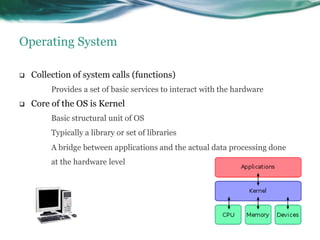
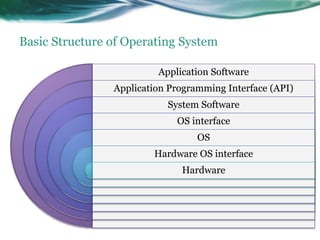
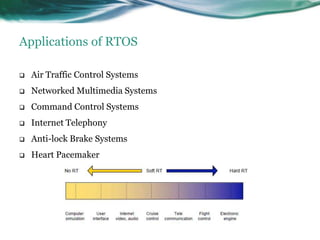
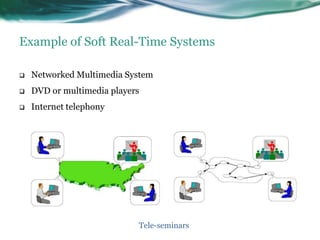
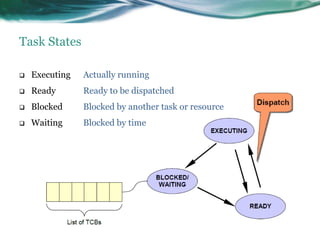
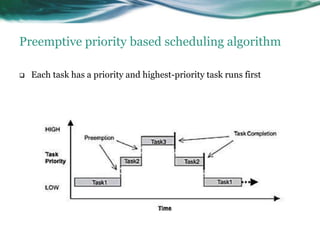
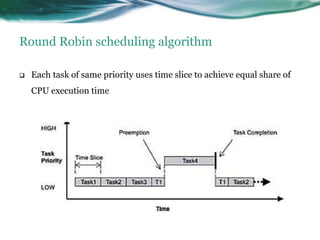
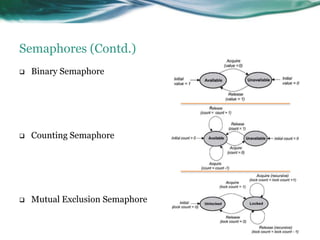
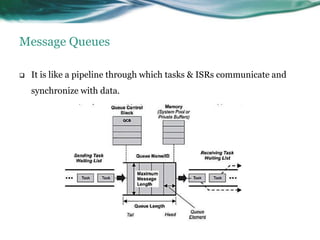
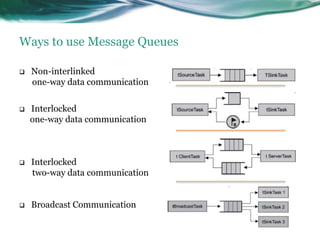
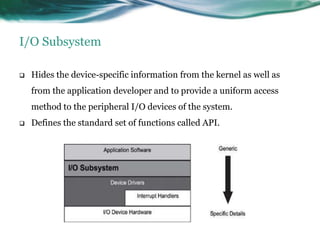
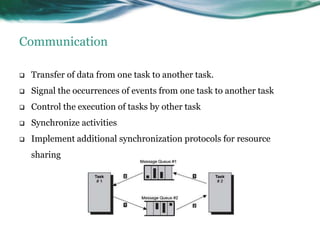
This document provides an overview of real-time operating systems (RTOS). It discusses that an RTOS completes tasks on time through deterministic and time-constrained execution. It also notes examples of hard and soft real-time systems. Key components of an RTOS include tasks, schedulers, semaphores, message queues, and exceptions/interrupts for task synchronization and communication. Popular RTOS distributions include RTLinux, VxWorks, QNX Neutrino, Windows CE, OSE, and freeRTOS.