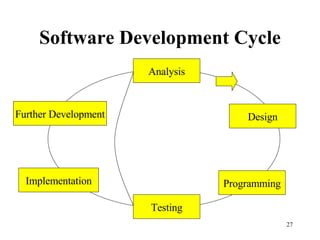
The document discusses software, including what it is, different types of software like system software and application software, and operating systems. It covers the basic input/output system (BIOS), functions of operating systems, classifications of operating systems, and the graphical user interface (GUI). It also discusses application software, types like word processors and spreadsheets, free and open source software, and the software development cycle.