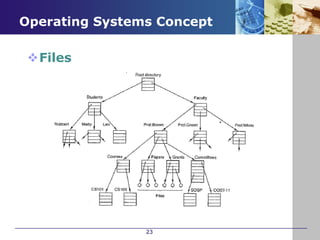
The document provides an introduction to operating systems, including their definition, roles, functions, and history. It defines an operating system as the software that manages hardware and allows it to be usable. Operating systems manage system resources, files, memory, processors, and input/output. Examples of common operating systems include Windows, Mac OS, Unix, and Linux. The document then outlines the evolution of operating systems from early vacuum tube computers through personal computers, and describes basic operating system concepts like processes, address spaces, files, and protection.